Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) Cafetaria Scheme
The RKVY Cafeteria Scheme is a Centrally Sponsored initiative that empowers states to plan and implement agriculture projects, incentivizing investment, enhancing infrastructure, value chains, risk mitigation, and farmer incomes.
Quick facts
- Purpose: Incentivizes States to increase public investment in Agriculture & allied sector
- Type: Centrally Sponsored Scheme
- Coverage: All States / UTs shall be eligible for funding under RKVYRAFTAAR
- Flexibilities to states: States can select projects and programmes under the scheme as per their need priorities and agro-climate requirements.
Objectives
- To strengthen the farmers‟ efforts through creation of required pre and postharvest agri-infrastructure
- To provide autonomy, flexibility to States to plan and execute schemes as per local/ farmers‟ needs
- To promote value chain addition linked production models that will help farmers increase their income
- To mitigate risk of farmers with focus on additional income generation activities.
- To attend national priorities through several sub-schemes.
- To empower youth through skill development, innovation and agrientrepreneurship.
Salient Features
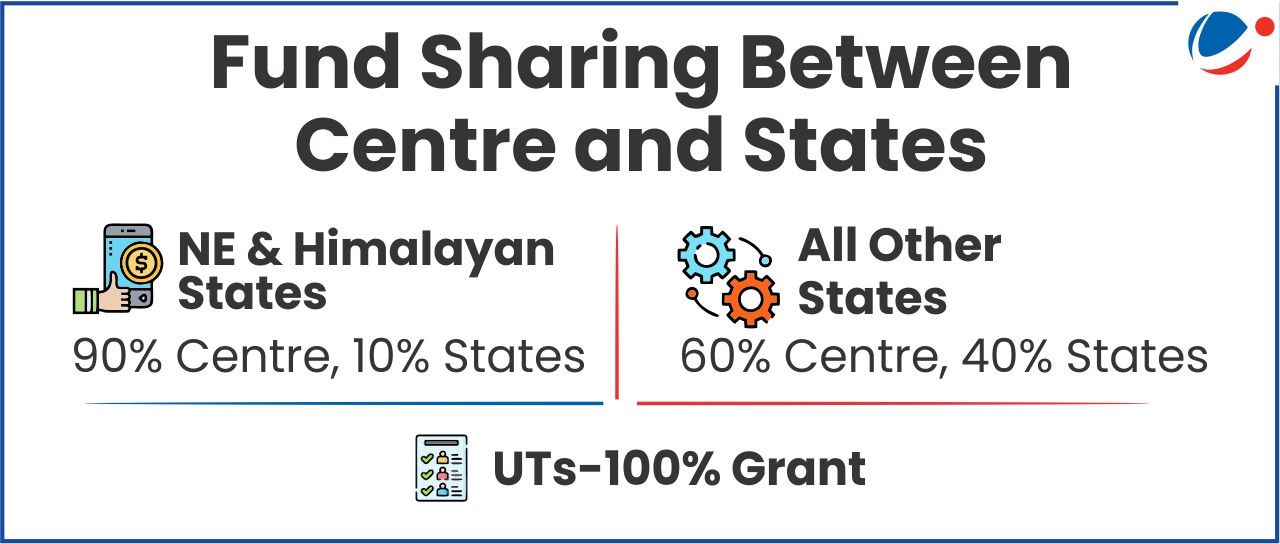
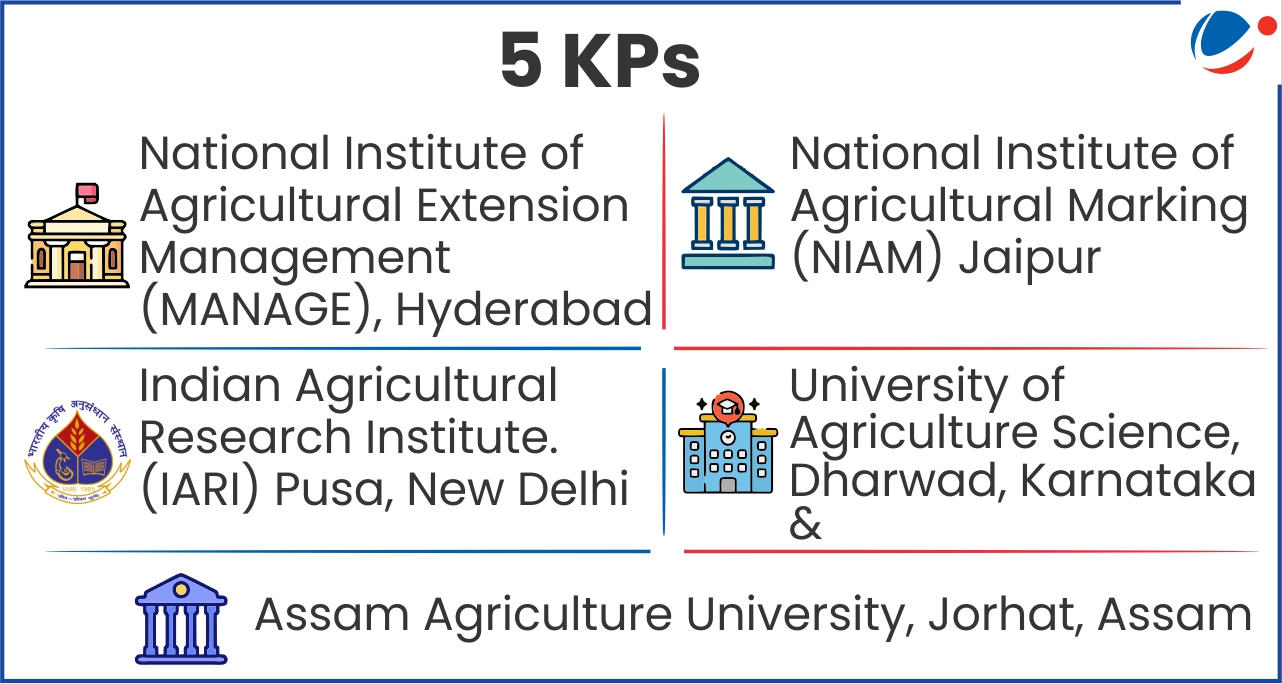
Major schemes merged under RKVY cafeteria scheme 
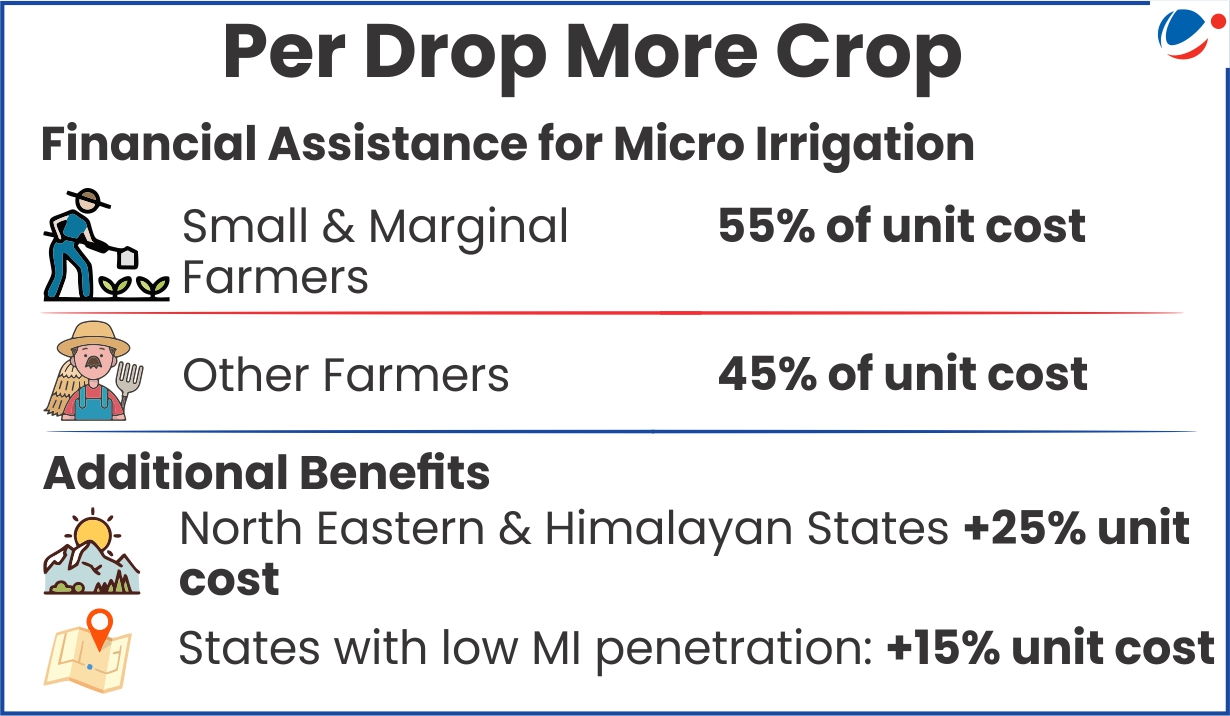
|

