The innovation ensures brain-computer interfaces respect user privacy by requiring mental passwords before decoding thoughts into text or audio.
What is a Brain-Computer Interface?
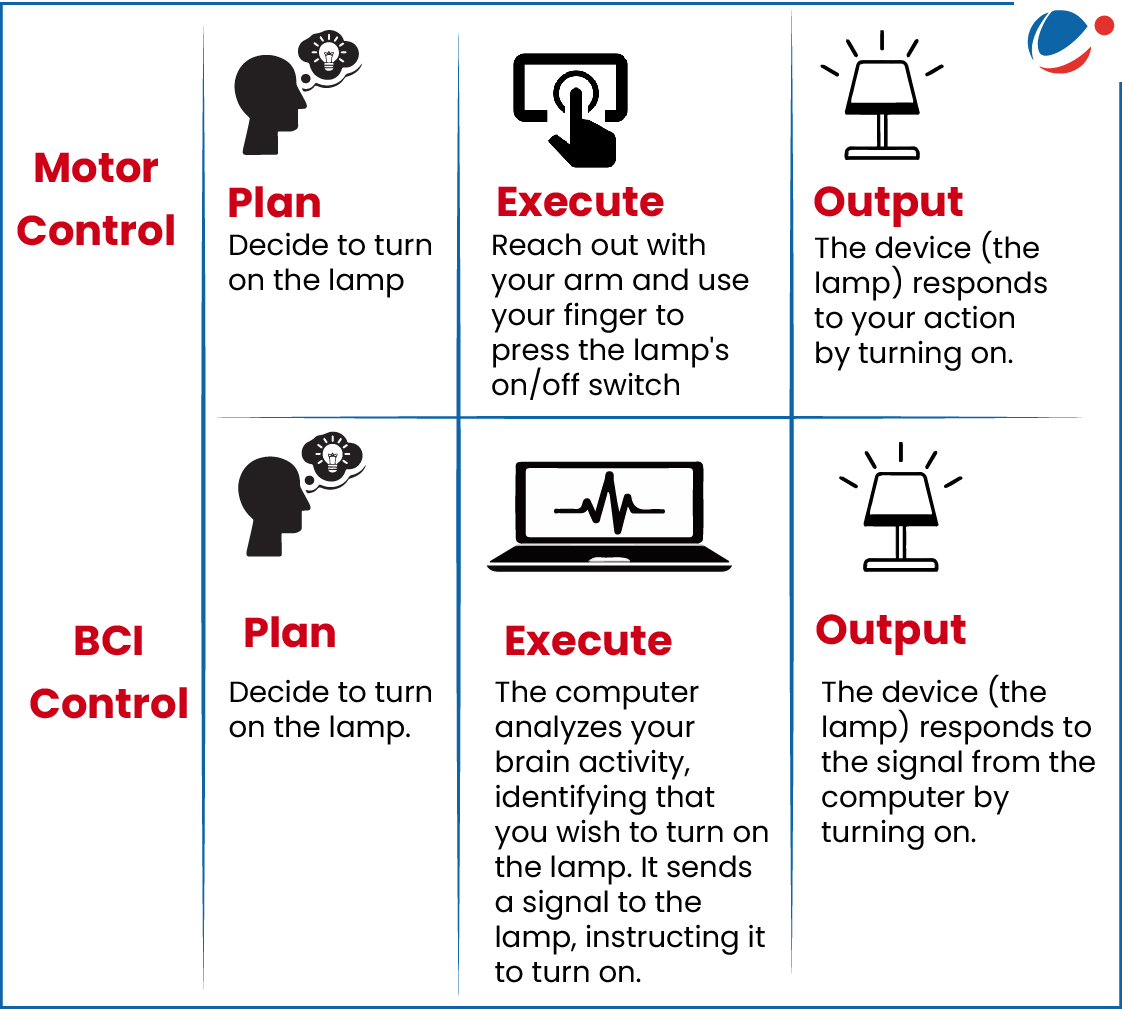
- A BCI enables direct brain-to-device communication, translating neural signals into commands.
- This bypasses muscular control, allowing users to operate applications with thought alone.
- BCIs acquire brain activity (via invasive implants or non-invasive wearables), process signals, and send commands, with feedback crucial for user adaptation.
Key Applications of BCIs:
- Medical: Restoring mobility and speech for patients with paralysis, ALS, or stroke.
- Mental Wellness: Providing feedback for mental health management.
- Gaming/Industry: Enabling immersive gaming and decision support systems.
- Cognitive Enhancement: Potential for enhancing memory, attention, and decision making.
Key Concerns Related to BCIs:
- Cybersecurity: Risks like brain tapping (intercepting private thoughts/beliefs), misleading stimuli attacks (mind control), and adversarial attacks on AI components.
- Privacy: Protecting sensitive neural data from unauthorized access.
- Cognitive Liberty: Threat to an individual's mental self-determination.
- Health Impacts: Unclear long-term consequences of BCI use.
- Regulatory & Cost: Lack of standardized regulations and high costs limit accessibility.
Way Forward
- Robust Regulations: Implementing tailored data privacy laws, ensuring transparency and informed consent.
- Enhanced Security: Developing BCI-specific access controls and defense strategies.
- Establishing neurorights: To safeguard mental privacy, cognitive autonomy, and freedom of thought of individuals from exploitation and unauthorized interference.







