Indonesia was also the chief guest country on India's first Republic Day in 1950.
- Both sides signed pacts on maritime security, health, traditional medicine etc. and working on framework agreement for defense cooperation and technology sharing projects including surface-to-surface missiles, air defense systems, and submarine construction technology transfers.
- India also welcomed Indonesia’s decision of early joining the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure.
India- Indonesia Bilateral Ties
- Political: Both were part of Bandung Conference 1955 which led to establishment of Non-Aligned Movement (1961).
- Trade: US$29.4 billion in FY2023-24.
- Military Exercises: Samudra Shakti, India-Indonesia Coordinated Patrol.
Significance of Indonesia for India
- Geo-Economic: Indonesia is India’s second-largest trading partner in ASEAN, with
- Key imports: Coal, palm oil, and rubber.
- India exports: Refined petroleum, telecom equipment, and agricultural products.
- Geopolitical: Both are members of groups like BRICS, G20, IORA, and East Asia Summit.
- India's Act East Policy and Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative and Indonesia's Global Maritime Fulcrum vision synergize, enhancing geopolitical engagement.
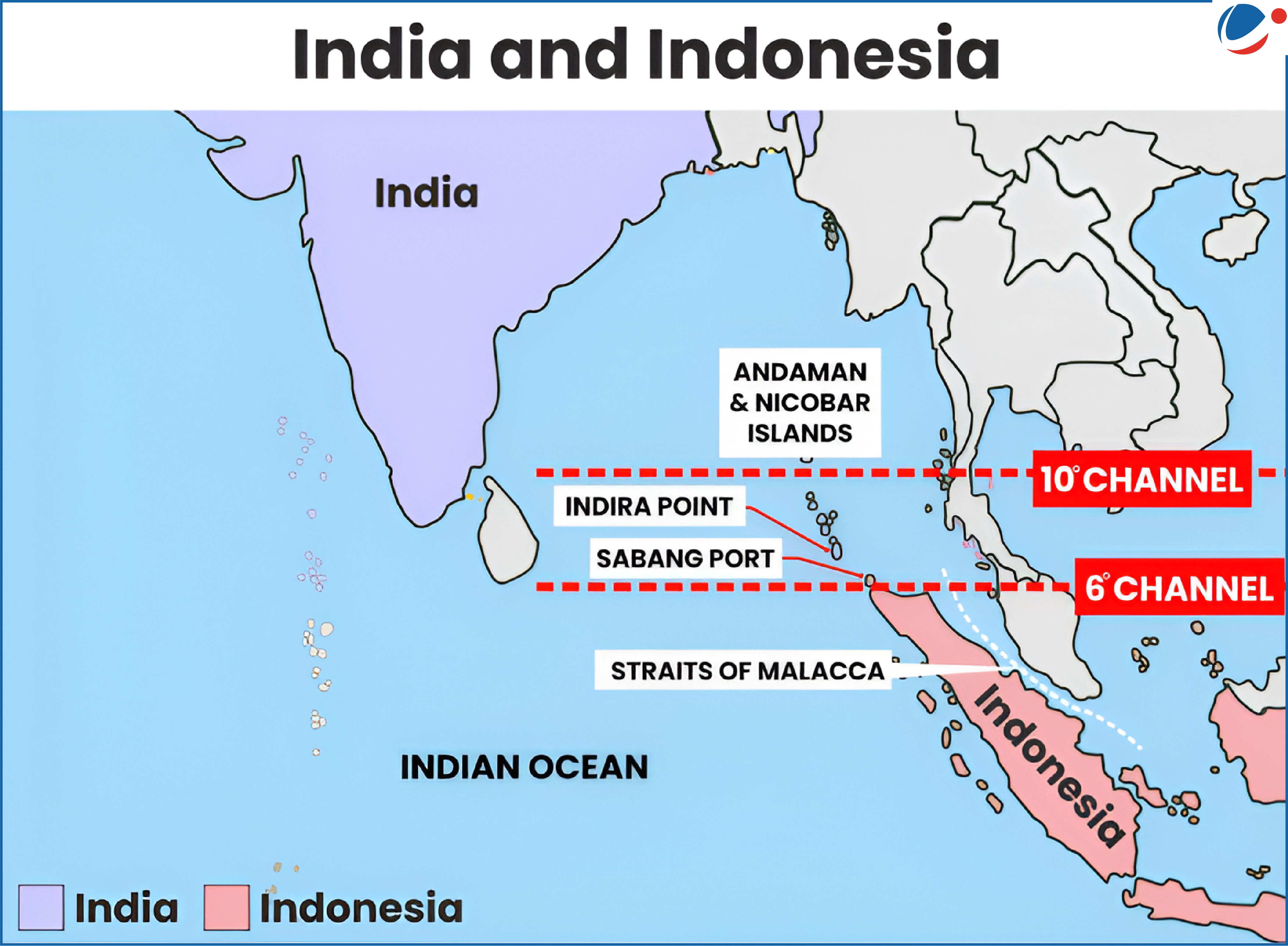
- Geostrategic: It is strategically located between Indian and Pacific Oceans, making it important for India’s SAGAR initiative.
- Access to Sabang Port will secure trade through Malacca strait, and aid in counterbalancing China's influence in Indo-Pacific.
- Cultural Significance: Indonesia’s culture is shaped by Hinduism with Ramayana and Mahabharata deeply influencing its art and folklore, strengthening people-to-people ties.





