Functional foods and smart proteins were recently mentioned in the news in the context of India’s nutritional security.
What are Functional Foods?
- They are foods that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition, either naturally or leveraged through technologies such as nutrigenomics, bio-fortification, 3D food printing, and bioprocessing.
- Examples: Vitamin-enriched rice, omega-3-fortified milk, probiotic yoghurt.
What are Smart Proteins?
- These are proteins sourced using biotechnology that aims to reduce reliance on conventional production.
- It includes:plant-based proteins (to mimic animal meat and dairy), fermentation-derived proteins, cultivated meat, etc.
INS Sahyadri participates in the 29th edition of Malabar naval exercise taking place in Guam, a strategic US military base, in the western Pacific Ocean.
About Malabar Exercise
- Aim: To strengthen cooperation and security in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Participating countries: India, Australia, Japan, and the United States of America.
Indian researchers have identified biochemical markers in the blood that could help detect kidney complications in diabetic patients.
About Biochemical Markers
- Meaning: They are small molecules (like sugars, amino acids, lipids) produced during metabolic processes in the body and are used by doctors for ascertaining disease risks.
- For e.g., cholesterol tests are used to assess heart disease risk.
- Components for identifying kidney complication: arabitol, myo-inositol, ribothymidine, and a toxin-like compound called 2PY, etc.
Union Government has decided to remove 50% export duty on molasses.
About the Molasses
- Molasse is a byproduct of the sugar beet and sugar cane refinement processes.
- It is a dense, viscous liquid of dark brown tint, rich in sugars, and containing a small percentage of water.
- It has different names according to the region, such as exhausted honey, poor honey, etc.
- Molasses contains more nutrients such as calcium, iron, magnesium and potassium and similar amounts of calories than other liquid sugars like honey.
- Key Applications: Beverage production, Ethanol production, fertilizers etc.
Government is going to announce a sustainable aviation fuel policy.
About Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF)
- Meaning: It is an alternative fuel made from non-petroleum feedstocks that reduces emissions from air transportation.
- It can help reduce carbon emissions by up to 80 per cent compared to conventional fuels.
- Sources: Waste fats, oils and greases, municipal solid waste, agricultural and forestry residues, etc.
- Benefits: Engine and infrastructure compatibility; Lesser emissions compared with conventional jet fuel, etc.
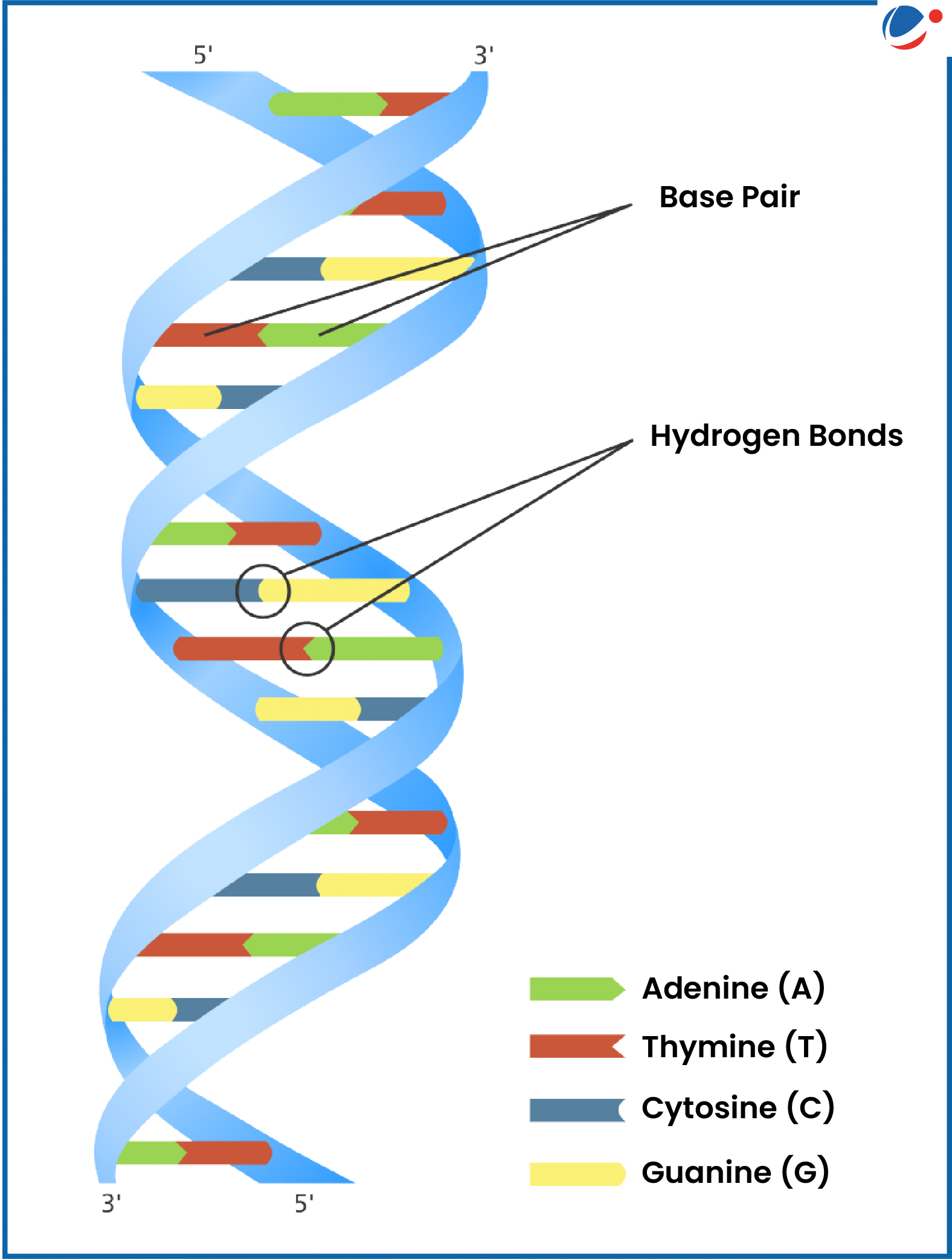
The Nobel laureate James Watson co-credited with the pivotal discovery of DNA's double-helix structure died recently.
About double helix structure
- Double helix is the term used to describe the shape of our hereditary molecule, DNA.
- It consists of two strands of DNA twisted around one another and connected in the center by hydrogen bonding.
- Hydrogen bonds form specifically between the nitrogenous bases (adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine) of complementary nucleotides on opposite DNA strands.
Article Sources
1 sourceThirty-Seventh Meeting of the parties to the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer (MOP37) has recently concluded.
- It highlighted discrepancies in HFCs emissions between reported and measured data, lack of atmospheric monitoring stations in many regions, etc.
About Montreal Protocol
- Signed: in 1987
- It is a global legally binding treaty to eliminate production and use of Ozone depleting Substances (ODS).
- Implemented under the Vienna Convention (adopted in 1985).
- Kigali Amendment to Montreal Protocol: Adopted in 2016 to phase-down production and consumption of HFCs (non-ODS but potent greenhouse gases).




