Report by India Energy & Climate Centre highlights need to scale up energy storage to meet clean energy goals such as installing at least 500 GW of non-fossil based power generation capacity by 2030.
- India will need 61 GW of energy storage by 2030 and 97 GW by 2032 to support clean energy capacity, a massive leap from today’s 6 GW (mostly pumped hydro).
- Due to significant cost reductions, battery storage is anticipated to dominate the overall energy storage mix.
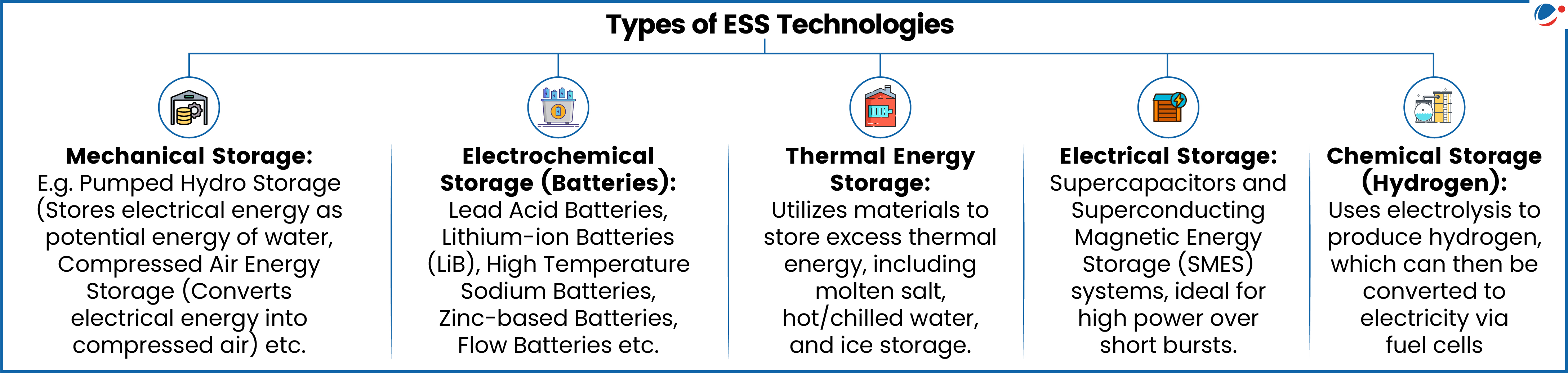
About Energy Storage Systems (ESS)
- ESS can be used for storing available energy from Renewable Energy and further can be used during peak hours of the day.
Significance of ESS in India
- Enables higher penetration of Variable Renewable Energy (VRE) into the grid.
- Increased Electric Mobility adoption
- Maintain grid stability and power quality
Policy and Regulatory Recommendations
- Adding Storage to Existing RE Projects: To maximize grid infrastructure efficiency and address regulatory challenges.
- Mandatory Co-located Energy Storage for New RE Projects
- Expanding Viability Gap Funding (VGF): Extend existing VGF scheme for standalone Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) to solar + storage projects.
- Promoting Domestic Manufacturing and Supply Chains: Expand schemes like PLI program specifically targeted at advanced chemistry cells (ACC) and R&D.
- Making strategic investments to secure key supply chains (such as strategic lithium or rare earth reserves with partner countries).







