This is significant because La Nina is the "cooler" phase of the El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and typically has a cooling effect on global temperatures.
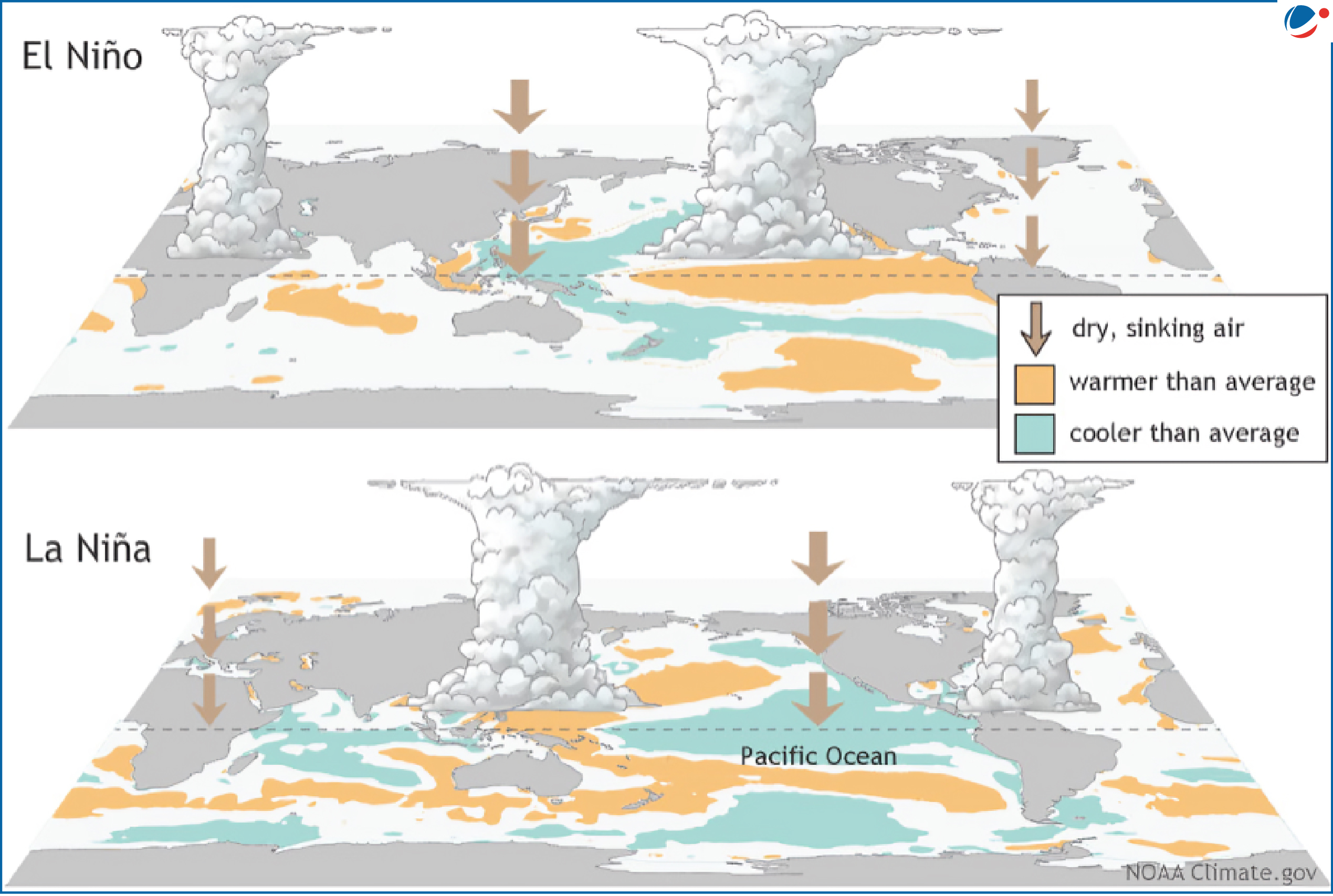
About El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO):
- It is a recurring natural phenomenon characterised by fluctuating ocean temperatures in the equatorial Pacific, coupled with changes in the atmosphere
- El Nino and La Nina are the oceanic components, while the Southern Oscillation is the atmospheric counterpart of the system.
La Nina Phase
Meaning: This cold phase of ENSO occurs when trade winds strengthen, pushing warm water further west toward Asia and allowing cold water to rise in the eastern Pacific.
Impact on India:
- Monsoon: Generally beneficial, bringing normal to above-normal rainfall, which supports agriculture.
- Winter: Triggers colder-than-normal winters and frequent cold waves in northern India.
- Extreme Events: Increased risk of floods and severe cyclonic activity in the Bay of Bengal.
El Nino Phase
Meaning: This warm phase of ENSO occurs when trade winds weaken, allowing warm water to move toward South America.
Impact on India:
- Monsoon: Typically weakens the southwest monsoon, often leading to below-normal rainfall or droughts.
- Agriculture: Suppresses yields for summer crops like rice, sugarcane, and oilseeds, which can increase food prices.
- Heat: Associated with harsher summers and increased heat stress.







