The report highlights that water cycle has become increasingly erratic and extreme, swinging between deluge and drought.
Key Highlights of Report
- Glacier Melt: All glacier regions worldwide report losses due to melt for third straight year.
- Many small-glacier regions have already reached or are about to pass the so-called Peak Water Point - when a glacier's melting reaches its maximum annual runoff, after which this decreases due to glacier shrinkage.
- Erratic Water Cycle: Two thirds of global river catchment area have too much or too little water.
- This is leading to increasing extreme events – unusual heavy rainfall in Africa’s tropical zone, extensive flooding in Europe and Asia, drought in Amazon Basin etc.
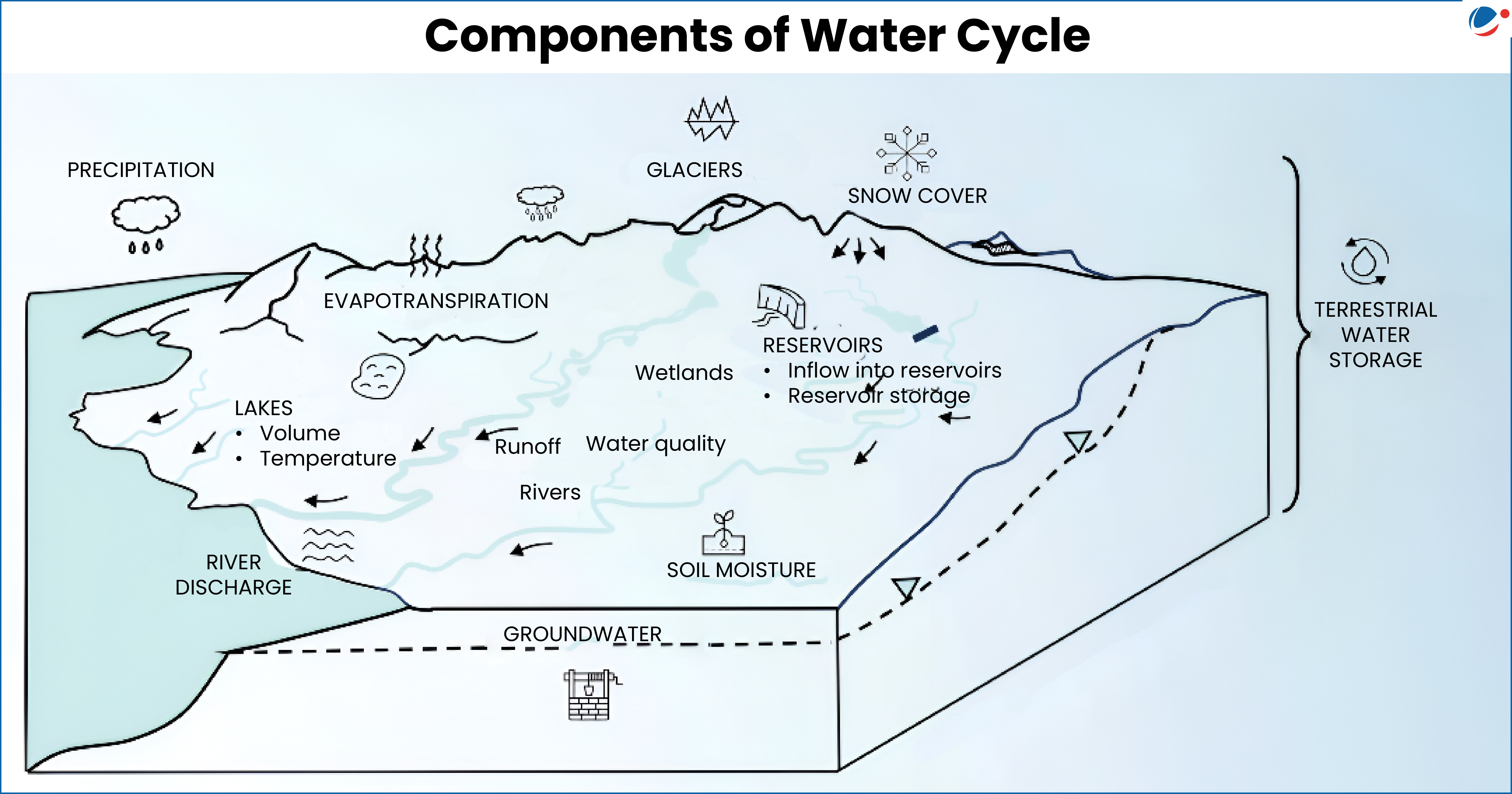
Water Cycle
- Water cycle describes the continuous movement of water within the Earth and atmosphere and involve pools and fluxes.
- Pool refers to many forms and places where water is stored like lake, glacier, atmosphere etc.
- Fluxes are ways that water moves between the pools, including state changes like evaporation or condensation.
- Impact of Climate Change: Warming global climate intensifies water cycle as it increases the role of evaporation.
- It leads to more water being stored in atmosphere, increasing extreme weather events such as droughts, heavy precipitation, and hurricanes.
- It is causing sea level rise through melting glaciers and expansion of ocean water, flooding coastal areas.