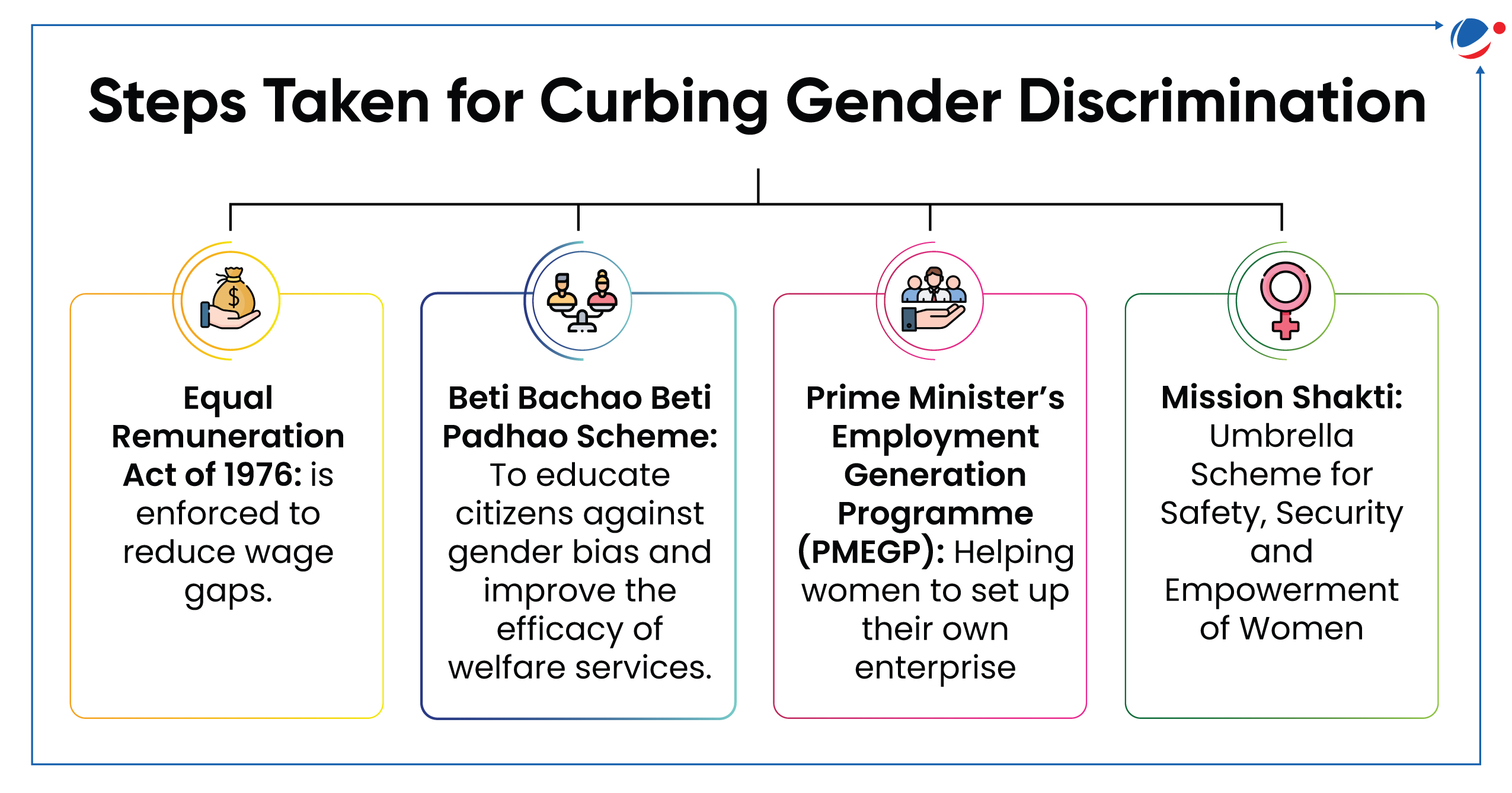
Vice-President emphasized on paying attention to pervasive subtle gender discrimination in society.
- Gender discrimination in overt forms (e.g. Lack of gender sensitive infrastructure) has ostensibly vanished but it has assumed subtle forms.
- Subtle gender discrimination manifests through attitudes and behaviors that seem supportive but reinforce traditional gender roles and perpetuate inequality.
Subtle forms of Gender Discrimination:
- Reinforce Stereotyping: Positive comments that reinforce traditional gender roles and undermine women’s capabilities.
- Hiring, Promotion, and Evaluation: Unconscious bias towards male candidates for roles traditionally perceived as requiring physical strength or leadership.
- Microaggressions: For instance, implying that women are less committed to their careers due to family reasons.
- Work-Life Balance Assumptions: Assumptions about work-life balance needs might affect women more due to societal expectations around caregiving and family responsibilities.
Addressing Subtle Forms of Gender Discrimination
- Blind evaluation: E.g. Hiding a job applicants’ physical attributes
- Creating a Culture of Inclusivity: Promoting workplace that respects input from everyone regardless of gender.
- Assess unconscious gender bias at workplace: Through a variety of methods, including perceptions surveys, language analysis, analysis of gender gaps in pay and career advancement.
- Need to Change male mindset: Through wider gender sensitization
National Pension System Vatsalya (NPS Vatsalya) scheme, a pension scheme for minors, has been launched.
NPS Vatsalya Scheme
- Eligibility: All minor citizens (age below 18 years).
- On attaining the age of majority, plan can be converted seamlessly into a normal NPS account.
- Regulation and Administration: Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA).
- Objective: Promoting long-term financial planning and security, inculcate habit of savings and dignified life in old age.
- Subscriber Contribution:
- Minimum: Rs 1000/- per annum.
- Maximum: No limit.
- PFRDA will provide multiple investment choices to subscribers such as government securities, corporate debt, equity etc.
Article Sources
1 sourceMinistry of Education (MoE) defined Literacy and Full Literacy under New India Literacy Programme (NILP).
To support adult education/literacy as emphasized in NEP 2020 and SDG 4.6 (ensuring all youth and adults achieve literacy and numeracy by 2030), it is essential to define both Literacy and Full Literacy.
- Literacy: Ability to read, write, and compute with comprehension, i.e. to identify, understand, interpret and create along with critical life skills like digital and financial literacy etc.
- Full Literacy (to be considered equivalent to 100% literacy): Achieving 95% literacy in a State/UT that may be considered as equivalent to fully literate.
About New India Literacy Programme (NILP)
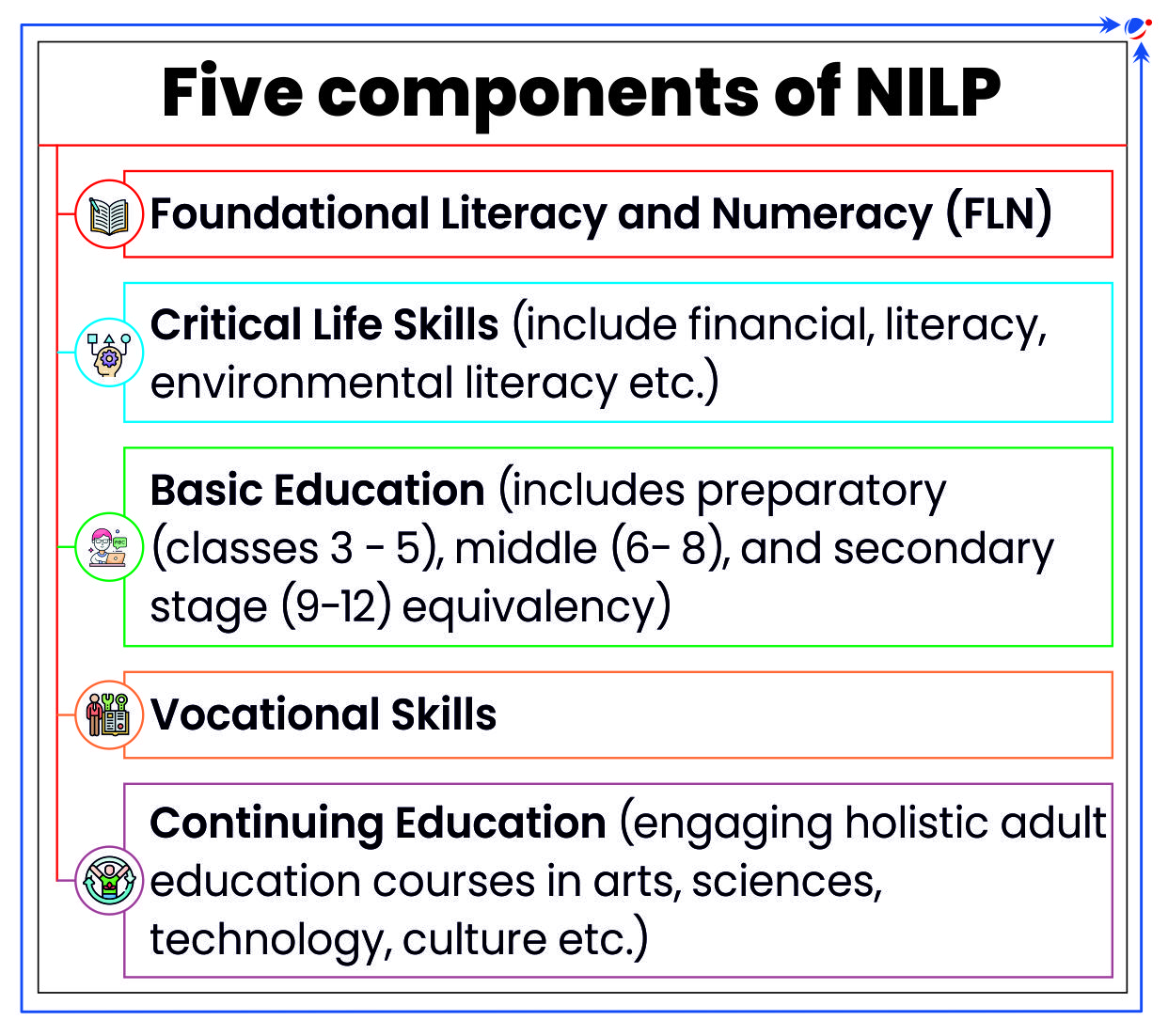
- Also known as ULLAS (Understanding of Lifelong Learning for All in Society).
- Launched by MoE, it is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
- Tenure: FYs 2022-27 (5 years).
- Objective:
- Targets all non-literates of age 15 years and above, with more focus on females and educationally backward states.
- Target 5 crore learners (1.00 crore per year) by using “Online Teaching, Learning and Assessment System (OTLAS)” in collaboration with National Informatics Centre, NCERT and NIOS.
- Implemented through volunteer teachers, students of schools and Higher Education Institutions and Teacher Education Institution.
- It is in alignment with recommendations of NEP 2020.
- Need: Absolute number of non-literates in 15 years and above age group is 25.76 crore (Census 2011).





