The report has been released by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
Key findings
- Increase in severity: 40% of the world’s land area faces increasingly frequent and severe droughts.
- Some of the recent examples of major droughts include Europe (2022), California (2021), Horn of Africa & Somalia, etc.
- Economic impact: 3% - 7.5% annual increase in the economic cost of an average drought episode.
- Countries like India, Australia, etc. may face water-related disruptions in the operations of hydroelectric power stations.
- Inland water transport is impacted (E.g. recent drought in panama canal).
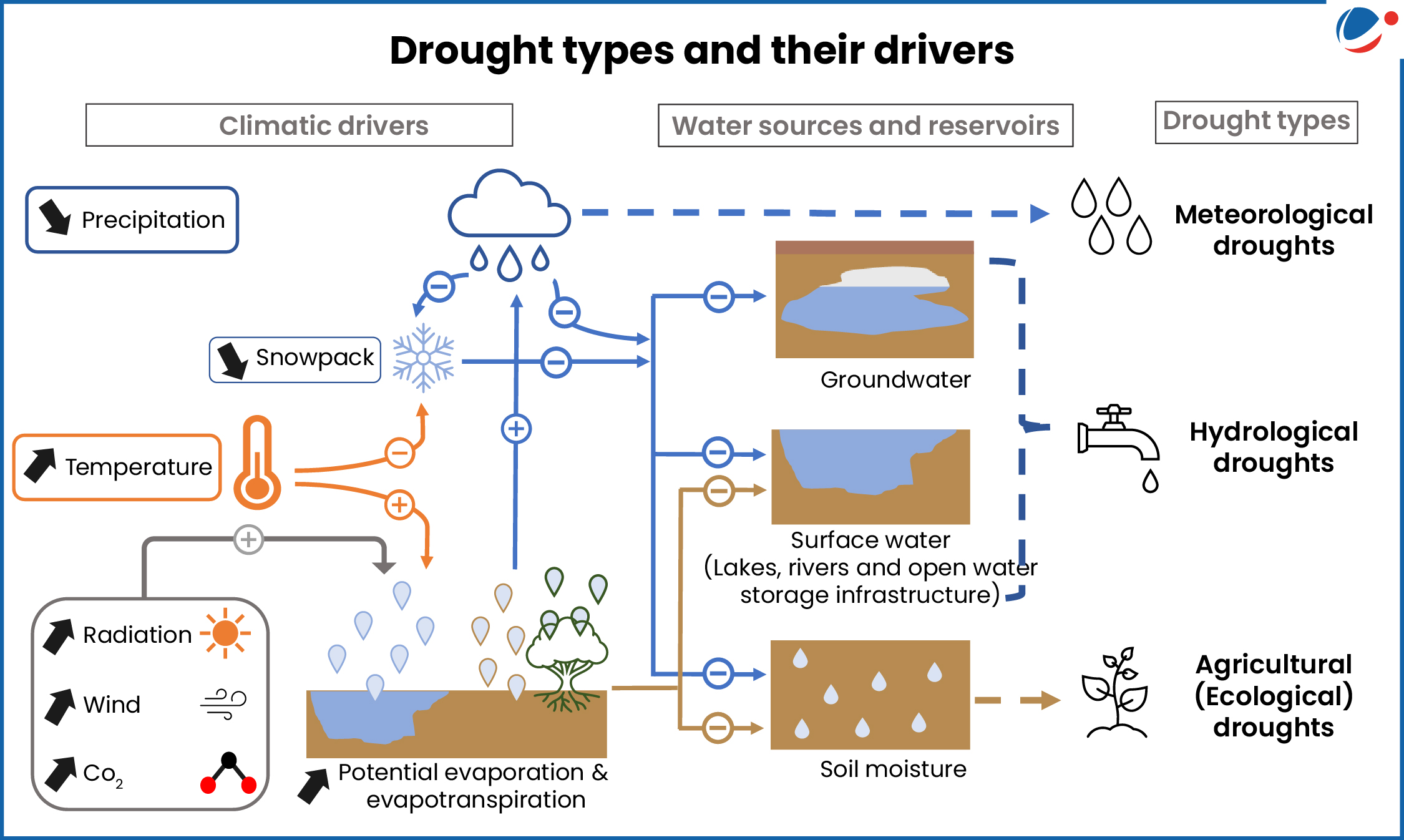
- Crop yields can decline by up to 22%.
- Ecological:
- Reduction in soil moisture: Since 1980, 37% of global land has experienced significant soil moisture decline.
- Groundwater decline: Groundwater levels are falling globally, with 62% of monitored aquifers in decline.
- Other:
- Droughts are responsible for 34% of disaster-related deaths (World Meteorological Organization (WMO), 2021) and exacerbate poverty, inequality and displacement.
Key Initiatives for prevention of Droughts
|





