The Viksit Bharat–Guarantee for Rozgar and Ajeevika Mission (Gramin) (or VB–G RAM G Bill), 2025 seeks to replace the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), 2005.
- State governments will notify a scheme consistent with the Bill, within six months from its commencement.
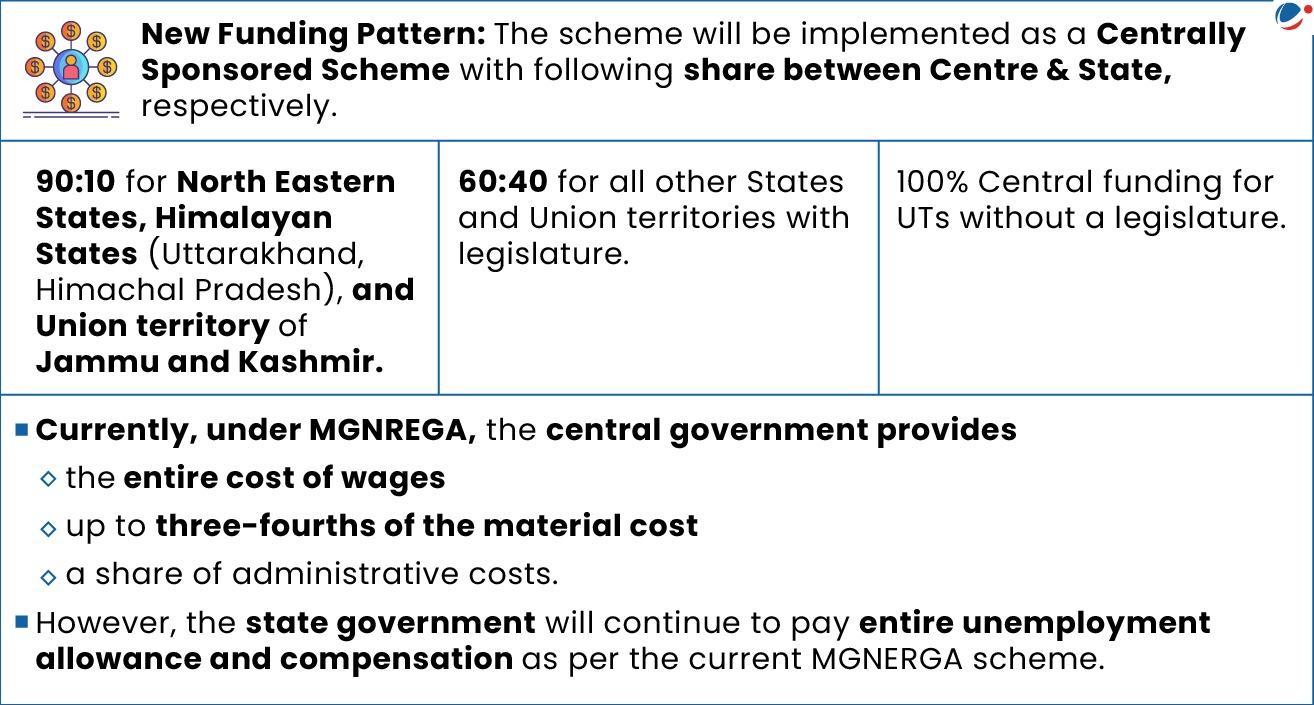
Key Features of the Bill
- Employment Guarantee: Increased to 125 days (from 100 days) per financial year to every rural household to undertake unskilled manual work.
- State governments now can suspend the scheme for a period of up to 60 days to ensure availability of agricultural labour during sowing and harvesting season.
- Durable Asset Creation (under four priority themes): Water Security, Core Rural Infrastructure, Livelihood-related Infrastructure, and Special Works for Extreme Weather Events.
- Planning Architecture:
- Viksit Gram Panchayat Plans (VGPPs) prepared by Gram Panchayats will be integrated with PM Gati Shakti.
- VGPPs will be aggregated through the Viksit Bharat National Rural Infrastructure Stack (VB-NRIS) to enable coordinated national rural infrastructure planning.
- Panchayats will be graded based on development levels.
- Higher allocations towards underperforming panchayats to reduce regional disparities.
- Viksit Gram Panchayat Plans (VGPPs) prepared by Gram Panchayats will be integrated with PM Gati Shakti.
- Institutional Oversight:
- Central and State Gramin Rozgar Guarantee Councils: for reviewing, monitoring, and advising on scheme implementation.
- National and State Level Steering Committees: to provide recommendations on financial allocations, inter-ministerial convergence, and strategic oversight.
- Transparency & Monitoring: Focus on digitization (e.g. biometric authentication, AI-enabled analytics); Social Audit by Gram Sabha & Grievance Redressal at Block and District levels.