Recently, multiple landslides were triggered by heavy rain in the Darjeeling and Kalimpong districts of West Bengal.
What is a landslide?
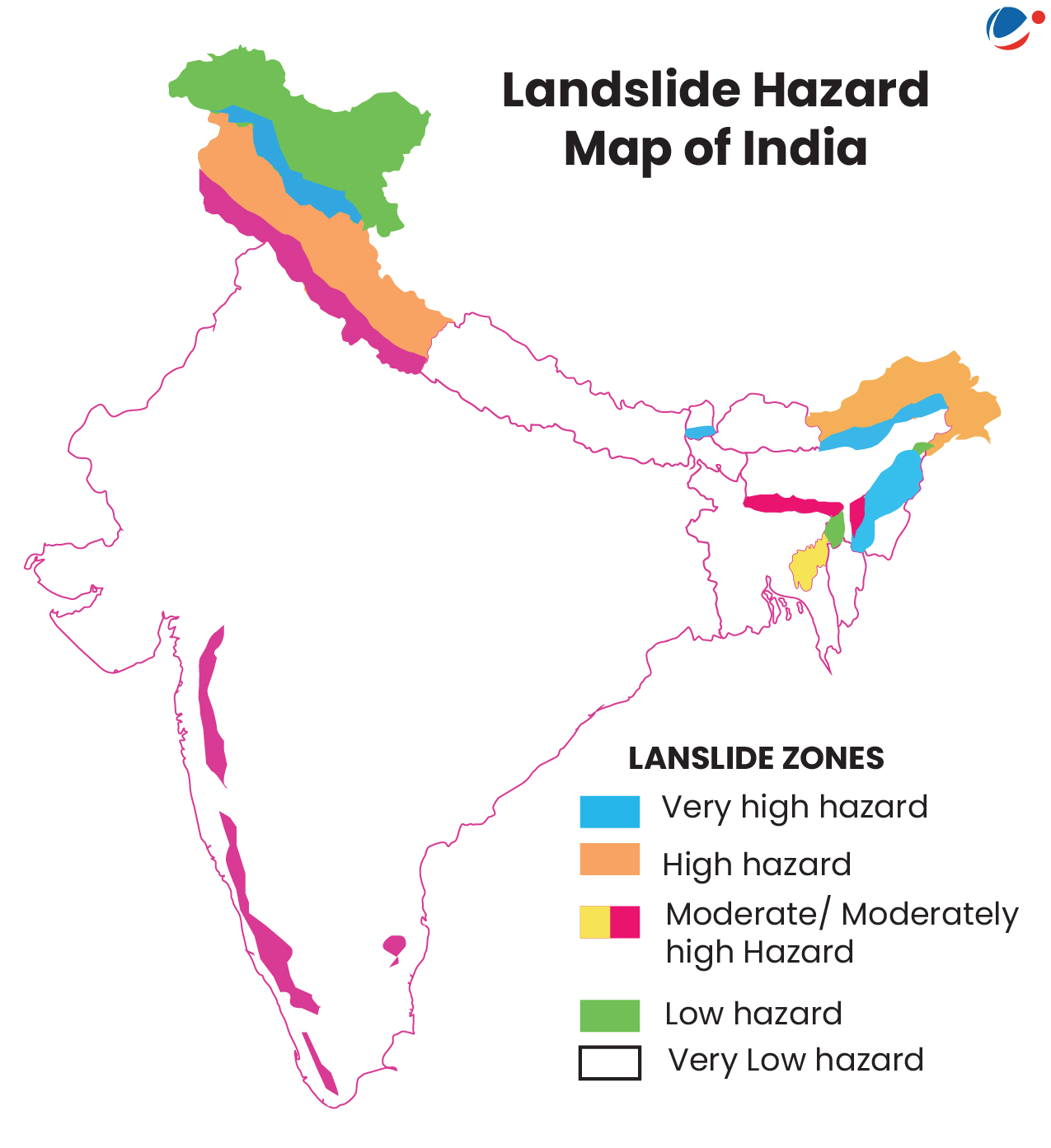
- Definition: A landslide is a mass movement of material, such as rock, earth or debris, down a slope, under the influence of gravity.
- India’s Vulnerability: 12.6% of land area is prone to landslide hazard as per ISRO’s 2023 Landslide Atlas of India.
- Of this, more than 3/4thlies in the Himalayan region alone.
Why is Himalayan region more vulnerable to landslides?
- Natural Causes:
- Tectonics & Geology: Formed by the collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates, Himalayas are young fold mountains characterized by faults and fractured rocks, making them inherently unstable.
- Rainfall & Weather Extremes: Monsoon rainfall along with cloudbursts and snow melt saturates soil, reducing stability of slopes.
- Climate Change has further increased the occurrence of extreme weather events.
- Other: Seismic activity, steep slopes, poor drainage and flash floods exacerbate instability.
- Anthropogenic Causes:
- Unplanned Construction: Road cuts, tunneling, etc. destabilize slopes.
- Other: Mining, land-use change from urbanization, deforestation and encroachments disrupt natural drainage.
Landslides Management Guidelines by the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
|







