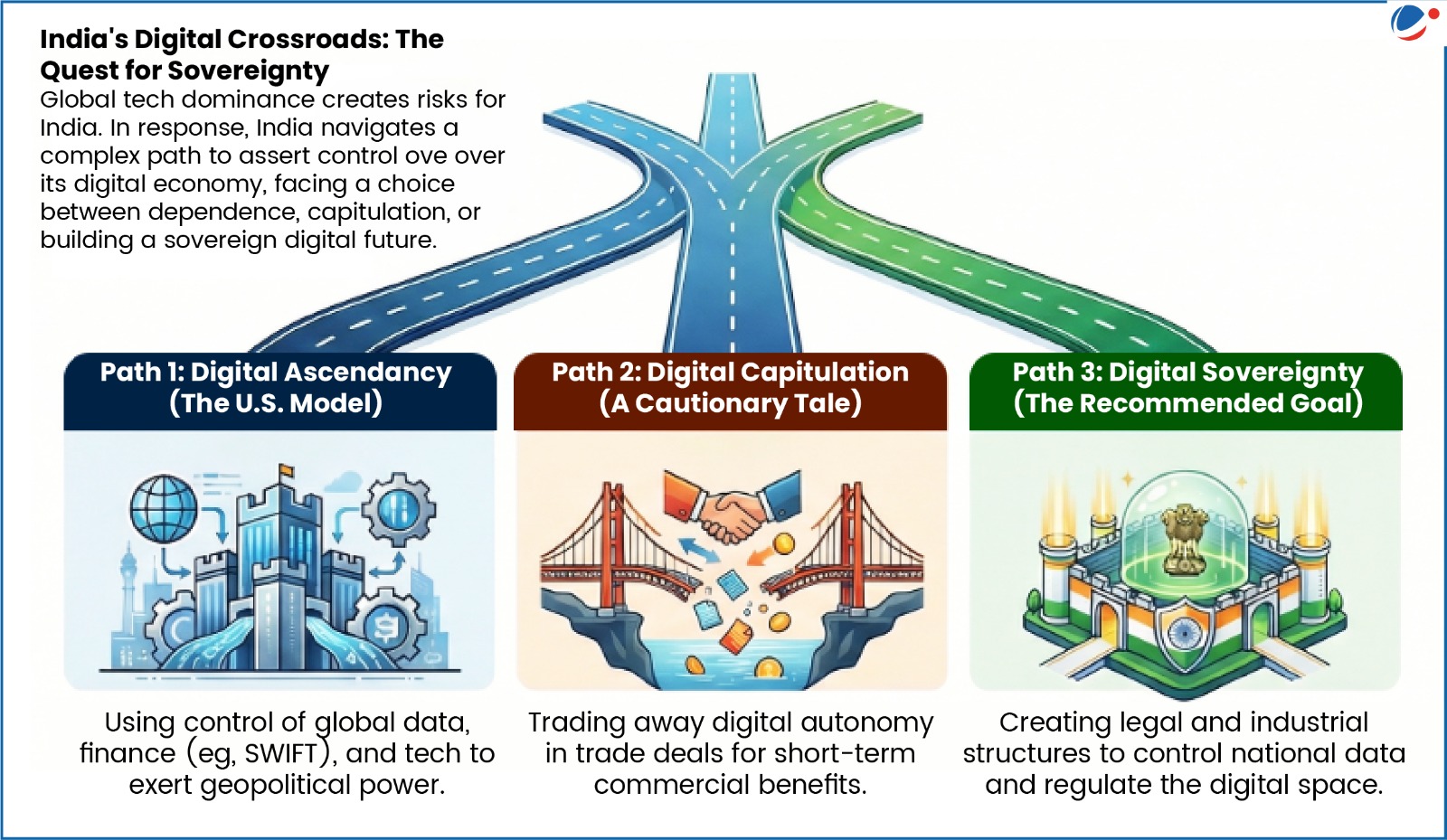
As the locus of geopolitical influence shifts from oil to data, India faces a trilemma of digital governance (refer infographic).
What factors are pushing India towards Digital Sovereignty?
- Geopolitical Volatility: Strained India–U.S. ties over trade, tariffs, Russian oil purchases, and regional issues create persistent uncertainty, pushing India toward tech self-reliance.
- Global Digital Dominance: The U.S.-led “digital ascendancy model” controls global data, internet, and financial infrastructure (e.g., SWIFT), weaponized against Iran, Russia, and indirect pressure on India’s energy trade.
- Vulnerability to Foreign Control: E.g. Microsoft’s sudden suspension of services to Nayara Energy (due to EU sanctions) exposed India’s risky dependence on foreign tech providers.
- Data as the New Currency: A nation’s digital footprint determines its strategic strength unlike traditional factors.
Pathways to Digital Sovereignty for India
- Digital Sovereignty Defined: creating legal and regulatory structures that ensure sovereign control over data exports and national digital space. E.g. through Digital Personal Data Protection Act.
- Digital Industrialization: Unlike China’s exclusion model (restricting foreign tech presence), India should develop a national digital industrialization policy framework.
- Foundational Initiatives (India Stack): through initiatives like the Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), the Aadhaar system, etc.
- Others: Sovereign AI (e.g. BharatGen); Free and Open Source Software (FOSS) approach, Indigenous Technology (e.g. Arattai, messaging app developed by Zoho), etc.
Challenges for India
|





