Why in the news?
Recently, Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEFCC) released the ‘Status of Leopards in India, 2022’ Report.
More on news
- Fifth cycle leopard population estimation (2022) was carried out by National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) and Wildlife Institute of India (WII).
- It was in collaboration with State Forest Departments, as part of quadrennial “Monitoring of Tiger, Co-predators, prey and their habitat” exercise in tiger range States.
National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA)
Wildlife Institute of India (WII)
|
Key findings of report
- Leopard population: Estimated at 13,874 with a 1.08% per annum growth compared to 2018.
- Central India and Eastern Ghats registered largest growth, while Shivaliks and Gangetic plains registered decline in leopard population.
- Regional distribution: Madhya Pradesh houses the largest population of leopards followed by Maharashtra, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
- Tiger Reserves with highest leopard population: Nagarajunasagar Srisailam (Andhra Pradesh and Telangana) followed by Panna and Satpura (Madhya Pradesh) tiger reserves.
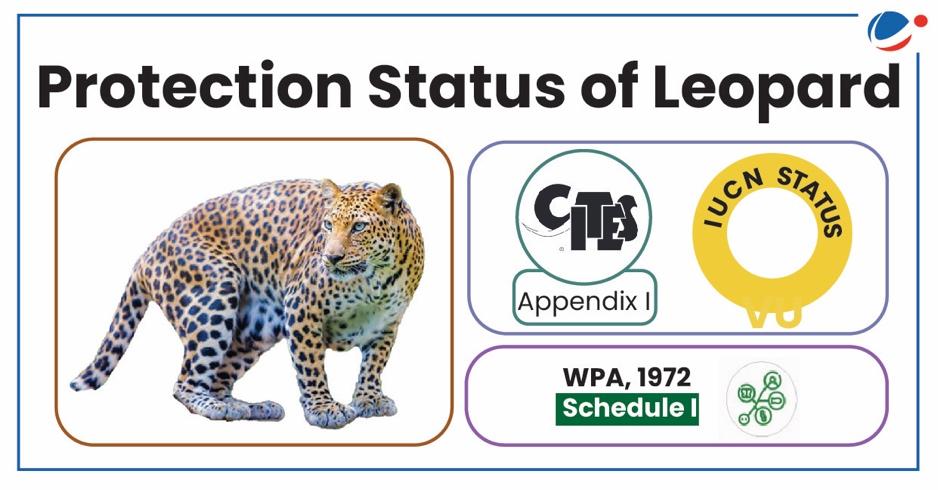
About Indian Leopards (Panthera pardus fusca)
- Leopards occupy a prominent position in trophic pyramid alongside tigers, lions and dholes exhibiting adaptability in habitat and dietary preferences.
- Leopards commanded great reverence in ancient cultures (Egyptian, African and Indian cultures), symbolizing traits of power, agility, and nobility.
- Habitat Distribution: India, Nepal, Bhutan, and parts of Pakistan, excluding mangrove forests and deserts.
- Importance of Leopard:
- Maintaining ecological balance of their mountain ecosystems.
- Regulate populations of their prey species, which in turn helps in harvesting medicinal plants, maintain healthy vegetation and prevent overgrazing.
- Major attraction for tourism, which helps to generate revenue for local communities.
Threats associated with Leopards
- Habitat Loss: Rapid human population growth intensifies pressure on land for agriculture, livestock grazing, and infrastructure development diminishing the forests and reducing the prey base for leopards.
- Poaching: Leopards are highly valued for their fur, bones, and other body parts, which are used in traditional medicine and as luxury items. This led to illegal trade in leopard products.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: Human encroachment on leopard habitats sparks conflict as they prey on livestock, prompting retaliation by herders.
- Climate Change such as melting glaciers, changing weather patterns, and altered vegetation growth, are affecting their habitats and prey populations.
Initiatives to Conserve Leopard
|






