‘Healing Soils in India: For Better Crop Health and Human Nutrition’ Report has been released by Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations (ICRIER).
Primary Causes of Soil Degradation
- Distorted Fertilizer Policy: Highly subsidized urea (a source of N) receives over 80% subsidy, while subsidies for P and K are significantly lower. This price distortion encourages farmers to overuse N.
- Faulty Farming Practices: Intensive tillage, prolonged water stagnation in rice cultivation, heavy reliance on monocropping (e.g. cereal-cereal rotations), and burning of crop residues accelerate native carbon loss and damage soil structure.
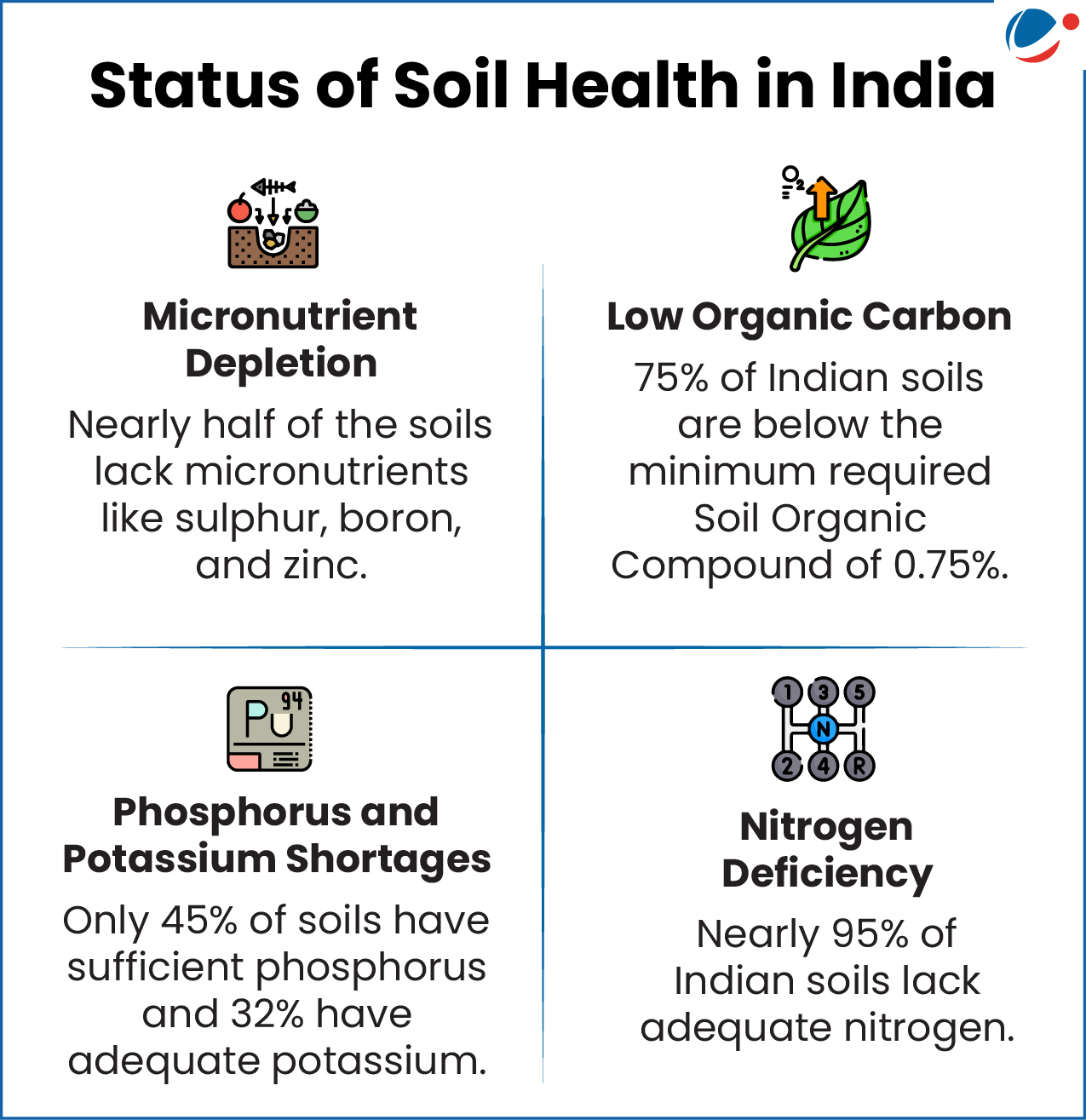
- Massive Soil Erosion: India loses about 5.3 billion tonnes of topsoil annually to water and wind erosion. This strips away 5.4–8.4 million tonnes of primary nutrients every year.
Negative Impact on Crop and Human Health
- Dropping Crop Efficiency: Plants can no longer absorb nutrients well. This reduces the efficiency of crop production.
- Loss of Nutritional Quality: Weak soils produce crops deficient in essential micro nutrients such as zinc and iron.
- Rise of Hidden Hunger: Nutrient deficient crops cause stunting, wasting, malnutrition in children.
- Water Contamination: Over-dose of fertilizer leaches out in groundwater making it unsafe for drinking.
Way Forward
Government Initiative to Promote Soil Health: Soil Health Card Scheme; PM-PRANAM Scheme; Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana; Neem-Coated Urea, etc. |




