Prepared by Department of Science & Technology (DST), the roadmap offers Three Phased Research & Development Program in Carbon Capture, Usage and Storage (CCUS).
Three Phases Include
- Integration of the current state-of-the-art CCUS technologies or their improved versions as End-Of-Pipe (EP) solution in the existing emitting industries.
- Integration of advanced CCUS technologies in new industrial manufacturing plants using CCUS Compliant Design (CCD).
- Integration of emerging CCUS technologies like photo-bio-electro-catalytic conversions as CCUS in One Pot (COP) strategy in new low-emission industrial manufacturing technologies.
About CCUS
- Technologies that enable the mitigation of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from large point sources like power plants, or removing existing CO2 from atmosphere and storing it either in seawater, deep-sea sediments, or geological sites, etc.
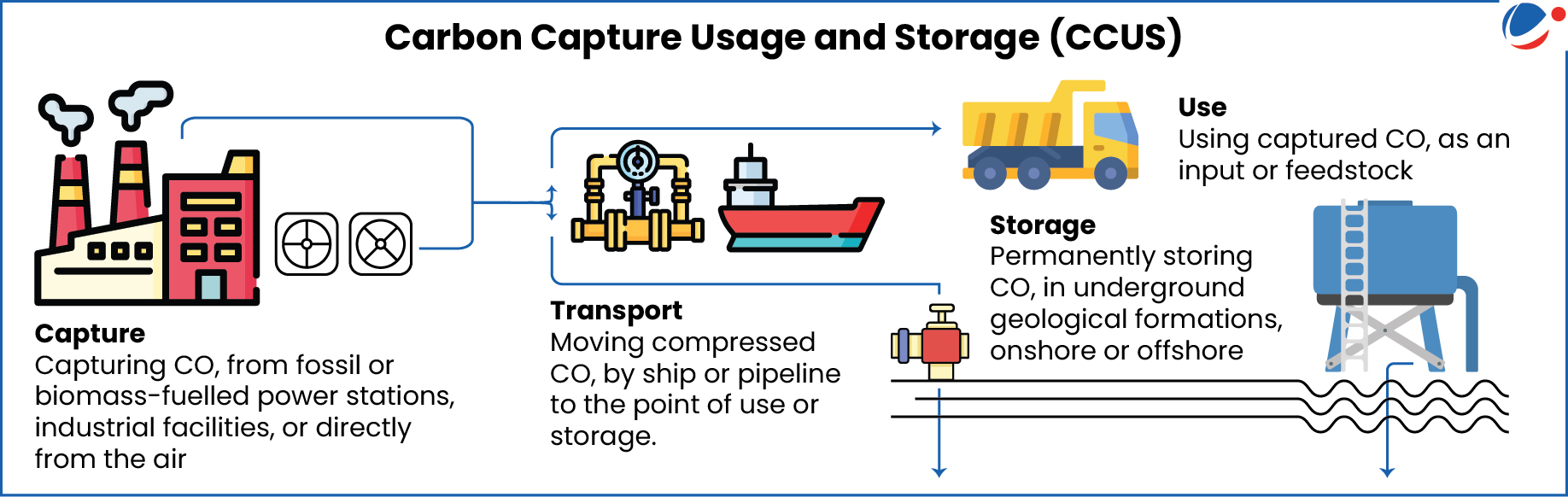
Role of CCUS in Mitigating Climate Change
- Reducing emissions in ‘hard-to-abate’ industries: Mainly industries that are difficult to decarbonise including iron, steel and chemicals.
- Producing low-carbon electricity and Hydrogen: CCUS can be installed on power plants running on coal, gas, biomass or waste.
- Removing existing CO2 from atmosphere: Through either Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) or Direct Air Carbon Capture and Storage (DACCS) – both having technological foundation with CCUS.
- DACCS enables the capture of CO2 directly from the atmosphere while BECCS can result in CO2 removal on a net basis where the biomass is sustainably sourced.





