This announcement marks a historic shift in India's nuclear policy, as the Atomic Energy Act of 1962 did not permit private sector participation in nuclear energy generation.
- BSRs are aligned with global trends where Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are gaining attention.
- Unlike SMRs, which are an entirely new concept involving factory-made, easily assembled reactors, BSRs are based on India's existing Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor technology.
- They can enhance the contribution of Nuclear energy in India’s energy basket (current share of nuclear energy is 1.6%).
About Small Modular Reactors
- They are advanced nuclear reactors that have a power capacity of up to 300 MW(e) per unit.
- There are more than 80 SMR designs and concepts globally. Most of them are in various developmental stages.
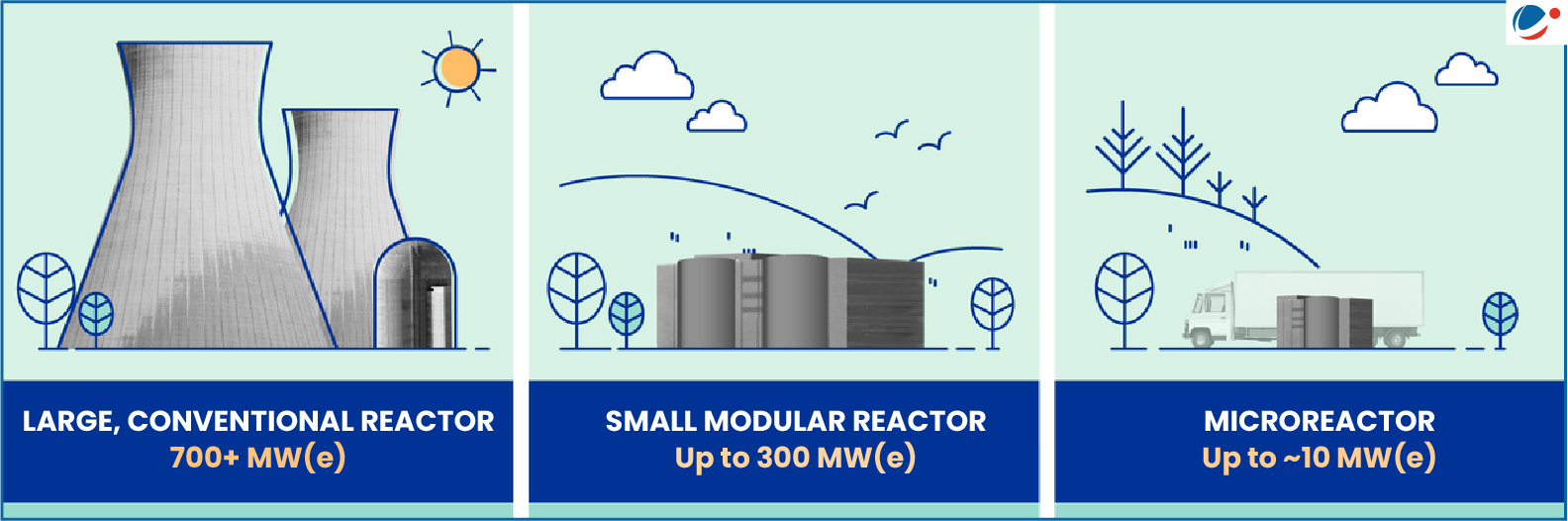
Significance of the SMRs
- Reduced fuel requirements, require less frequent refueling, every 3 - 7 years, compared to 1 -2 years for conventional plants (IAEA).
- Saves construction time as prefabricated units of SMRs can be manufactured, shipped and installed on site.
- Eliminate or significantly lower the potential for unsafe releases of radioactivity to the environment.







