Why in the News?
The Supreme Court recently observed that Bitcoin trading resembles a refined form of hawala while hearing a bail plea.
More on the News
- Supreme court also highlighted the absence of a clear regulatory framework for virtual currencies in India.
- Earlier in 2020, the Supreme Court in a landmark judgment quashed the RBI's 2018 circular prohibiting banks from offering services for virtual currencies.
- It doesn't have a central issuing or regulating authority, instead using a decentralized system to record transactions and issue new units.
About Cryptocurrency and Hawala SystemCrypto Currency: It is any form of currency that exists digitally or virtually and uses cryptography to secure transactions. Bitcoin is the best-known example.
Hawala System Hawala is an Informal funds transfer system used for transferring funds from one location to another through service providers known as hawaladars.
|
Cryptocurrency-Hawala Nexus
- The crypto hawala nexus refers to the convergence of traditional hawala with modern cryptocurrency technologies, creating a potent channel for laundering illicit funds and bypassing formal financial regulations.
- For instance, the Enforcement Directorate (ED) uncovered that ₹1,300 crore was routed through such hybrid channels involving shell accounts, crypto exchanges, and hawala.
- In blockchain, nodes may be seen as analogous to hawaladars, as both rely on mutual trust or consensus to sustain the integrity of their respective networks (see infographic).
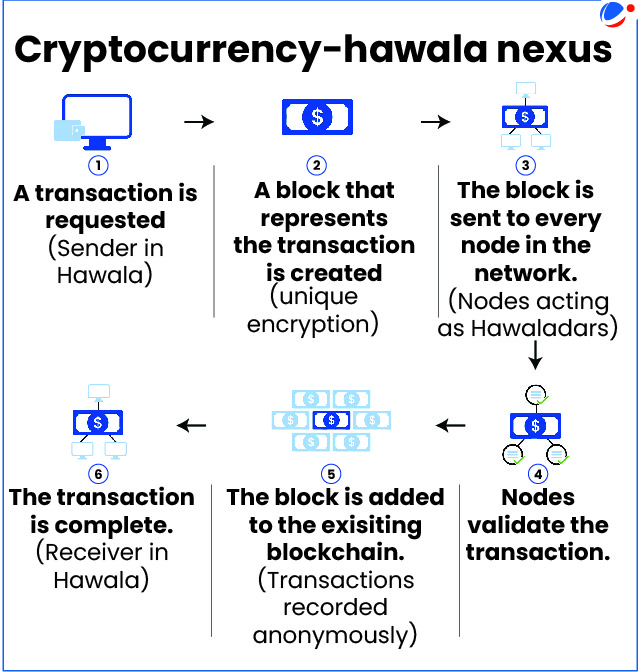
Reasons for linking Crypto Currency and Hawala
- Anonymity and Complexity: The combination of crypto currency's anonymity/ pseudonymity and complexity with the traditional, unregulated hawala system, which requires minimal documentation, makes tracking financial flows difficult.
- Bypassing Traditional Finance: Both systems can be used to bypass formal, regulated financial institutions, which may be necessary in regions with unstable governance, area of conflict, restrictive regulations etc.
- Facilitating Illicit Activities: The characteristics of both systems make them attractive for illicit activities such as money laundering and terror financing.
- Block chain reinforces and scales Hawala: By adding transparency and smart contracts, block chain strengthens hawala's trust-based model, making it faster, modern, and globally scalable.
- Compatibility of Principles: Both blockchain and hawala operate without a central authority, making their systems naturally compatible.
Concerns of the Cryptocurrency Hawala Nexus
- Tracking Challenges: Cryptocurrency's pseudo-anonymity enables large illicit transfers, creating a complex web that hinders regulators.
- For instance, stealth addresses and ring signatures (e.g., Monero), or zk-SNARKs in Zcash, which obscure transaction details.
- Use in Illicit Finance: This nexus is exploited for money laundering and terror financing. Examples include the Murarka case involving over $20 million and terrorist groups Hamas raising millions or using crypto for operational funding.
- Regulatory Challenges: Existing regulations need adaptation to include cryptocurrency transactions. The legal standing of blockchain and cryptocurrencies remain ambiguous in India.
- Tax Avoidance: The nexus can be used to transfer remittances and black money to tax havens.
- Security Risks: Digital wallets are targets for hackers, leading to significant losses. Vulnerabilities in cryptocurrency systems can be exploited through cyberattacks like deanonymization, spending denial, theft, and systemic attacks.
Way Forward
- Importance of International Cooperation: Global collaboration and evolving regulations are vital, with law enforcement and intelligence coordination key to deanonymizing and tracking funds. Example: UN Global Programme against Money Laundering.
- Enhanced Compliance using Technology: Blockchain and other emerging technology can potentially be used to track fund usage and ensure proper allocation of money. Example: Value-driven-Transactional tracking Analytics for Crypto compliance (VTAC) approach, TRM Labs etc.
- Strengthening Regulations: Clear laws on virtual currencies are the need of the hour, with FATF guidelines and the EU's MiCA framework serving as useful references to enhance transparency and strengthen AML/CFT measures.
- Need for Comprehensive Approach: Approach involving strict regulations, combating money laundering and terrorist financing, and utilizing advanced technologies like AI and machine learning are essential.




