Japan has elected Sanae Takaichi as the country’s first female Prime Minister reflecting a gradual shift toward inclusivity and gender balance.
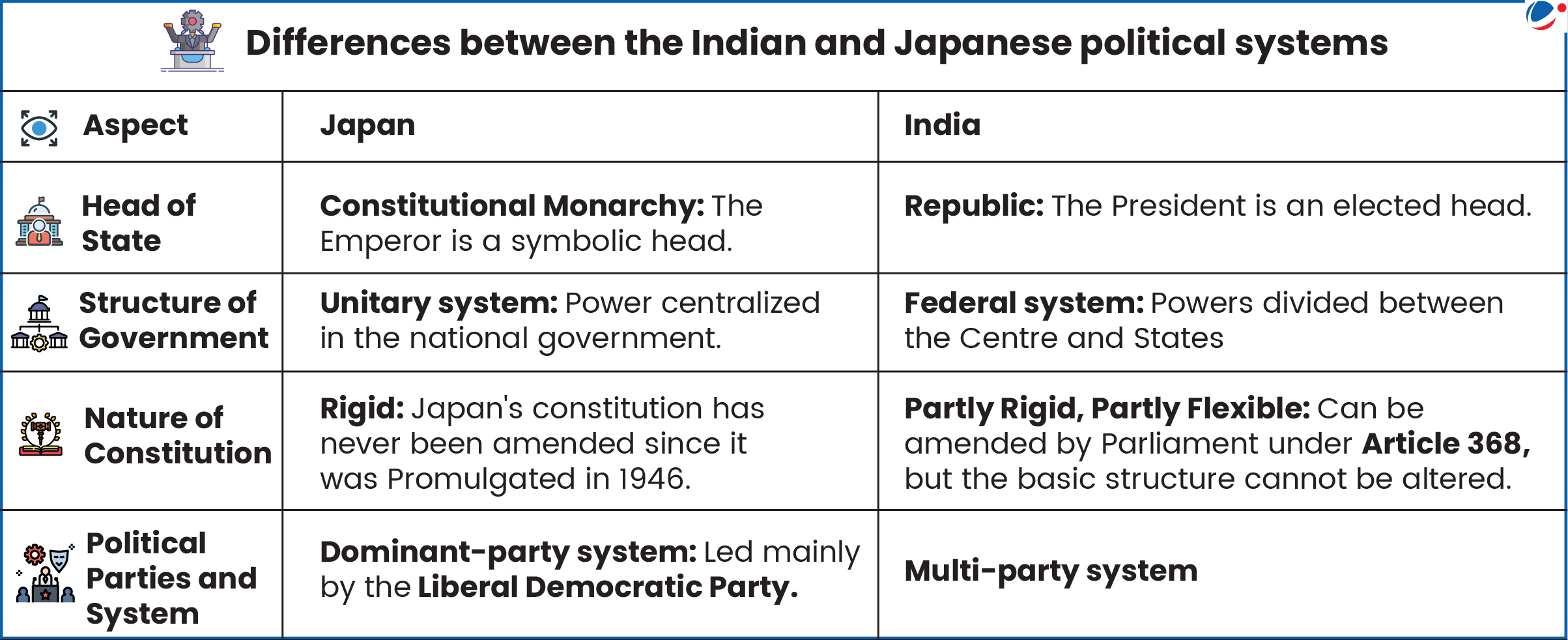
Similarities between the Indian and Japanese political systems
- Written constitutions: India’s constitution is the lengthiest in the world, while Japan has a small constitution with utmost 5000 word.
- Parliamentary Democracies: Both are parliamentary democracies with a Prime Minister as the real executive head.
- Bicameral Legislatures: Japan’s National Diet consists of the House of Representatives and the House of Councillors, while India’s Parliament comprises the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha.
- Fundamental Rights: In Japan, Chapter III (Articles 10–40) guarantees equality, liberty, and human dignity, while in India, Part III (Article 12-35) ensures 6 fundamental rights.
- Other: Independent judiciary, Universal Adult Franchise, Constitutional Supremacy etc.