Storing captured carbon subsea, in depleted oil and gas wells or aquifers — is ramping up as a climate solution globally.
About Ocean based CCUS
- It involves capturing CO2 from sources (generally from large point sources like power generation or industrial facilities using fossil fuels) and storing it in seawater or deep-sea sediments.
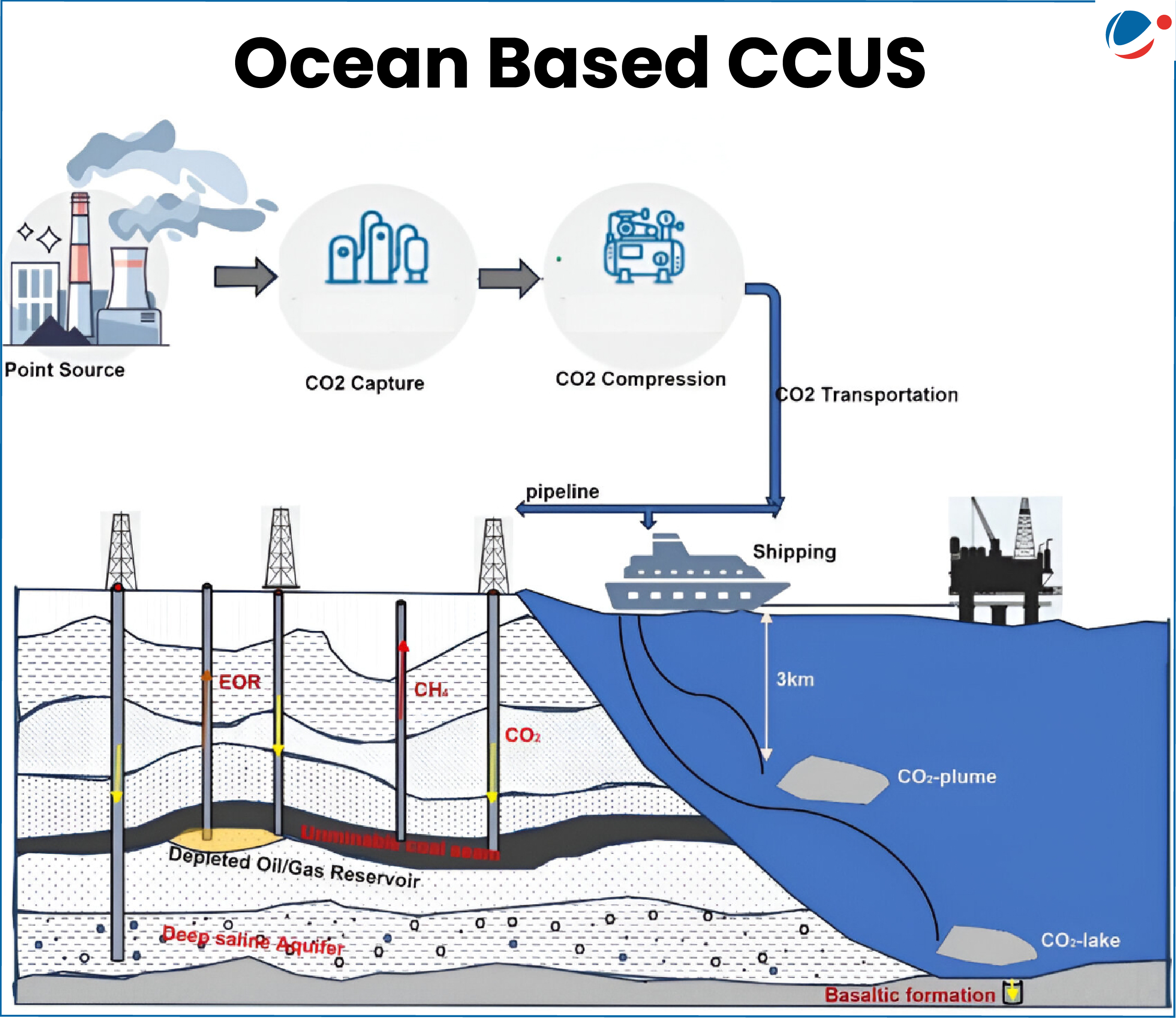
Key Techniques
- Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement (OAE): It accelerates CO2 absorption by adding pulverized minerals (e.g., Lime) or electrochemically boosting rock weathering.
- Ocean fertilisation: Promotes the growth of phytoplankton by adding required micronutrients, like phosphorus, nitrogen, etc., facilitating deep-ocean carbon storage.
- Other methods: Biological Carbon Capture, which utilizes marine ecosystems and the Enhancement of Blue Carbon Sinks like mangroves.
Key Benefits of Ocean-Based CCUS
- Durable Storage: Techniques like OAE could store carbon for up to 100,000 years.
- Vast Storage Capacity: Ocean is the largest natural carbon sink, storing 50 times more carbon than atmosphere.
- Safety and Scalability: It uses low temperatures and high pressure to stabilize CO2 in liquid form, thus minimizing leakage, preventing groundwater contamination, etc.
- Carbon Utilization: Captured CO2 can be repurposed for industrial applications, including green hydrogen, biofuels, biopolymers, etc.
- Climate Mitigation: It can reduce global CO2 emissions by 14% by 2060.
- Benefits for India: Achieve its Net-zero target by 2070; sustainable Blue growth; India’s vast coastline offers huge potential.
Currently, the technology is in early stages of development and is cost and capital intensive. It requires suitable funds for research, innovation with detailed techno-economic and environmental impact analysis before implementation.







