Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC) launched an AQMX in the backdrop of International Day of Clean Air for Blue Skies (7 September).
- Led by UN Environment Programme (UNEP), this year’s theme focuses on ‘Invest in Clean Air Now’.
About Air Quality Management Exchange Platform (AQMx)
- It is a one-stop-shop that provides the latest air quality management guidance and tools proposed to meet WHO Air Quality Guidelines interim targets.
- It is a component of CCAC Clean Air Flagship and contributes to implementation of UNEA-6 Resolution to increase regional cooperation and action on improving air quality globally.
Need of AQMx
- Menace of air pollution: Causes more than 8 million premature deaths annually, particularly affecting poor and vulnerable.
- Capacity gaps: AQMx helps to address air quality management capacity gaps with curated guidance on air quality monitoring, health impact assessments etc.
- Knowledge sharing: Allow regional and sub-regional communities to exchange knowledge about air quality management best practices.
About CCAC
- Founded in 2012, and convened within UNEP, CCAC is a voluntary partnership of more than 160 governments, intergovernmental organizations, and NGOs. India joined CCAC in 2019.
- It works to reduce powerful but short-lived climate pollutants– methane, black carbon, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), and tropospheric ozone – that drive both climate change and air pollution.
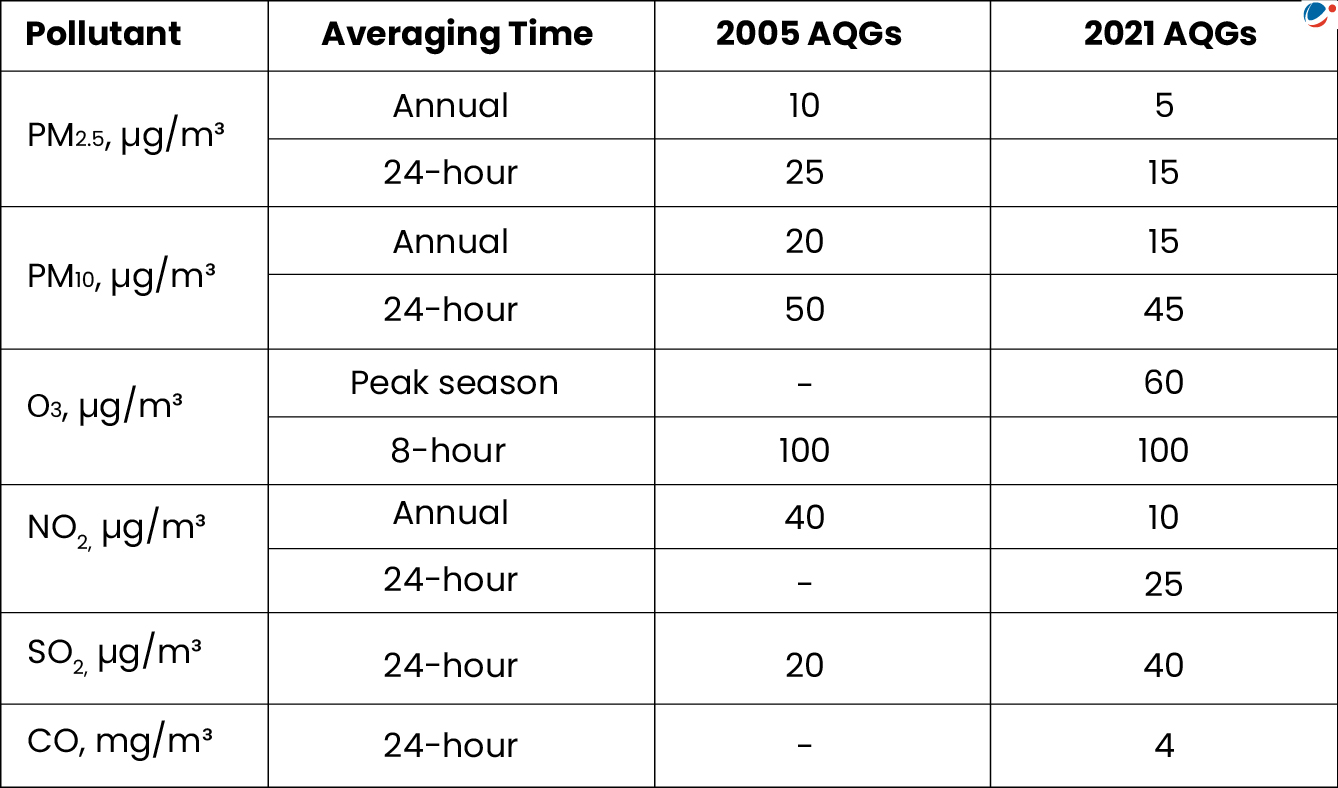 WHO Air Quality Guidelines (AQG)
|
This annual bulletin, released by United Nations’ World Meteorological Organization (WMO), reports on the state of air quality and its connections to climate change.
Key findings
- Global PM2.5 concentrations: Europe and China show lower PM2.5 pollution, while North America and India see increased emissions from anthropogenic activities.
- Particulate Matter smaller than 2.5 micrometers in diameter is referred to as PM2.5.
- Global PM hotspots: Include agricultural areas in Central Africa, Pakistan, India, China and South-East Asia.
- Impacts of PM on crops: Reduces crop yields by 15% as it reduces sunlight reaching leaf surfaces.
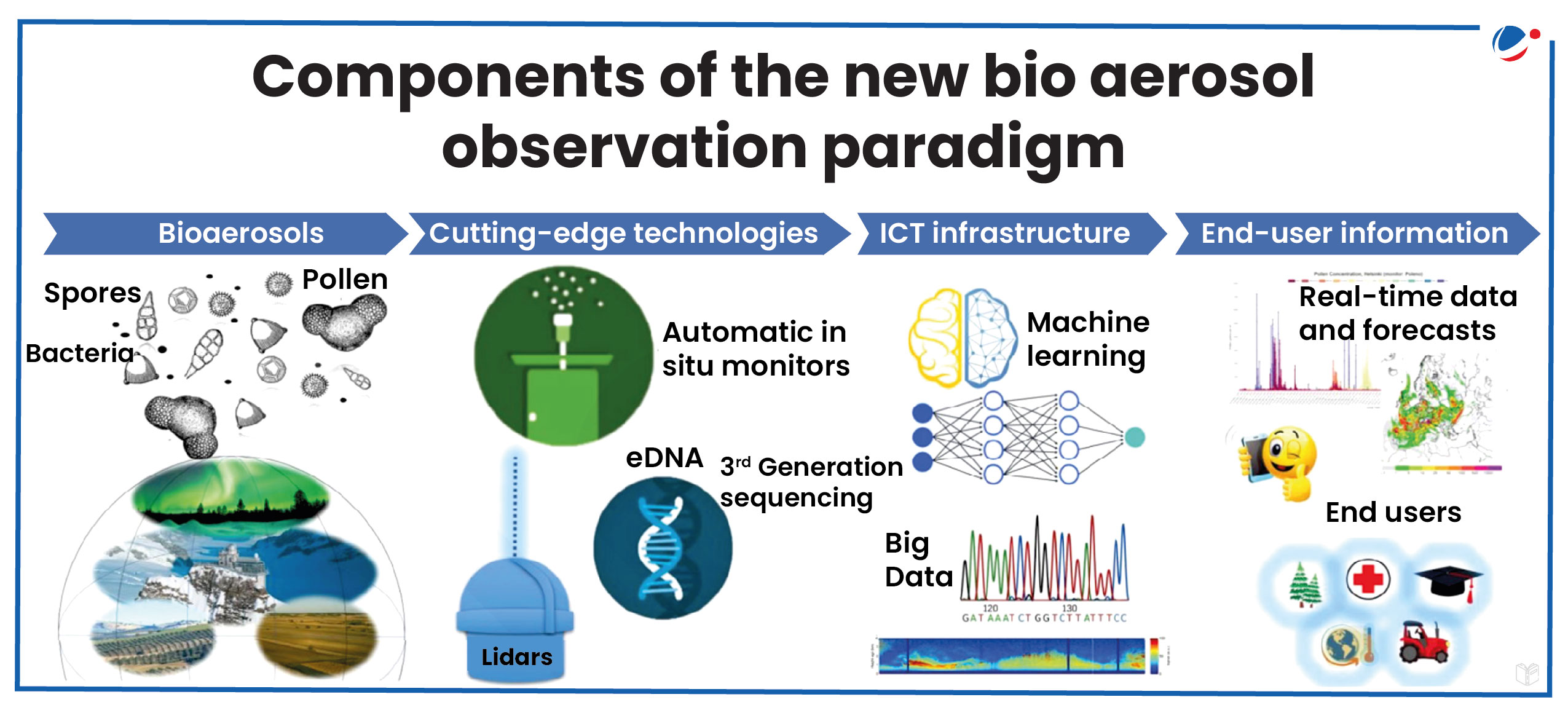
- Aerobiology Advancements: New technologies have enabled real-time bioaerosol monitoring.
About Aerobiology
- Aerobiology is the study of the movement and impact of airborne biological particles, or bioaerosols, on human, animal, and plant health. Bioaerosols include:
- Bacteria, fungal spores, pollen grains, viruses, etc.
- Bioaerosols reflect changes in biodiversity, plant flowering patterns, and distribution, all sensitive to climate shifts.
- Hence, new technologies are needed to improve understanding of Bioaerosols which would further enhance forecasting and climate change impact assessments.
- New observational techniques: Such as high-resolution image analysis, holography, multi-band scatterometry, fluorescence spectrometry and nanotechnology for DNA sequencing.
Article Sources
1 sourceIndia’s first ‘teal carbon’ study undertaken at Keoladeo National Park (KNP).
- The study depicted the potential of teal carbon as a tool to mitigate climate change, if the anthropogenic pollution in the wetlands can be controlled.
- Study also reveals elevated methane emissions can be reduced by use of a specialized type of biochar, which is a form of charcoal.
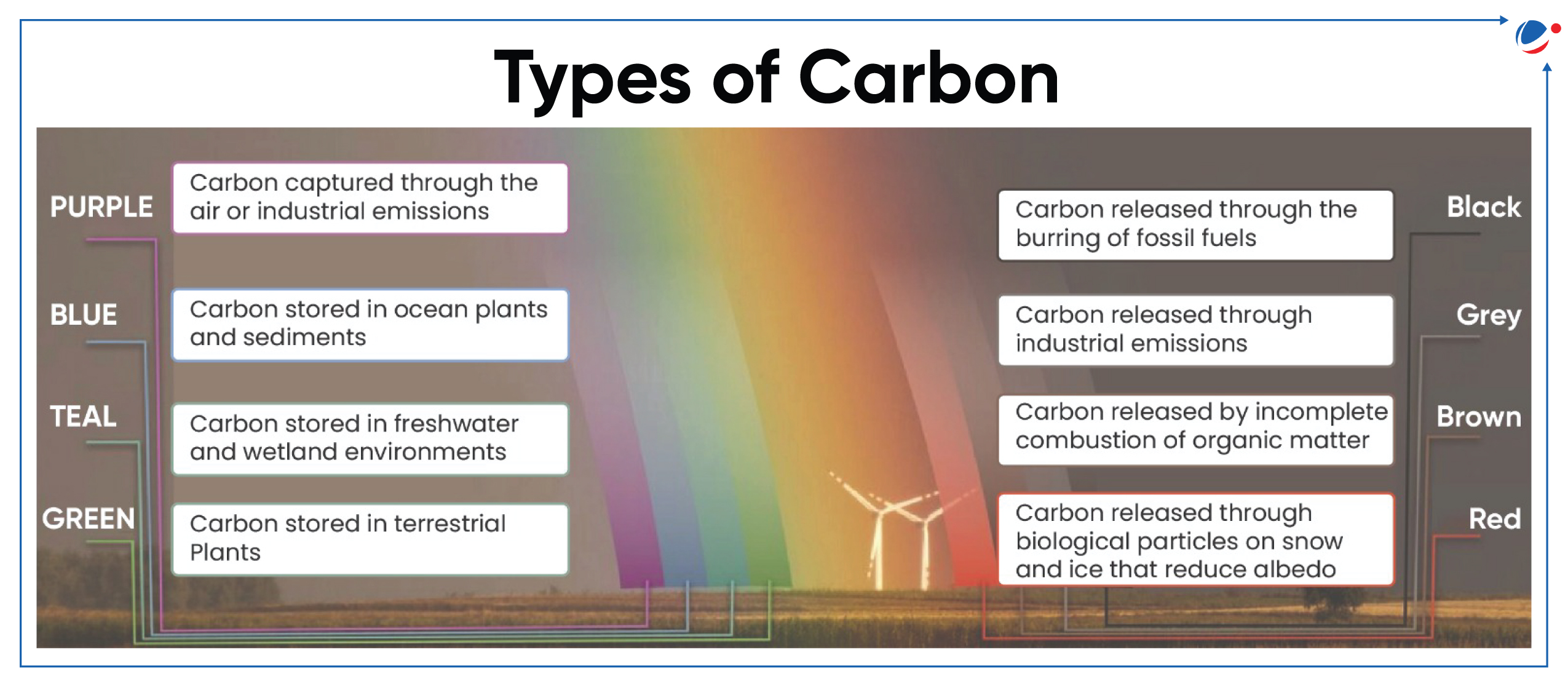
About Teal Carbon
- Teal carbon refers to carbon stored in non-tidal freshwater wetlands, encompassing carbon sequestered in vegetation, microbial biomass, and dissolved and particulate organic matter.
- Teal carbon, being a color-based terminology (refer infographics), reflects the classification of the organic carbon based on its functions and location rather than its physical properties.
- In contrast, black and brown carbon are produced by incomplete combustion of organic matter and contribute to global warming.
- Significance: It contributes to an increase in the ground water level, flood mitigation and heat island reduction, supporting a sustainable urban adaptation.
About Keoladeo National Park (Bharatpur, Rajasthan)
- Declared a national park in 1982 and a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1985.
- Home to over 370 species of birds and animals like pythons, Siberian cranes etc.
- Placed on the Montreux Record (Ramsar Convention) in 1990 due to "water shortage and an unbalanced grazing regime”.
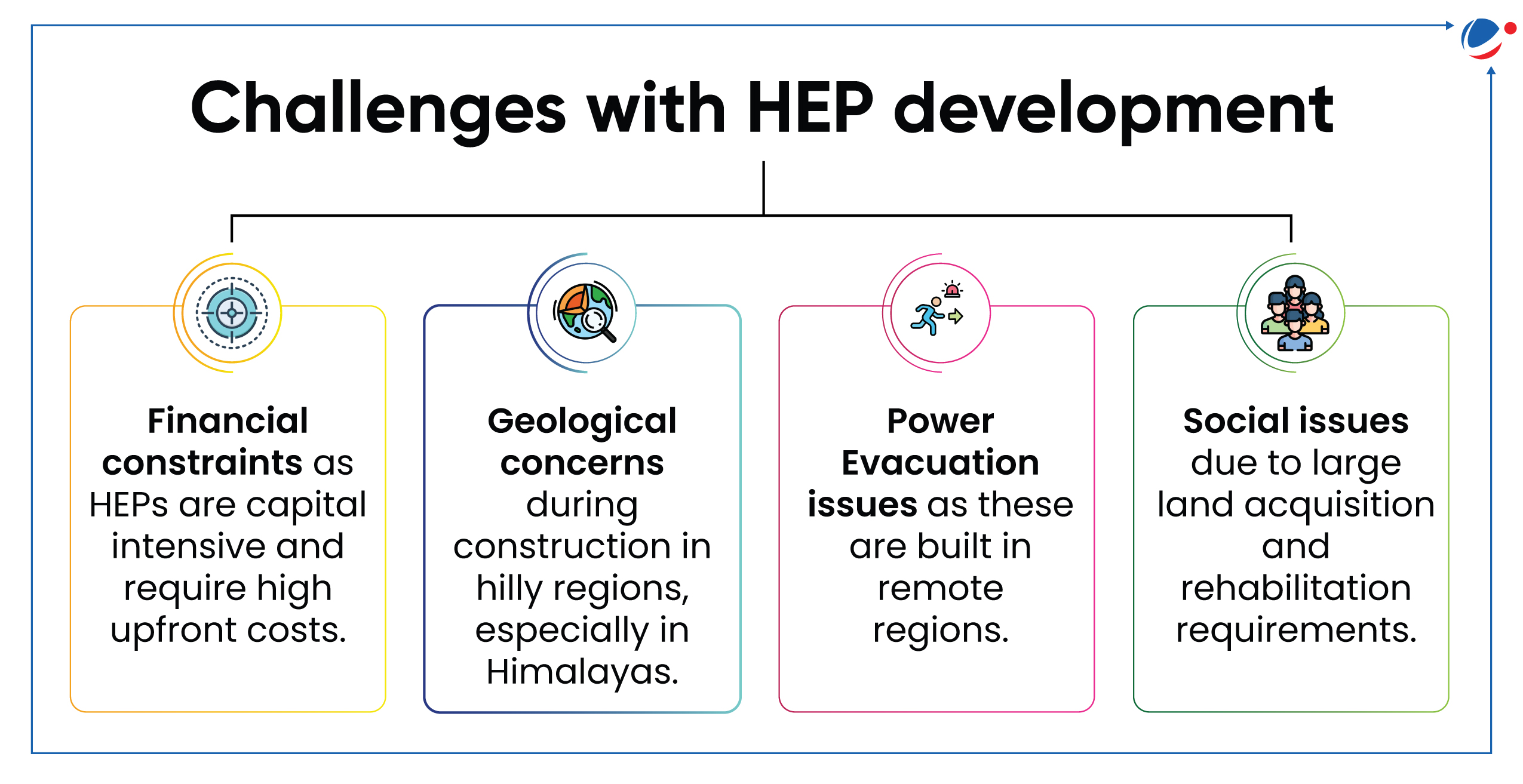
Union Cabinet approved modification of scheme of budgetary support for the cost of enabling infrastructure for Hydro Electric Projects.
- Union Cabinet modified the scheme for faster development of Hydro Electric Projects (HEP) and improvement of infrastructure in remote and hilly project locations.
- Scheme of Budgetary support for cost of enabling infrastructure for HEP was launched by Ministry of Power in 2019, along with other measures to promote hydropower sector in India.
- It provided budgetary support for constructing roads and bridges connecting major dam, power house and other project infrastructure with nearest state/national highway.
Modified Scheme
- Funding: Total outlay of Rs.12,461 crore for cumulative generation capacity of about 31,350 MW.
- Implementation Period: FY 2024-25 to FY 2031-32.
- Expansion: Scheme expanded to include costs for constructing transmission lines, ropeways, railway sidings, and communication infrastructure, in addition to roads and bridges.
- Eligibility: HEPs >25 MW capacity including private sector projects and all Pumped Storage Projects (PSPs).
Other Measures for Development of HEP
- Declaring Large Hydro Power projects (> 25 MW projects) as Renewable Energy sources.
- Hydro Power Purchase Obligations (HPOs) requiring entities to purchase electricity from HEPs.
- Tariff rationalization measures for bringing down hydropower tariff
- Budgetary support for flood moderation / Storage HEPs.
Guidelines, issued by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) under the Battery Waste Management Rules 2022, aim to promote proper battery waste management practices and enhance environmental sustainability across the country.
What is Environmental Compensation (EC)?
- 2022 Rules empower the CPCB to impose and collect EC from producers and entities involved in refurbishment and recycling of waste battery, in case of noncompliance of the rules.
- It can also be levied to entities carrying out activities without registration, providing false information / wilful concealment of material facts by the registered entities, etc., based on the polluter pays principle.
- It shall also be levied on Producer operating with respect to non-fulfilment of their Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) targets, responsibilities and obligations set out in these rules.
- EPR means responsibility of any Producer of Battery for Environmentally sound management of Waste Battery.
- Payment of EC, however, shall not absolve Producer of EPR obligation set out under the rules. For instance, unfulfilled EPR obligation for a particular year will be carried forward to the next year.
Key Highlights of the Guidelines issued
- EC to be levied is divided in to two regimes:
- EC Regime 1 – EC will be levied to the Producers for non-fulfilment of metal-wise (For Lead Acid Batteries and For Lithium-ion and Other Batteries) EPR Targets.
- EC regime 2 – EC will be levied to any entity for non-compliances of BWM Rules, 2022 based on application fees.
Click here to know more about the Battery Waste Management Rules and Amendment 2024.
A study by Researchers at the University of Chile found that Chile’s Atacama salt flat is sinking due to lithium brine extraction.
About Atacama Salt Flat
- Also known as Salar de Atacama, it is the biggest salt deposit in Chile.
- It has a rough white surface below which there is a large salt lake.
- Lake under the salt flat has one of the largest lithium reserves in the world.
- It lies in Chile’s Atacama Desert, probably the driest place on the planet.
- The northern part of the basin is the San Pedro River delta.
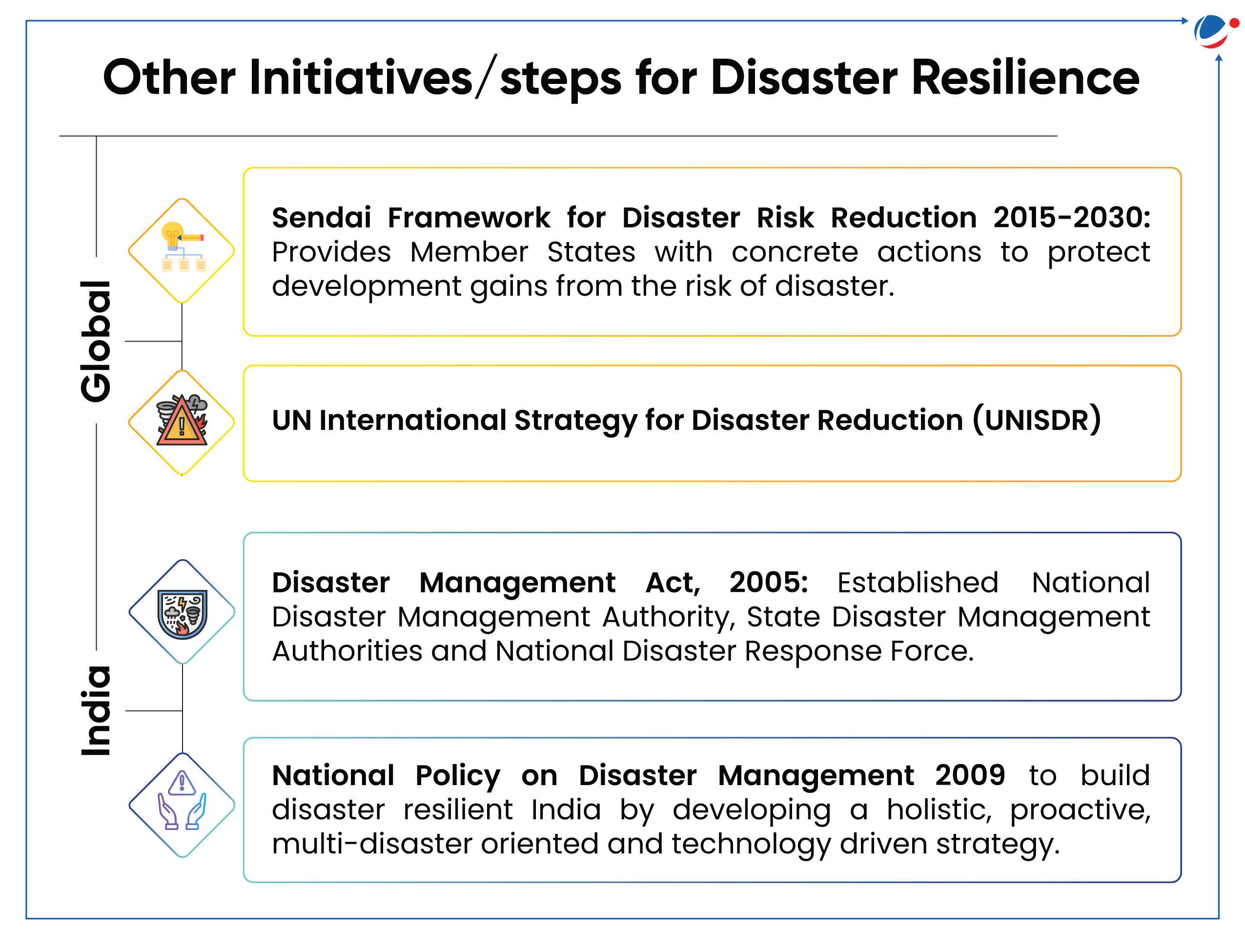
National Disaster Management Authority and Southern Command of the Indian Army are set to host the Exercise AIKYA in Chennai (Tamil Nadu).
- The exercise's primary objective is to improve disaster preparedness and foster strong collaboration among key stakeholders.
- The exercise will incorporate simulations, technology discussions, and expert insights into various disaster management roles.
- Since 1900, India has suffered an economic loss of $150 billion with largest loss from floods and storms (SBI Ecowrap 2023).
Article Sources
1 sourceWater spinach now reached the door of the farmers with the technology developed by the Indian Institute of Vegetable Research (IIVR).
About Water spinach
- Native to tropics and subtropics, this semi-aquatic perennial plant is believed to have been the first domesticated in Southeast Asia.
- Benefits
- Rich in folic acid (vitamin B9); Contains medium levels of beta carotene, calcium, vitamin E and C.
- Helps prevent neural tube defects in unborn children.
- Being rich in iron, it’s beneficial for people with anemia.
- Has great potential as a purifier of aquatic habitats.
Phrynarachne decipiens has been recorded for the first time in the country from Assam’s Kamrup district and Kokrajhar district.
About Phrynarachne decipiens
- Popularly known as the bird dung or bird-dropping crab spider.
- Spiders of the genus Phrynarachne resemble a blob of bird dropping, and even smell like feces or urine.
- This may help it attract and ambush prey, and avoid the notice of predators
- Generally found in Malaysia and Indonesia’s Java and Sumatra.
Recently, a study of the first tardigrade fossil has enabled Scientist to classify them and retrace their evolutionary history.

About Tardigrades (Water Bears or Moss Piglets)
- They are tiny eight-legged aquatic animals found in almost all habitats on Earth.
- They comprise of two main classes: Heterotardigrada and Eutardigrada.
- They can survive extreme environmental conditions like punishing heat, freezing cold, ultraviolet radiation and even outer space.
- They are able to survive harsh conditions, as they are capable of almost stopping their metabolism (known as cryptobiosis), reviving only when conditions are better.
India-Germany Platform for Investments in Renewable Energies Worldwide launched at 4th Global Renewable Energy Investor’s Meet and Expo (RE-INVEST).
- RE-INVEST is organized by Ministry of New and Renewable Energy.
About India-Germany Platform
- Aims to develop concrete & sustainable solutions for accelerated expansion of renewable energy in India and Globally.
- It will serve as an international forum for stakeholders from across globe to develop solutions to support India in attaining goal of 500 GW non-fossil energy capacity by 2030.
- It is an initiative under Green and Sustainable Development Partnership (GSDP), signed in 2022 between India & Germany.
Article Sources
1 source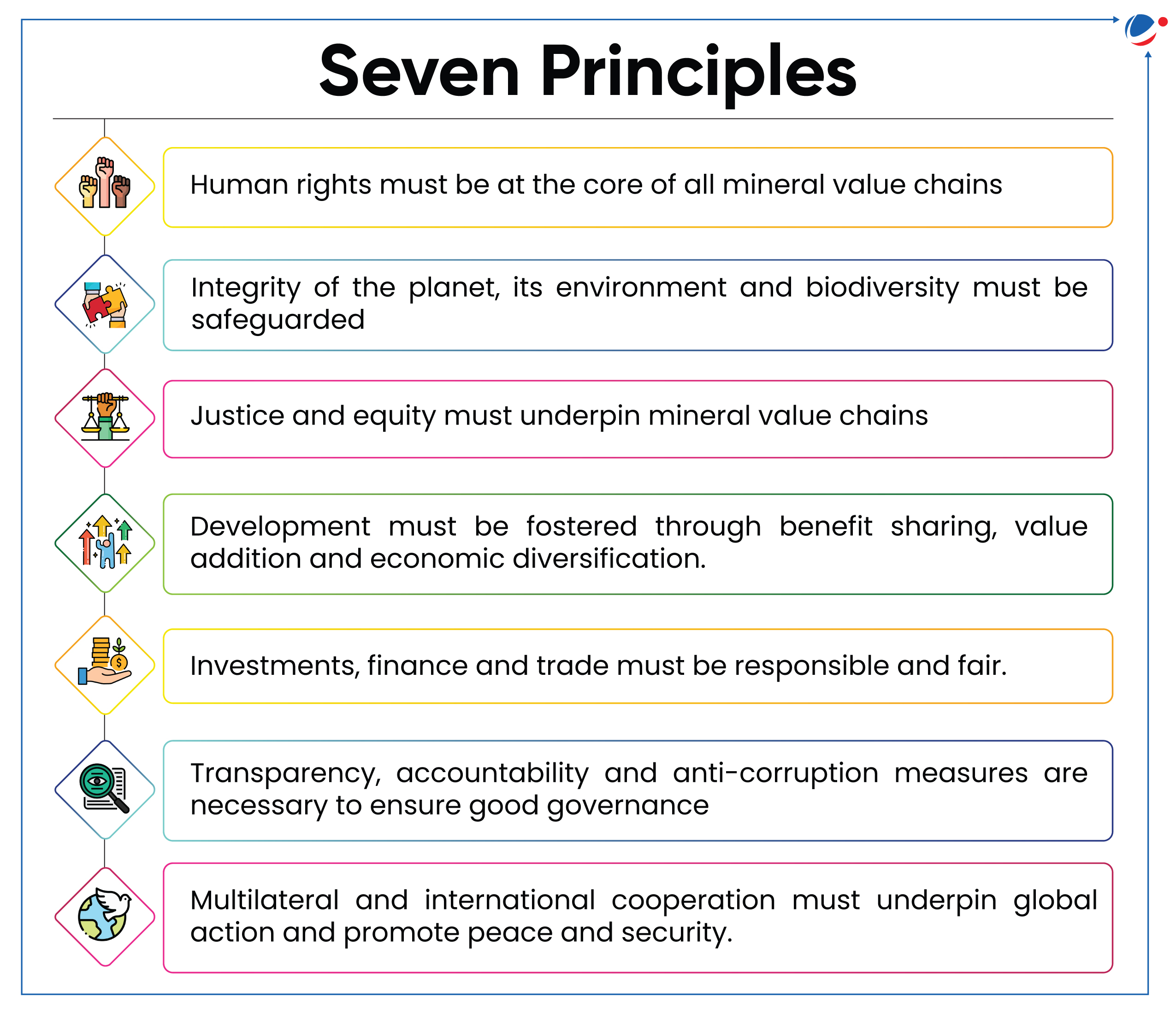
“Resourcing the Energy Transition: Principles to Guide Critical Energy Transition Minerals Towards Equity and Justice” report released by UN Secretary-General’s Panel on Critical Energy Transition Minerals (CETMs).
- Panel on CETM was established to develop guiding principles for energy transition.
- CETMs are minerals necessary to construct, produce, distribute and store renewable energy.
- They include Rare Earth Elements, copper, cobalt, nickel, lithium, graphite, cadmium, selenium etc.
- Demand for CETMs expected to triple by 2030 as the world transitions from fossil fuels to renewable energy.
About the Report
- Report outlines seven Guiding Principles (see infographic) and five Actionable Recommendations to ground the renewables revolution in justice and equity.
- Guiding principles are required as increasing demand for CETMs risks perpetuating commodity dependence, exacerbating geopolitical tensions and environmental and social challenges, and undermining efforts towards the energy transition.
Actionable Recommendations include establishment of:
- A high-level expert advisory group to accelerate greater benefit-sharing, value addition and economic diversification in CETMs value chains.
- Global traceability, transparency, and accountability framework along entire mineral value chain.
- Global Mining Legacy Fund for strengthening financial assurance mechanisms for mine closure and rehabilitation.
- Initiative that empowers artisanal and small-scale miners for responsible mining.
- Material efficiency and Circularity targets to balance consumption and reduce environmental impacts.
IRF, initially called International Black Rhino Foundation in 1991, is dedicated to survival of world’s rhino species.
Key findings of report
- With all five species combined, there are just under 28,000 rhinos left in world.
- Rhino poaching in Africa increased by 4% from 2022 to 2023.
- Number of white rhinos increased but greater one-horned rhino (Indian Rhino) number remained same.
- White rhino populations in South Africa are on rise despite poaching.
About Rhino
- Five species of rhino: 2 African (White Rhino, Black Rhino) and 3 Asian (Indian rhino, Sumatran Rhino, and Javan Rhino).
- Rhino conservation initiatives: National Rhino Conservation Strategy 2019 to conserve Indian rhino; New Delhi Declaration on Asian Rhinos 2019; Indian Rhino Vision 2020 etc.
Difference between African Rhino and Asian Rhino
Features | African Rhino | Asian Rhino |
Size | White Rhino is second-largest land mammals after elephants. | Indian Rhino is largest of all Asian rhino species. |
Appearance and Behaviour
| Less armoured look More aggressive 2 horns Poor swimmers and they can drown in deep water (so they wallow in mud) Fights with their horns Feed low to the ground | More armoured look Less aggressive 2 horns (Sumatran rhino) and 1 horn (Indian Rhino and Javan rhinos) Good swimmers Fights with its bottom teeth Graze on tall grasses, shrubs, leaves. |
Habitat | Grasslands, savannas and shrublands; deserts | Tropical and subtropical grasslands and savannahs, Tropical moist forests |
Conservation status (IUCN) | White Rhino: Near threatened Black Rhino: Critically Endangered | Indian Rhino: Vulnerable; Schedule I (Wildlife Protection Act, 1972) Sumatran Rhino: Critically Endangered Javan Rhino: Critically Endangered |
Recently, Union Cabinet approved continuation of Centrally Sponsored Scheme of Integrated Development of Wildlife Habitats (IDWH) for the 15th Finance Commission cycle.
- While strengthening existing fundamental & core components of scheme, the scheme envisages boosting technological interventions in different thematic areas in tiger and wildlife-bearing forests.
About IDWH
- Objective: It is a centrally sponsored umbrella scheme launched by Ministry of Environment for development of wildlife habitat in India.
- Components of IDWH
- Support to protected areas (national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, conservation reserves, and community reserves).
- Protection of wildlife outside protected areas.
- Recovery programs for saving critically endangered species and habitats.
- So far, 22 species have been identified under the Species recovery program.
- Sub-schemes Under IDWH
- Project Tiger (1973): It benefits a total of 55 Tiger Reserves spread across 18 tiger range states, distributed in 5 landscapes of the country.
- It also supports the ambitious Project Cheetah in the country.
- Development of Wildlife Habitats: Project Dolphin and Project Lion are implemented under this sub-scheme.
- Project Elephant (1992): To protect elephants, their habitat, & corridors to address issues of human-animal conflict and welfare of captive elephants.
- It is being implemented in 22 elephant range states/UTs.
- Project Tiger (1973): It benefits a total of 55 Tiger Reserves spread across 18 tiger range states, distributed in 5 landscapes of the country.
Note: Project Tiger and Project Elephant schemes have been merged w.e.f. FY 2023-24 and now known as Project Tiger & Elephant.
Article Sources
1 source
On this occasion, CDRI announced a $2.5 million fund under Urban Infrastructure Resilience Programme (UIRP) to enhance climate resilience of cities in 30 low and middle-income countries including India.
Significance of CDRI
- Funding: Provide a global mechanism for financing and coordination of the effective implementation of the aims of the CDRI.
- Technical Support and Capacity-building: This includes disaster response and recovery support; innovation etc.
Initiatives Taken by CDRI
- Infrastructure for Resilient Island States (IRIS): To promote resilient, sustainable and inclusive infrastructure in Small Island Developing States (SIDS).
- DRI Connect platform: Knowledge exchange, learning and collaborative platform
- International Conference on Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (ICDRI): Annual conference bringing together experts, decision-makers etc. to discuss challenges and identify good practices.
- Infrastructure Resilience Accelerator Fund (IRAF): Established with support of UNDP and UNDRR, to support global action on disaster resilience of infrastructure systems