The earthquake, with a depth of 10 km, was the strongest in two years. The shallow depth had intensified shockwaves, as they travelled from focus (Earthquake's origin point beneath surface) to surface.
- The quake’s epicentre (Ground surface directly above the focus) was located ~17 km from Mandalay (Myanmar).
What caused the Earthquake?
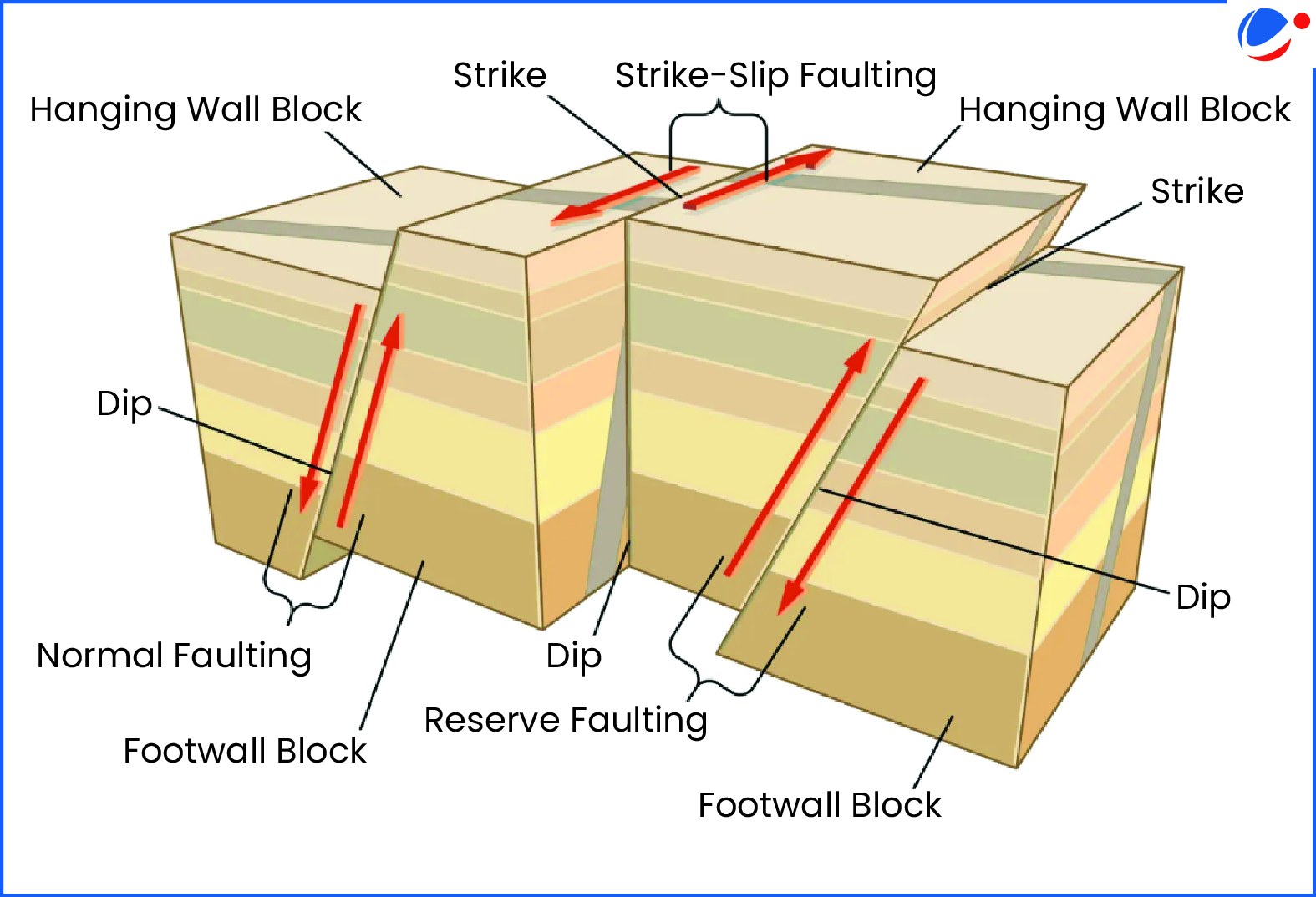
- Strike-Slip Fault: The Myanmar earthquake occurred due to "strike-slip faulting" (Sagaing fault) between the Indian and Eurasian plates.
- About the Sagaing Fault
- Location: Runs from north to south through Myanmar, and marks the boundary between Indian and Eurasian plates.
- Feature: It’s one of the longest and most activestrike-slip faults globally, spanning 1,500 km.
- Tectonic Movement: Indian plate is moving northward compared to Eurasian plate, causing stress along fault.
About Fault
- Definition: Faults are fractures in the Earth's crust where rocks move relative to each other, caused by tectonic stress.
- The movement along these fault planes releases accumulated strain, leading to earthquakes.
The primary types of faults are (See image):
|



