Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disease caused by the death of brain cells.
- Presence of environmental toxins and toxic proteins, causes fragmentations and dysfunctions in mitochondria. E.g. Manganese induced Parkinsonism.
- Researchers have found that inhibiting Dynamin-related protein (Drp1) activity could restore mitochondrial function and serve as a potential treatment.
- Naturally abundant in cells, Drp1 protein travels to mitochondria when they divide into smaller sizes for higher mobility and quality control.
- However, too much Drp1 activity causes excessive division, leading to fragmented mitochondria with impaired function.
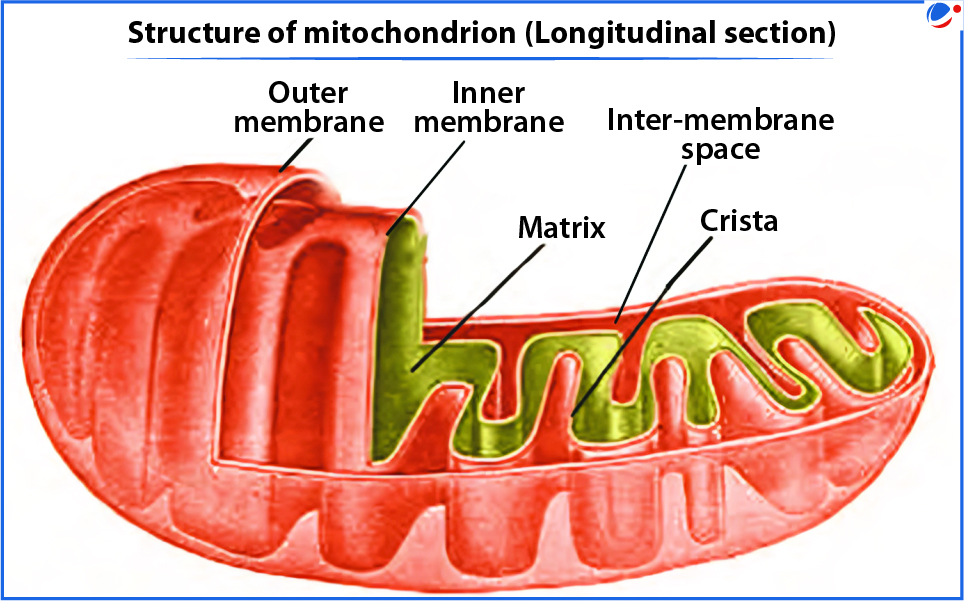
Mitochondria
- Mitochondria are membrane-bound cell organelles that generate most of the cell's energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
- Functions
- Energy Production: Sites of aerobic respiration, producing ATP, hence termed the power houses of the cell.
- Genetic Material: Contains its own circular DNA (Mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA), RNA, ribosomes, and components for protein synthesis.
- mtDNA is useful for tracing genetic lines.
Mitochondrial Diseases
- These are caused by genetic mutation of mtDNA or nuclear DNA.
- mtDNA is inherited exclusively from the mother, making these diseases maternally inherited.
- Mitochondrial Replacement Therapy (MRT) prevents the transmission of mitochondrial diseases from mother to child.





