Signed with the participation of Indian External Affairs Minister, Foreign Ministers of Arab States and the Secretary-General of the League of Arab States.
Key Highlights of the Delhi Declaration
- Peace and Security: Support for multilateralism, respect for sovereignty of states, counterterrorism efforts, and reforms of United Nations Security Council.
- Economic Stability and Security: Declaration cited Suez Canal–Red Sea Economic and Maritime Development Initiative (STREAM) as a regional framework to support economic integration.
- Key Country Specific Highlights: Palestine (sovereign, independent and viable State of Palestine, welcomed 2025 Sharm El-Sheikh Peace Summit concerning ceasefire in Gaza); Yemen (condemned attacks by Houthi militias; protection of vital Bab al-Mandab Strait), etc.
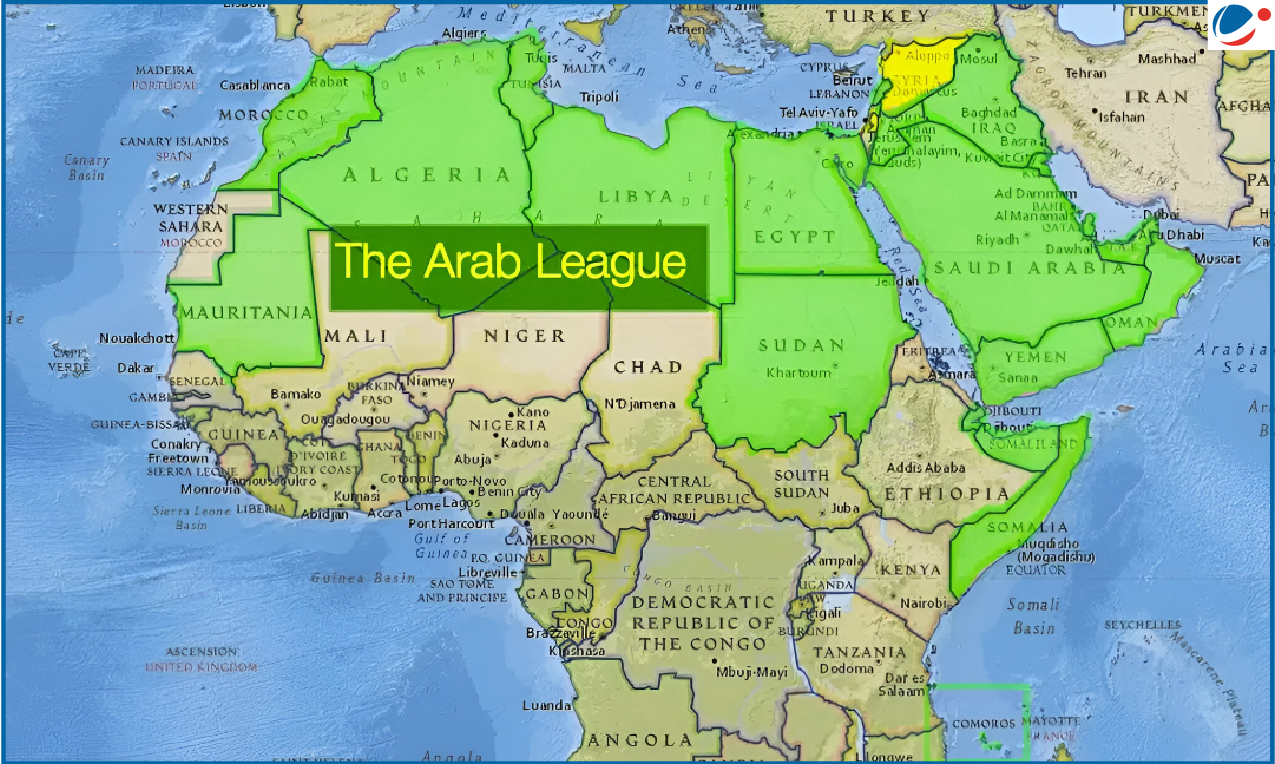
About Arab League
- Origin: Intergovernmental organisation encompassing all Arab states in Middle East and North Africa, established on March 22, 1945, following adoption of Alexandria Protocol in 1944.
- Members: 22.
- Founding members—Egypt, Iraq, Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Transjordan, and Yemen.
- Headquarters: Cairo, Egypt.
Importance of Arab League for India
- Economic: Trade between India and Arab States stands over US$240 billion.
- India imports over 47% of crude oil from Arab League countries, and 50% of fertilisers and related products.
- Strategic Significance: Most of India’s external trade passes through the Suez Canal, the Red Sea, and the Gulf of Aden.
- Diaspora: Over 9 million Indian diaspora live in Arab League nations






