CJI emphasised that the values of discretion, empathy and judicial interpretation is irreplaceable and technology should be anchored in constitutionalism for Justice.
Key Applications of Technology in Judiciary
- Automated Case Management: Smart scheduling, Case prioritization, and Proactive Backlog Reduction using Deep Learning and Machine Learning algorithms.
- Predictive Analysis: Analysis of historical judgments and case data to offer predictive insights.
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and Natural Language Processing (NLP): Document digitization, ensuring faster processing and reducing errors.
- Blockchain Technology: Maintenance of Judicial deposits registers, prevent record tampering, etc.
- AI-Chatbots: For User assistance offering real-time information, procedural guidance, and essential legal updates.
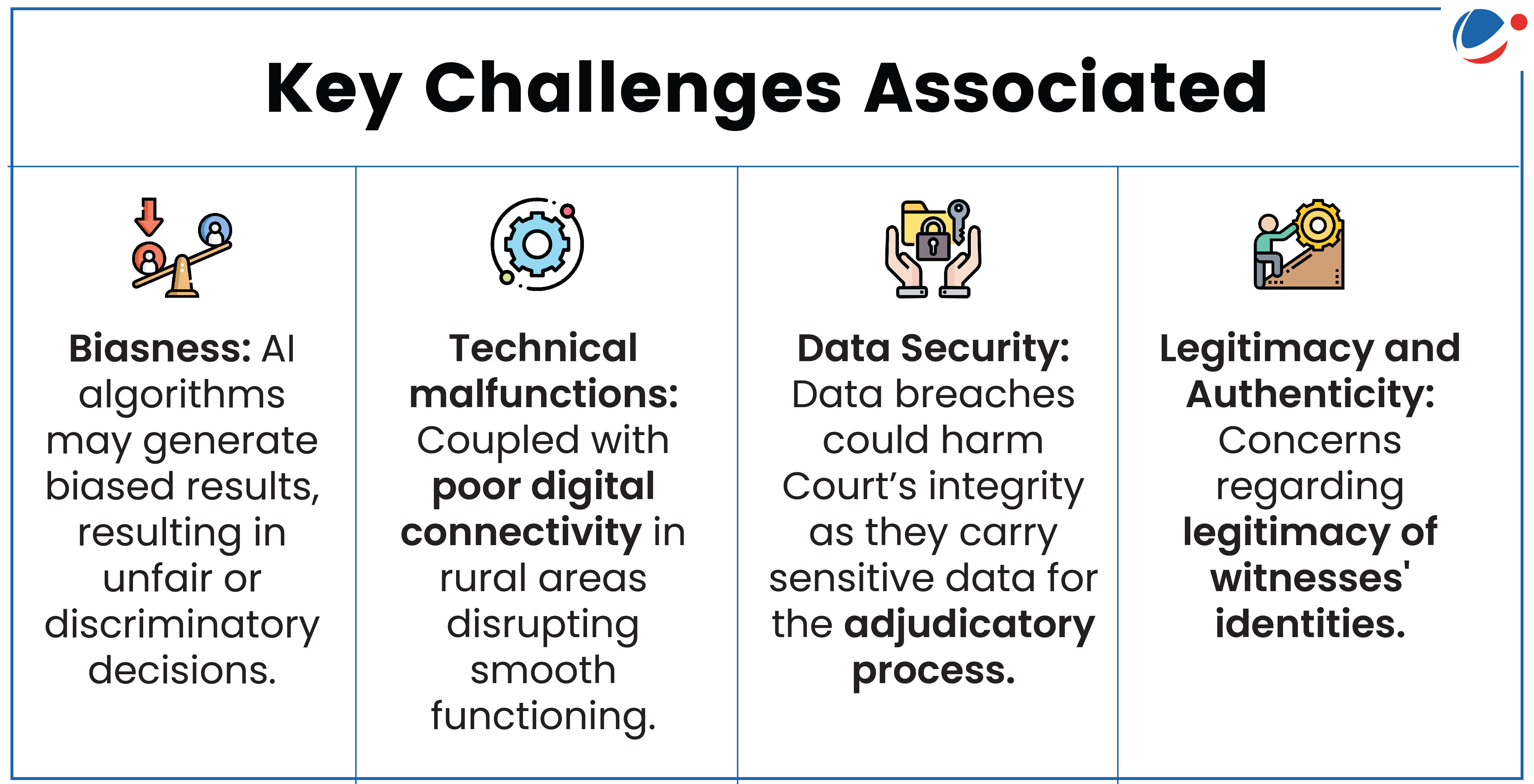
Key Initiatives to Integrate Technology with Judiciary
- National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG): Creates database of orders, judgments, and cases, under the eCourts Project.
- Case Information Software (CIS) based on customized Free and Open-Source Software (FOSS): Implemented in the District Courts and High Courts.
- eCourts Mission Mode Project: Under the National eGovernance Plan, implemented with e-Committee, Supreme Court and Department of Justice under three phases:
- Phase I (2011-2015): Involved computerization of the District Courts.
- Phase II (2015-23): Provides High Courts as Implementing Agency for projects under its jurisdiction.
- Phase III: Union Budget (2023-2024), announced Rs. 7000 crores for its implementation.







