Why in the News?
India and the United Kingdom (UK) announced the conclusion of a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) after three years of formal talks.
More on the News

- FTA will be implemented after the finalization of the legal document.
- It will consist of 27 chapters such as digital trade, environment, etc.
- Both countries also agreed to negotiate a reciprocal Double Contributions Convention (DCC).
- DCC is a type of Social Security Agreement.
- It will support business and trade by ensuring that employees moving between both countries and their employers, will only be liable to pay social security contributions in one country at a time.
- It will include employees temporarily working in the other country for up to 3 years.
- It will not affect individuals' rights to access benefits from the country in which they pay social security contributions or the requirement to pay the UK immigration health surcharge.
- It will support business and trade by ensuring that employees moving between both countries and their employers, will only be liable to pay social security contributions in one country at a time.
Key Highlights of the India-UK FTA
- Zero-duty Market Access: Approximately 99% of Indian exports will enjoy zero-duty access to the UK market, covering almost 100% of the trade value.
- On the other hand, India will cut levies on 90% of British products sold in the country.
- Within a decade, 85% of British products sold will become tariff-free in India.
- Eases mobility for Indian Professionals: It includes contractual Service Suppliers; Business Visitors; Investors; Intra-Corporate Transferees, their partners and dependent children with right to work; and Independent Professionals like yoga instructors, etc.
- Ambitious commitment from UK in Services: Such as IT/ITeS, financial services, professional services, other business services and educational services.
- Allowed Participation of UK Businesses in Procurement: UK businesses will be able to compete for a wide variety of goods, services, and construction procurements, for the majority of central government entities and state-owned enterprises.
About Free Trade Agreement (FTA)
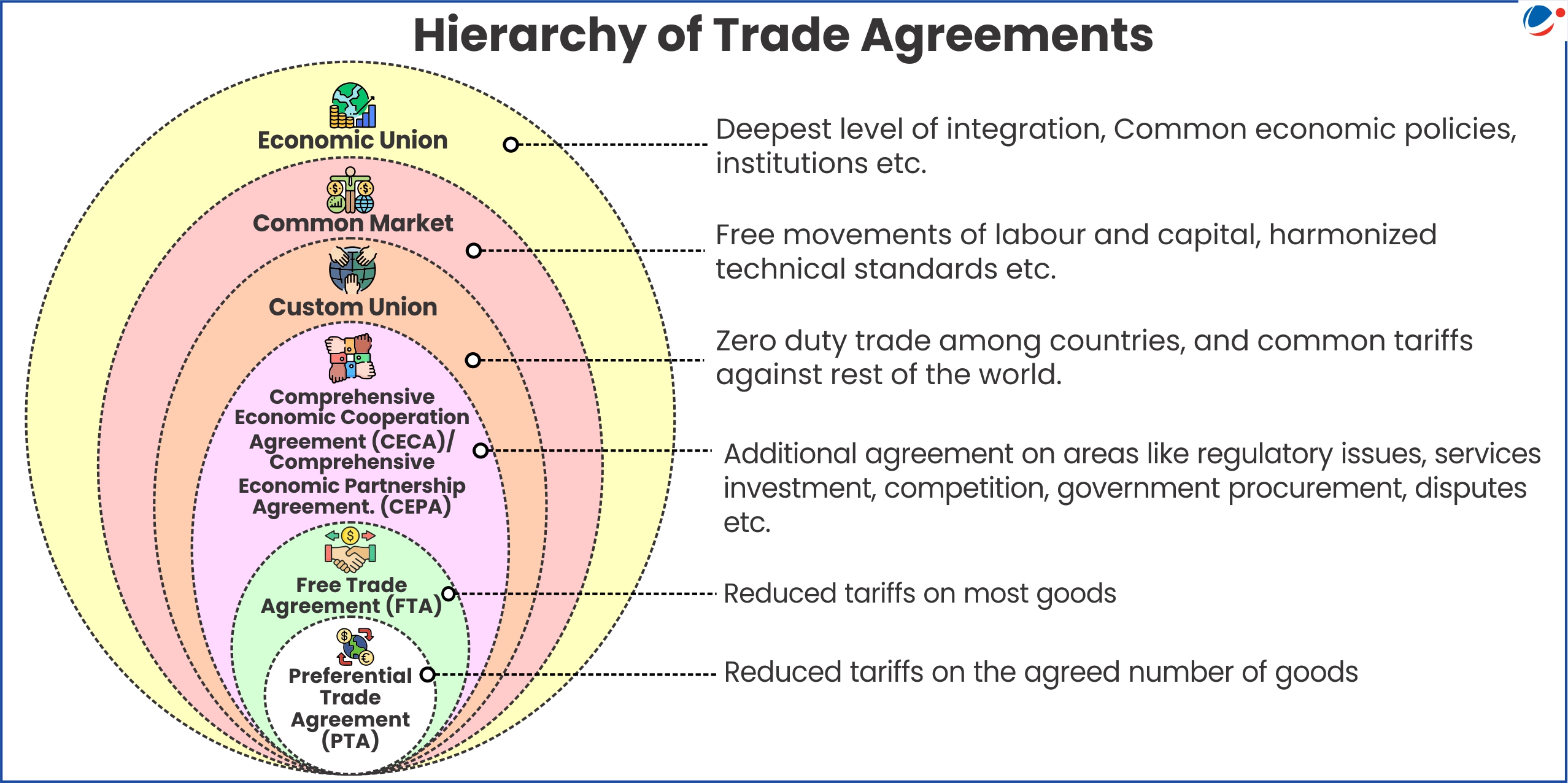 India's Experience with FTA's
Note: Assessment of Trade agreement cannot be done based on the trade balance only.
|
How the India-UK FTA can help shape Future FTAs?
- Swift Negotiations: India- European Union (EU) negotiations have been in process since 2007.
- Safeguard of Sensitive Sectors: Sensitive agri-products like dairy products, etc. are on the exclusion list.
- Also, Sensitive industrial goods like plastics, etc. have been included under the exclusion list, thus, protecting India's interest.
- Gradual Removal of Duties: In the India- UK FTA, the former agreed to cut or remove duties gradually over a longer period which ensures adequate time for domestic industries to adjust to increased competition.
- Emphasis on Mutual Benefits: E.g., UK car manufacturers will benefit from a quota that reduces tariffs from over 100% to 10%
Conclusion
The India-UK FTA not only strengthens bilateral economic ties but also serves as a strategic template for India's future trade agreements with developed nations. By addressing sensitive sectors, embracing modern trade issues, and ensuring a phased liberalization approach, it balances growth with domestic safeguards.







