Plant with capacity of 1.4 tons per day is being implemented under Public-Private Partnership with support from Department of Science and Technology.
About CO2-to-Methanol Conversion
- Currently, Carbon Utilization Technologies like CO2 to methanol are less developed compared to capture ones.
- CO2-to-methanol involves capturing carbon emissions before they enter atmosphere, particularly from industrial sources like power plants or directly from air via direct air capture technologies.
- Captured CO2 is then hydrogenated – reacted with hydrogen – to produce methanol.
- CO2-to-methanol conversion has potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and providing a sustainable fuel source.
- CO2-to-Methanol plant in Pune will advance indigenous Carbon Capture and Utilisation (CCU) technologies, marking significant step towards India’s Panchamrit declaration.
About Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS)
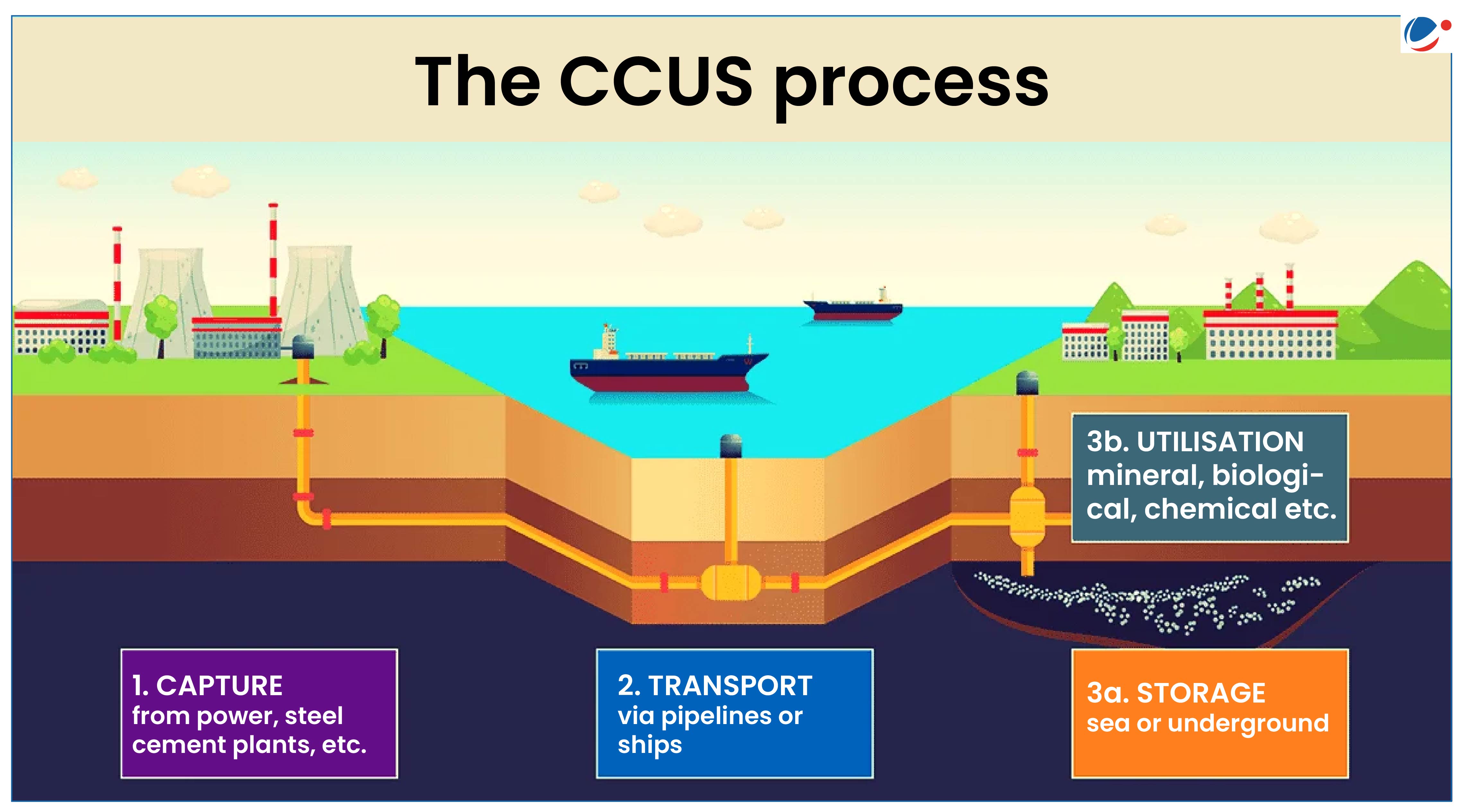
- Refers to Group of technologies for capturing of CO2 from large and stationary CO2 emitting sources like fossil fuel based power plants and other industries. (International Energy Agency)
- It involves transport of captured CO2 (by pipeline or through shipping, rail or trucks) to sites for utilization in different applications, injections into geological formations or depleted oil/gas fields for permanent storage and trapping of CO2.
Significance of CCUS
Issues with CCUS adoption in India
|






