A US District Court ruled that Google has violated Sherman Act (US’ anti-trust law) by maintaining its monopoly in two product markets – General Search Services (GSS) and General Text Advertising.
- Anti-trust laws prohibit Anti-Competitive Practices and monopolizing conduct to protect consumers from predatory business practices.
Google’s Monopoly (as highlighted by Judgement)
- Google enjoys an 89.2% market share for GSS, which increases to 94.9% on mobile devices.
- Google also controlled 88% of text advertising market in 2020.
- Google maintained its monopoly and stifled competition through:
- Near-complete control of key distribution channels, posing a major entry barrier for other search companies.
- Striking deals with Apple, Samsung and Verizon to be default search engine on their respective devices.
Issues with Monopolistic Tendencies of Big Tech Companies
- Abuse of dominant position: Access to large datasets provides information control which may be misused for profit maximization or controlling the market.
- Winner-take-most: Nature of digital market is conducive for quick scaling and domination, restricting democratic competition, discouraging new market participants and impacting local economies.
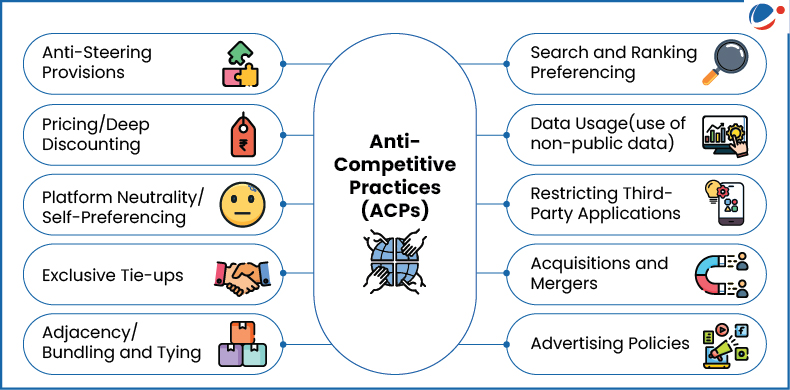
- Anti-Competitive Practices (ACPs): India’s Parliamentary Standing Committee Report identified ten predominant ACPs undertaken by large digital enterprises (see infographic).
Regulation of Big Tech Companies in India
|




