NGT while noting the “strategic importance of the project” upheld its environmental clearance and compliance with ICRZ (Island Coastal Regulation Zone) and CRZ norms.
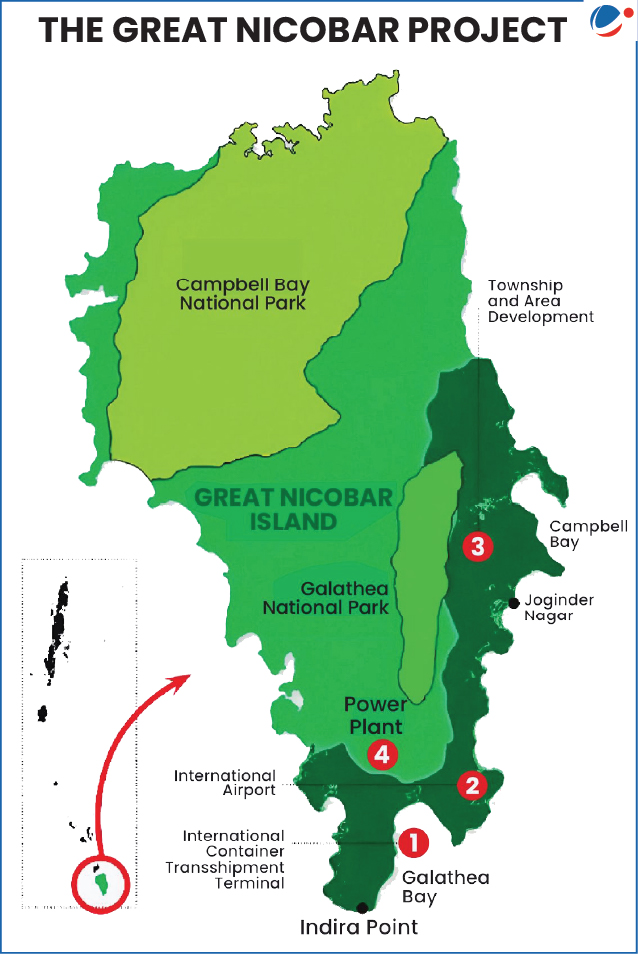
About the Great Nicobar Project
- Location: Great Nicobar Island (southernmost island of Andaman and Nicobar Islands) including parts of Galathea Bay, Campbell Bay and Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve.
- Objective: Project envisions transforming the remote outpost into a major transshipment and defence hub with integrated township, 450 MVA Gas and Solar-based power plant, dual-use civil-military airport, etc.
- Implementing Agency: Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation along with the NITI Aayog.
Concerns associated with the Project
- Regulatory Lapses:
- Environmental Impact assessment (EIA) relied on single-season data instead of comprehensive multi-season assessment.
- Proposed compensatory afforestation in Haryana is inadequate to offset loss of a tropical rainforest ecosystem.
- Forest Rights Act (FRA): Government has proceeded with project even after Tribal council withdrew its consent.
- Environmental Impact assessment (EIA) relied on single-season data instead of comprehensive multi-season assessment.
- Threat to Biodiversity: The project involves diverting approximately 130 sq. km of tropical rainforest (felling one million trees), home to the Nicobar megapode, Nicobar tree shrew, Giant leatherback turtles, corals, etc.
- Social Impact: Project might negatively impact tribal population, e.g. Shompen (Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group) and Nicobarese.
- Natural Disaster Vulnerability: The Island falls in the highest seismic-risk zone (Zone VI).
Significance of the Project for India
|








