As per the report, number of operational Carbon Pricing (CP) instruments has grown, from 5 (2005) to 80 presently, with India, Brazil, and Türkiye actively developing them.
Key Highlights of the Report
- Coverage: CP covers around 28% of global Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions, with 43 carbon taxes and 37 Emission Trading Systems (ETSs).
- Revenue Generation: Globally, ETSs and carbon taxes continued to generate over USD 100 billion (2024) for public budgets.
- Sector Wise Coverage: Power followed by industry sector have the highest coverage.
- Agriculture and Waste remains largely uncovered.
- Carbon Credit Supply Vs Demand: Supply continued to outstrip demand, with almost 1 billion tons of unretired credits in 2024, globally.
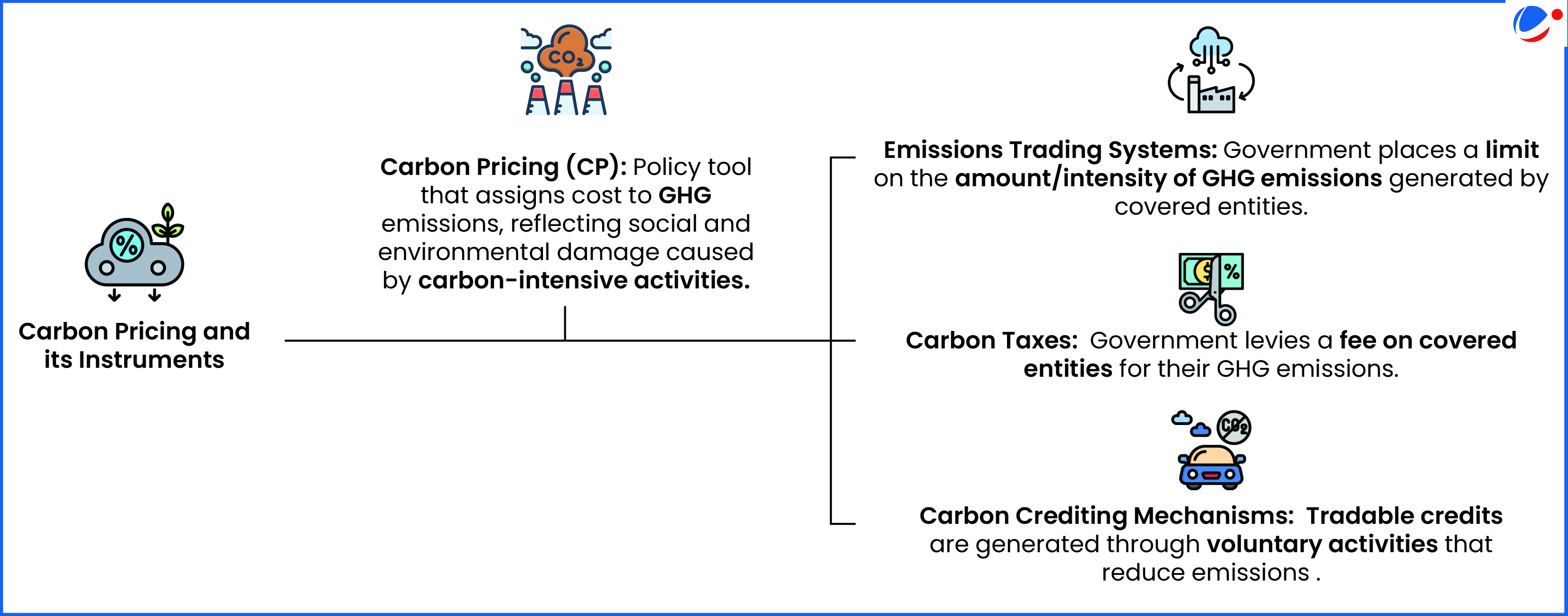
Key Provisions on CP
Global
- Article 6 of Paris Agreement (CoP 21, UNFCCC): Provides basis for facilitating international recognition of cooperative carbon pricing approaches.
- COP29 (Baku, Azerbaijan), UNFCCC (United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change) adopted the final rules for Article 6.2 (cooperative approaches) and Article 6.4 (the Paris Agreement Crediting Mechanism).
- Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanisms (CBAMs): Imposes Carbon price at the border on emissions from imported goods. E.g., EU’s CBAM.
India
- Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (2023): Provides two mechanisms,
- Compliance Mechanism: Obligated entities complies with prescribed GHG emission reduction norms.
- Offset mechanism: Non-obligated entities registers projects for GHG emission reduction/removal/avoidance for Carbon Credit Certificates.







