National Ocean and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), a US body, announced that the El Nino conditions prevailing since mid-2023 had ended and were replaced by El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) neutral phase.
- ENSO is a recurring climate pattern involving changes in the temperature of waters in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean.
- Occurs in irregular cycles of 2–7 years.
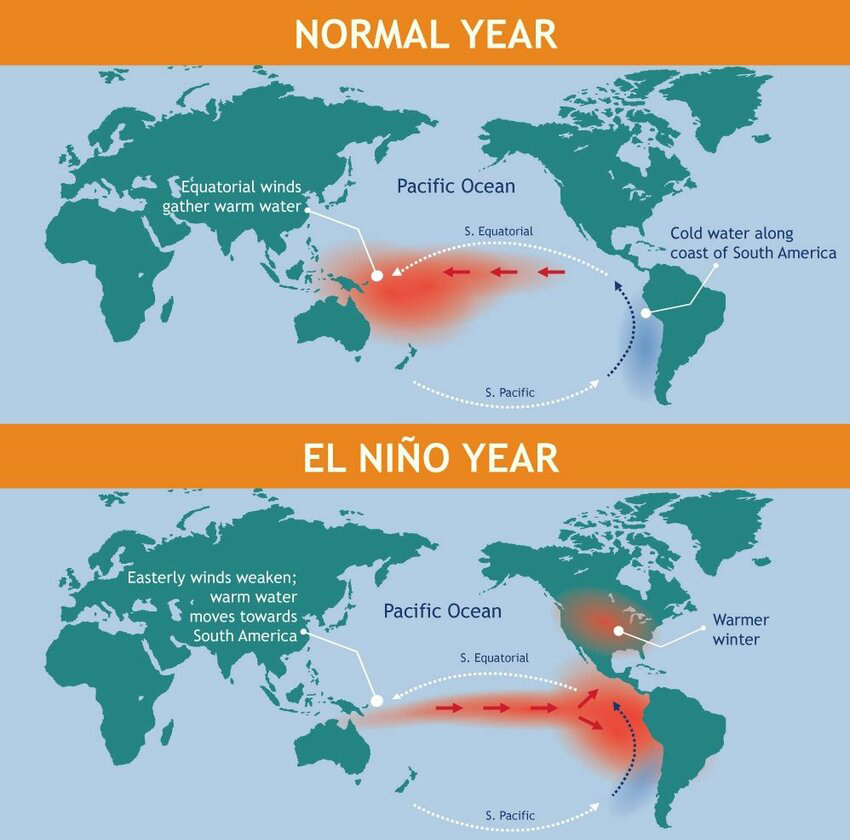
- El Nino (warm phase) and La Nina (cold phase) are extreme phases of the ENSO cycle; between these two phases is a third phase called ENSO-neutral.
- In the neutral phase, tropical Pacific sea surface temperatures (SST) are generally close to average.
About El Nino
- El Nino (the Christ Child) is a climate pattern associated with the warming of the ocean surface temperatures in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean.
- Key Impacts: It suppresses rainfall over India during monsoon.
- It brings rain to South America and droughts to Indonesia and Australia.
About La Nina
- La Nina refers (Little Girl) to the periodic cooling of ocean surface temperatures in the central and east-central equatorial Pacific.
- Key Impacts: It has the opposite effect of El Nino.
- It is associated with a strong monsoon and above average rains and colder winters in the subcontinent.




