India added 387 MW in data centre capacity in 2025, compared to 191 MW in 2024, reflecting a year-on-year growth of 103 per cent, according to a report.
- A Data Centre is a dedicated secure space where computing and networking equipment is concentrated for the purpose of collecting, storing, processing, distributing, or allowing access to large amounts of data.
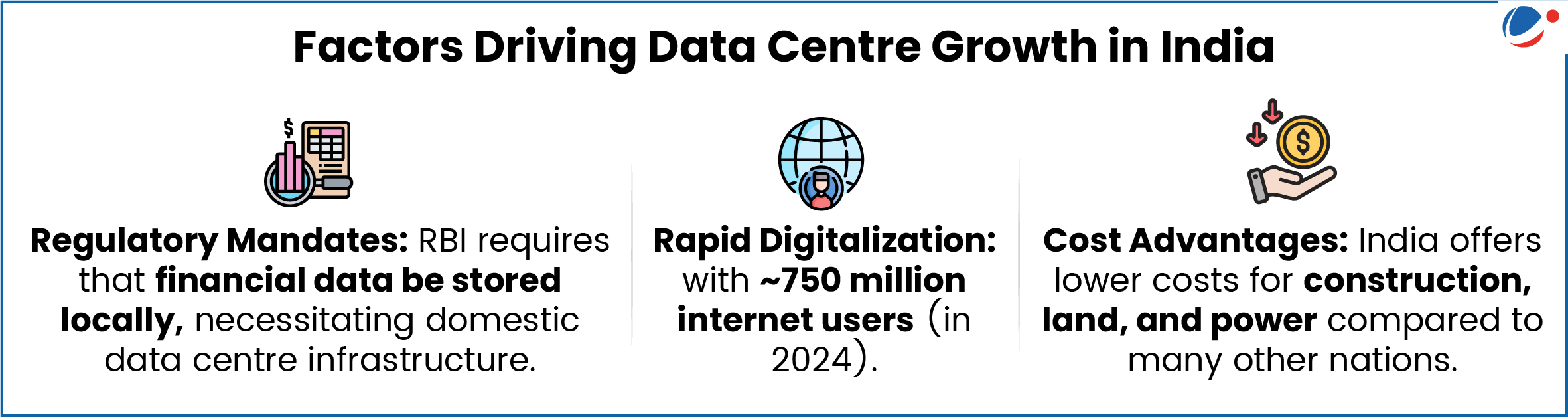
Significance of Data Centres for India
- Key enablers to the digital revolution in India, transforming Government services (Aadhar, UPI, ONDC) enabling remote work and education and fostering start-up innovation.
- Integration of emerging technologies such Artificial intelligence (AI), internet of things (IoT) etc. into different public services and judiciary.
- Other:
- Facilitating data localisation (eliminating risk of foreign surveillance), and enhancingNational security through access to data.
- Protecting privacy rights, attracting foreign investment, creation of jobs etc.
Challenges for India
- Regulatory: Need for a simplified and standardised regulatory framework across India to attract global investors.
- High operational expenses due to high power consumption, infrastructure maintenance etc.
- Environmental concerns such as high consumption of coal-based energy and ground-water.
- Other: Skill Gap, concentration in metro cities like Chennai, Mumbai, etc.
Way ahead
Robust compliance, energy-efficient R&D, and Tier-2 data centre expansion can ensure sustainable, secure, and balanced growth of the data centre ecosystem.
Initiatives to promote Data Centre Ecosystem in India
|





