One of the Centre will be built in in Andhra Pradesh, India as well.
- It will be 3rd such centre in India after Mumbai and Telangana.
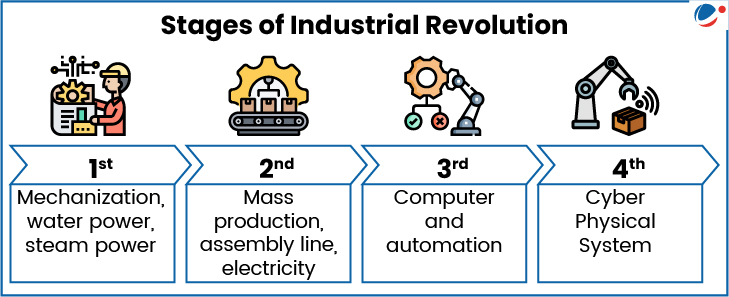
What is the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
- The term was coined by Klaus Schwab, founder of the World Economic Forum (WEF) in 2016.
- IR 4.0 describes the current era in which digital, physical and biological technologies converge such as AI, robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), quantum computing, etc.
- Unlike earlier revolutions, IR 4.0 is blurring boundaries between physical, digital and biological systems.
Significance of Fourth Industrial Revolution
- Economic growth: Enhances productivity and improves supply chain resilience through automation, data analytics and smart manufacturing.
- Inclusive development potential: Offers developing countries like India an opportunity to leapfrog legacy technologies and expand digital access.
- Environmental sustainability: Supports low-carbon and resource-efficient growth through smart grids, precision agriculture and circular economy practices.
- For example, "Lighthouse" factories have demonstrated significant reductions in CO2 emissions and water usage through predictive analytics and IoT.
- Human capital centrality: Shifts the focus from physical labour to skills, innovation, and lifelong learning.
Challenges and Risks
|





