About IMEC
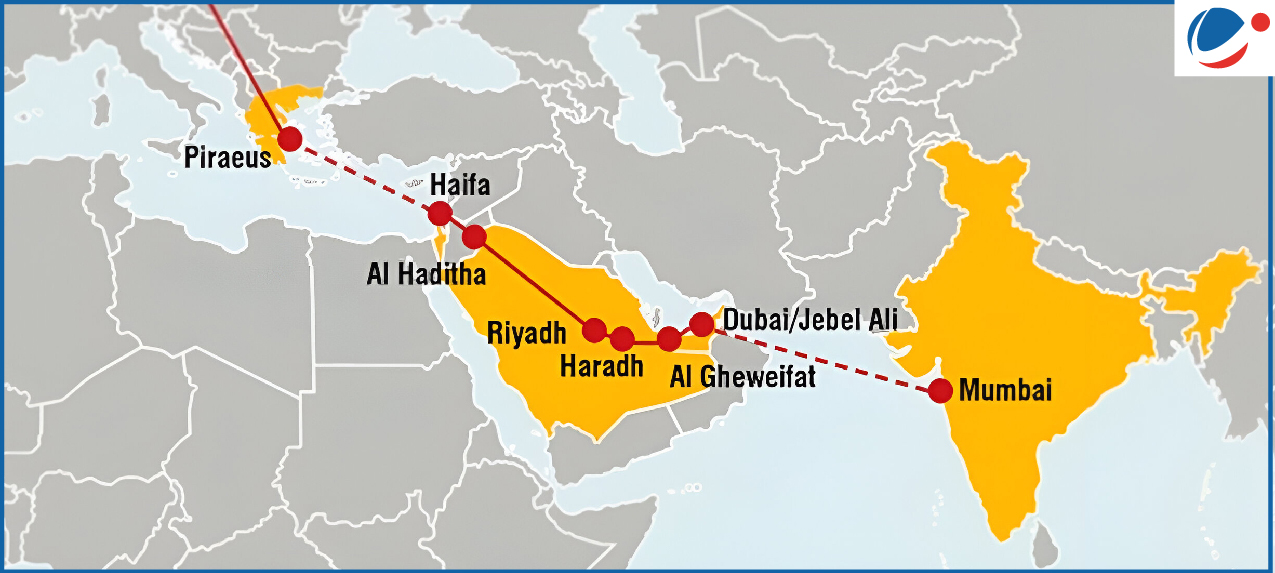
- A multi-modal connectivity project, formalized by an MoU signed between India, the European Union, France, Germany, Italy, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and the US at the G20 Summit (2023) in New Delhi.
- Objective: Developing infrastructure of ports, railways, roads, sea lines and pipelines to enhance trade between India, the Arabian Peninsula, the Mediterranean region, and Europe.
Significance of IMEC for India
- Trade Route Diversification: IMEC diversifies India–EU connectivity by reducing dependence on the Suez Canal.
- E.g., Houthi attacks on commercial shipping led to the Red Sea crisis of 2023-24
- Lower Logistics Cost and Time: IMEC is expected to reduce transit time by up to 40% and logistics costs by around 30%, helping exporters avoid delays.
- Port Optimization: It promises higher throughput for India's west coast ports (like Mumbai and Mundra) by integrating them more deeply into Mediterranean and Gulf logistics ecosystems.
- Upgradation in Global Value Chains: Improved connectivity with Europe enables India to move from low-value assembly to higher-value manufacturing and services.
Challenges
- Geopolitical tensions: E.g., Hamas–Israel war
- Port Capacity Mismatches: E.g., while the Jebel Ali port in the UAE can handle 90 million tonnes annually, Haifa port in Israel is limited to approximately 30 million tonnes.
- Financing Gaps: IMEC spans multiple countries with uneven fiscal capacities and credit profiles, making it difficult to secure traditional public funding.
To succeed, the IMEC requires a sophisticated financing structure that combines public investment, sovereign wealth capital, and multilateral guarantees, etc.







