Apart from being world’s leading market in terms of number of IPOs, India is third largest by value, with capital markets playing a central role.
- Initial Public Offering (IPO) is the process by which a private company sells its shares to public for the first time to raise equity capital transforming it to a publicly traded company.
- It is issued under the primary capital market which deals with issue of new securities.
- Key Achievements: 311 IPOs raised 1.7 trillion rupees in the first nine months of the current financial year.
- India’s market capitalisation-to-GDP ratio has risen sharply from 69% (FY16) to over 130%
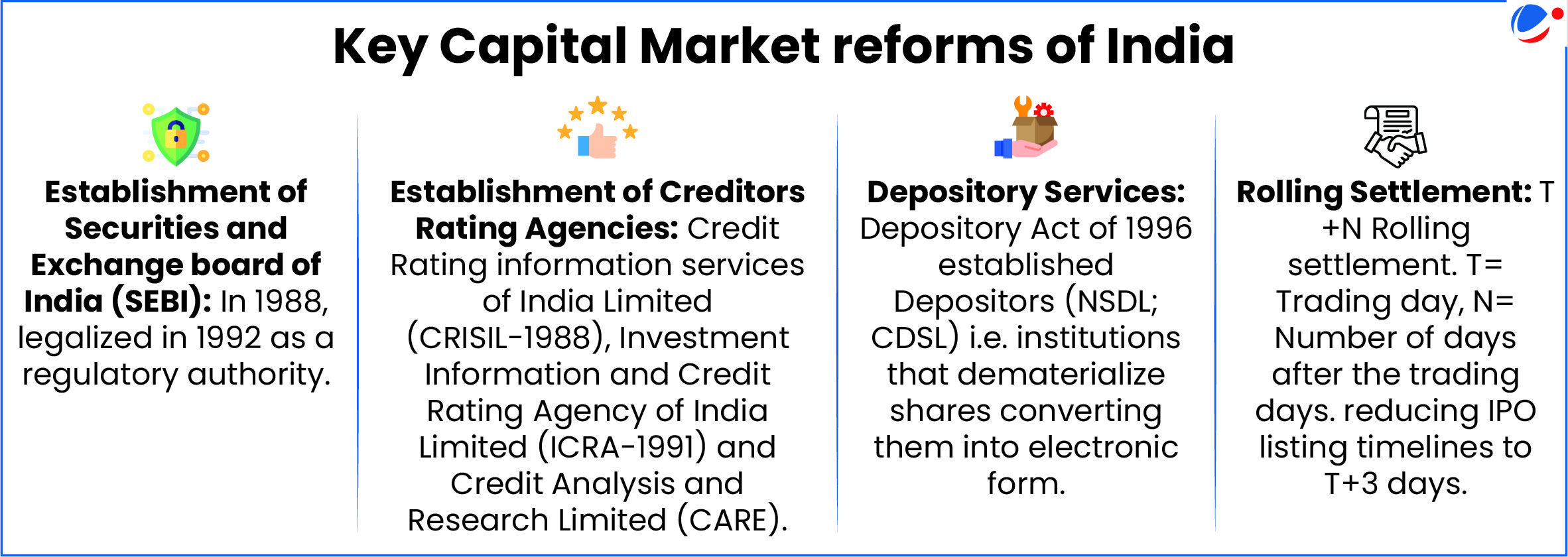
About Capital Market
- Meaning: Refers to facilities and institutional arrangements through which long-term funds, both debt and equity are raised and invested, putting them into productive use.
- Classification: Further divided Primary and Secondary Market.
- While primary market deals with new securities/shares, secondary market or stock market deals with purchase and sale of existing securities.
- Participants: Financial institutions, banks, corporate entities, foreign investors and ordinary retail investors from public.
- Instruments Used: Equity shares, debentures, bonds, preference shares etc.