At the 8th Global Platform for Disaster Risk Reduction (GPDRR) 2025 in Geneva, India identified the absence of a dedicated international financial mechanism to support establishment of DRR financing systems.
- In this regard, India called for the creation of a global facility, backed by the UN system & multilateral financial institutions, to provide catalytic funding, technical assistance, and a platform for knowledge exchange.
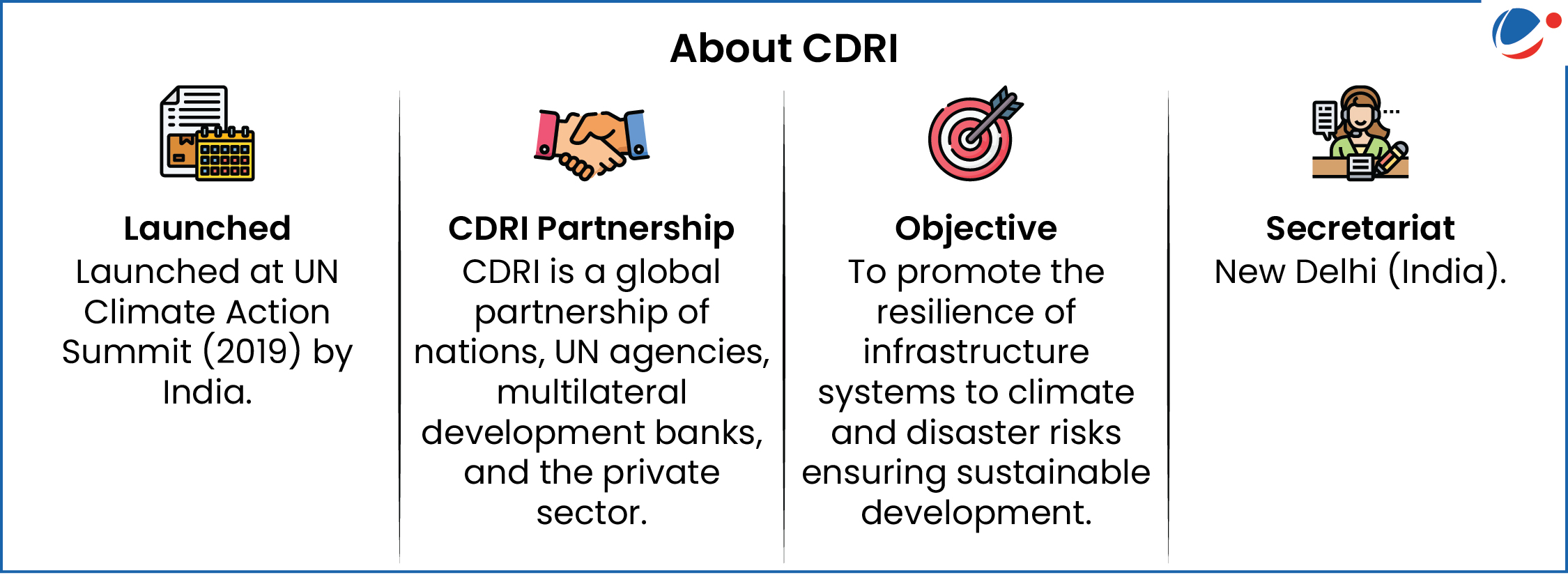
India’s Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) Financing System
- India’s Philosophy: India believes in a strong and responsive DRR financing architecture as a cornerstone of resilience.
- India’s Progress in DRR Financing:
- Initial Allocations: Early Finance Commissions allocated INR 60 million (~USD 0.7 million).
- Current Allocations: Under the 15th Finance Commission, the allocation exceeds INR 2.32 trillion (~USD 28 billion).
- DRR Finance Mechanism: India follows a pre-determined, rule-based allocations flowing from national to state and district levels, supported by the Disaster Management Act of 2005.
- This transformation ensured that disaster financing is structured and predictable rather than reactive.
- India’s DRR financing approach built on four key principles:
- First, Dedicated financial windows for preparedness, mitigation, relief, and recovery.
- Second, Prioritization of the needs of affected people and vulnerable communities.
- Third, Accessibility of financial resources across all government levels—central, state, and local.
- Fourth, Accountability, transparency, and measurable outcomes guiding all expenditures.
Related NewsAfrican Union Joins Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) as 54th Member
|





