Survey to be conducted during July 2026 to June 2027 would capture detailed information on extent/nature of migration, rural–urban and inter-state movement, key reasons, etc.
Recent Trends on Migration in India
- Overall migration rate stood at 28.% with sharp gender differences in patterns (Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) 2020-21).
- Migration rate was estimated at 10.7% among males and 47.9% among females.
Key Reasons for Migration
- Gender Specific: Marriage accounted for the predominant cause among females (86.8%) while employment (labour market opportunities) accounted for the major reason among males (22.8%).
- Pull Factor: Driven primarily by thepresence of job opportunities and the prospect of a better life. E.g., Case of Rural-to-Urban Migration.
- Nearly one in four rural Indians (26.8%) was a migrant in 2020-21. (Economic Survey 2025-26).
- Push Factors: Person tend to leave their native place due to lack of job opportunities, low wages or salaries, unfavourable environmental conditions and natural calamities, etc.
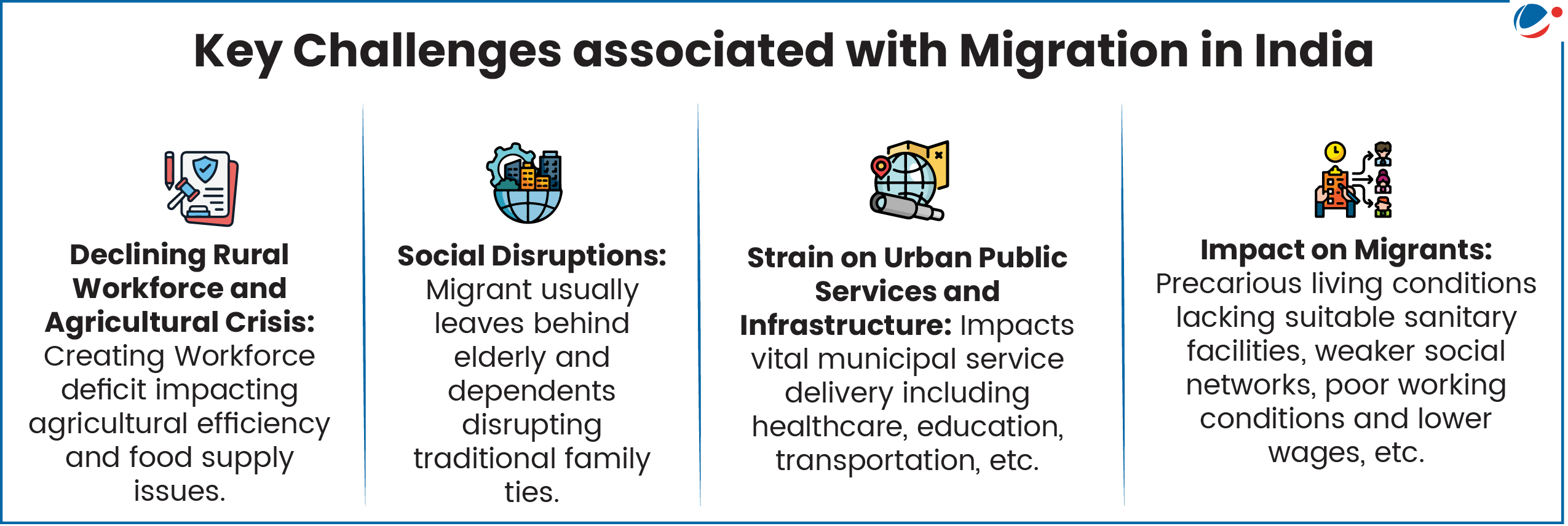
Key Measures to taken to address challenges
- Rural Development Initiatives: Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM); Viksit Bharat- Guarantee for Rozgar and Ajeevika Mission (Gramin) Act, 2025 strengthening rural employment, etc.
- Urban Resilience Initiatives: Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT); Smart Cities; Implementation of Transit-oriented Development (ToD), etc.
- Workers’ Welfare: Key Schemes like Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maan-Dhan Yojana (PMSYM); Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY); One Nation One Ration Card (ONORC) scheme for robust safety net for migrants, etc.






