TN-SHORE, approved in September 2025, is an ambitious ₹1,675-crore project, largely funded by the World Bank, designed to strengthen Tamil Nadu’s coastal economy and resilience.
- A core component of TN-SHORE is the restoration and plantation of 1,000 hectares of mangroves.
- World Bank funds will be channelled directly to village mangrove councils, which comprise local residents.
- Beyond mangroves, the initiative seeks to restore 30,000 hectares of seascapes and safeguard endangered species like dugongs and turtles.
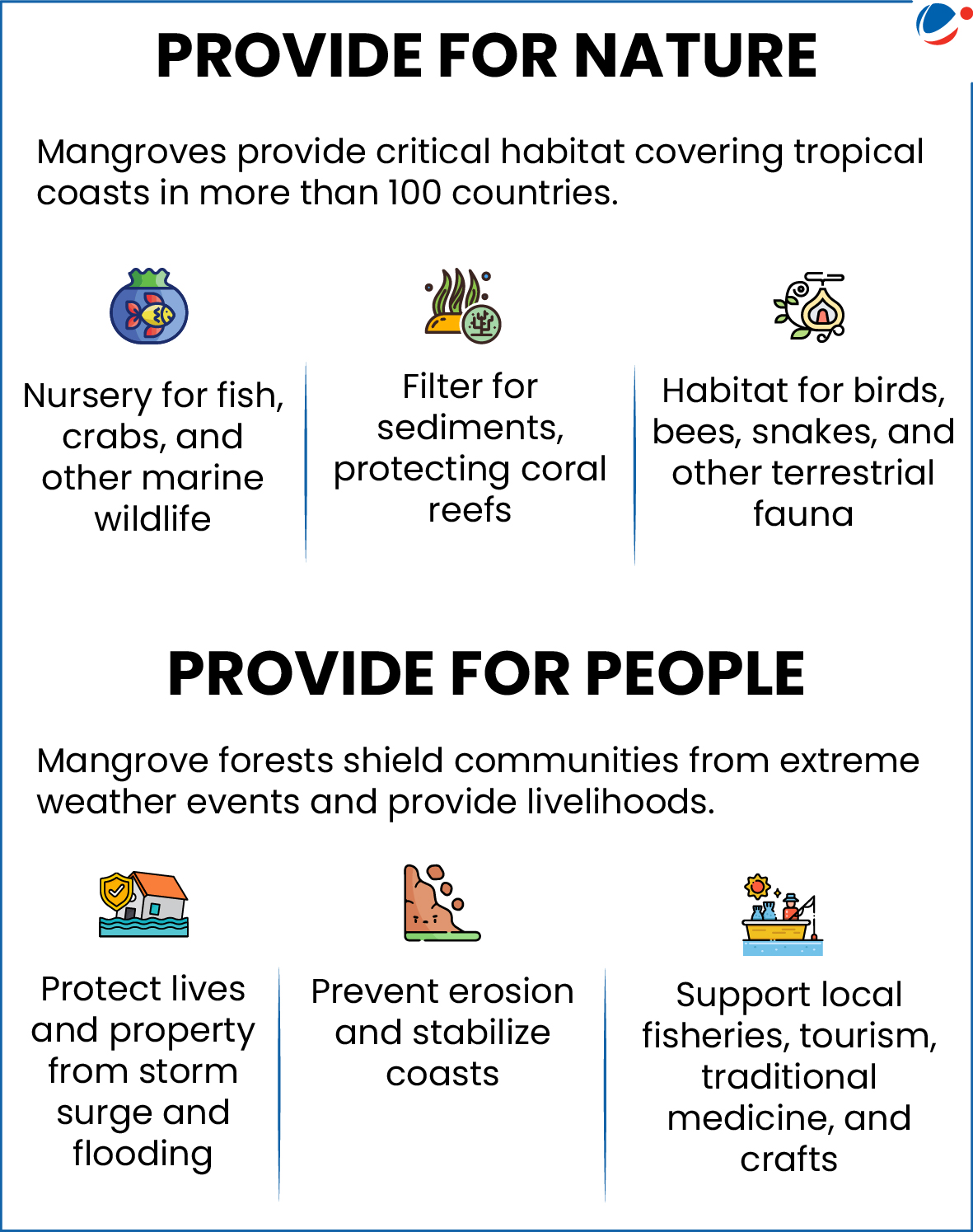
Mangroves and Their Significance
- A mangrove is defined as a salt-tolerant plant community found in tropical and subtropical intertidal regions.
- These ecosystems thrive in high-rainfall areas (1,000–3,000 mm) with temperatures ranging from 26°C to 35°C.
- Climate Role: Mangroves are termed "Nature’s Carbon Vault" because they store 7.5–10 times more carbon per acre than typical tropical forests.
- Livelihood: In Navghar, Maharashtra, mangrove restoration under a government project led women to secure stable, year-round employment through sustainable mud crab farming.
Mangroves in India
- As per the India State of Forest Report 2023 (ISFR-2023), India’s total mangrove cover stands at 4,991.68 sq. km.
- India recorded an 11.4% net increase in mangrove cover between 2001 and 2023.
- West Bengal holds the largest share of India's mangroves (42.45%), followed by Gujarat (23.32%).







