Report has been released by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research in collaboration with the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD).
Key Highlights of Report
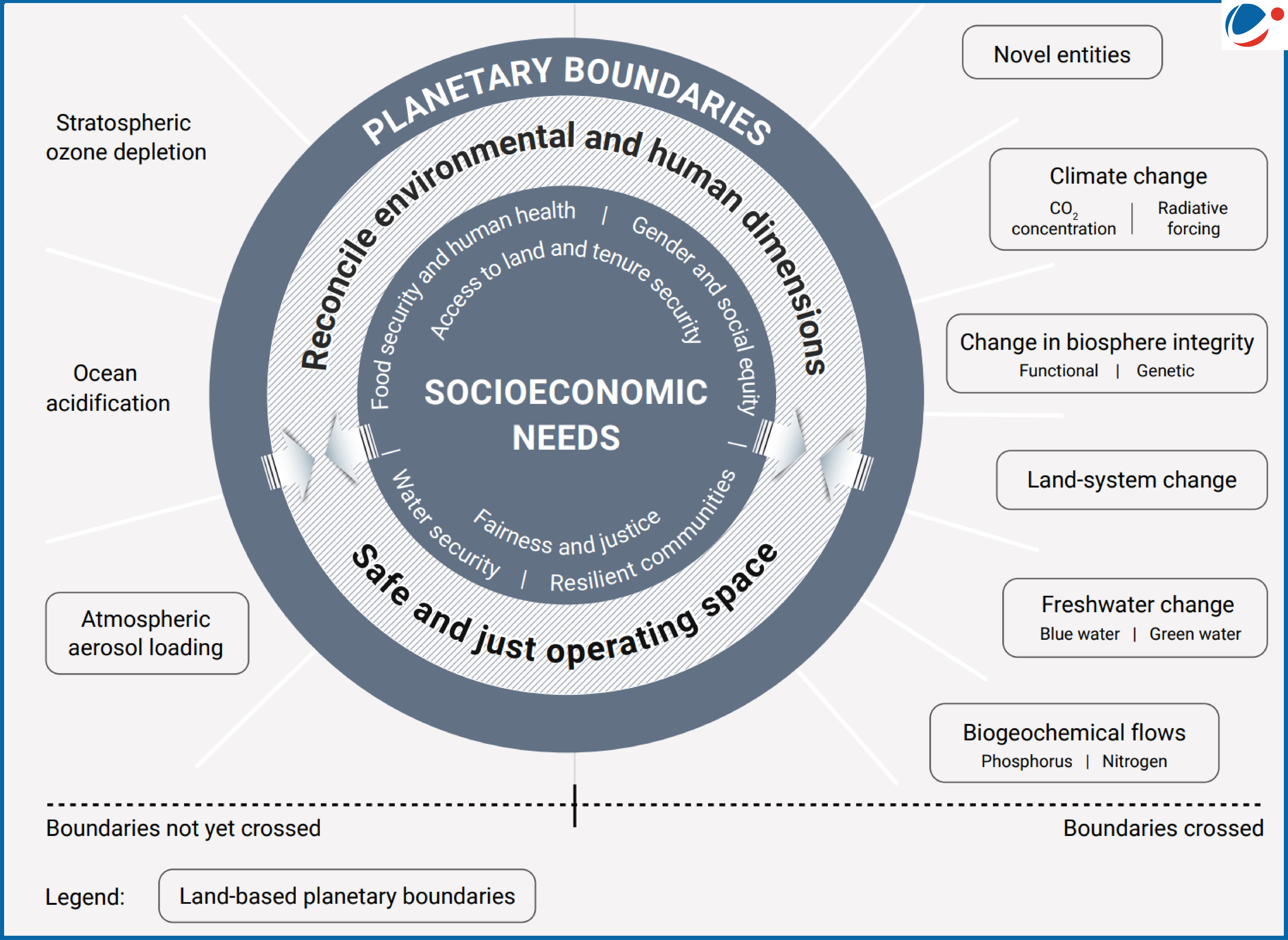
- Centrality of Land: Land is the foundation of Earth’s stability as it regulates climate, preserves biodiversity, maintains freshwater systems and provides food, water and raw materials.
- Land is central to seven of the nine planetary boundaries, which are scientifically determined thresholds within which humanity can operate safely.
- Crossing these thresholds can lead to catastrophic environmental change and destabilize the Earth system.
- Land is central to seven of the nine planetary boundaries, which are scientifically determined thresholds within which humanity can operate safely.
- Land Degradation: Driven by human activities, such as unsustainable agricultural practices, conversion of natural ecosystems, deforestation and urbanisation.
- Impact: Land degradation affects an area of 15 million sq km, and 1.2 billion people globally.
- Economic cost of land degradation is estimated to range between 6.3 and 10.6 trillion US Dollar annually.
Recommendations of the Report
- Enabling factors such as supportive frameworks, economic incentives, clear property and resource-use rights, and effective coordination between actors.
- Substantial public and private investments, in particular better integration and prioritisation of sustainable land use in all national and international funding.
- Scientific framework like the planetary boundaries can serve as a practical guide for policymakers to make evidence based policy decisions.






