The order was issued by National Green Tribunal (NGT) while hearing a case of unauthorised large-scale tree cutting, allegedly harming the forest areas and affecting recharging of Naini Lake.
Key Highlights of the Order
- Classification of town into development or prohibited zone and regulated zones based on environmental conditions.
- Rehabilitation of lakes: State government was directed to implement catchment area treatment plans for lakes in the district.
- Creation of master plans and determination of carrying capacity of Nainital based on factors such as hydrology, sanitation load bearing, vegetation and current tourism trends.
What is Carrying Capacity?
- It refers to the maximum threshold of population an area can bear in relation to the available resources.
- It depends on both biotic (e.g. vegetation, hydrology) and abiotic (e.g. terrain, climate) factors.
- Two major approaches for assessing Carrying Capacity:
- Planetary boundaries approach: Applied in the context of environmental crises such as global warming, land degradation, pollution, water stress.
- Biocapacity Overshoot approach: It is a sustainability metric about the demand humans put on the earth systems by consuming total annual productivity of natural systems within a few months every year. e.g., Earth Overshoot Day.
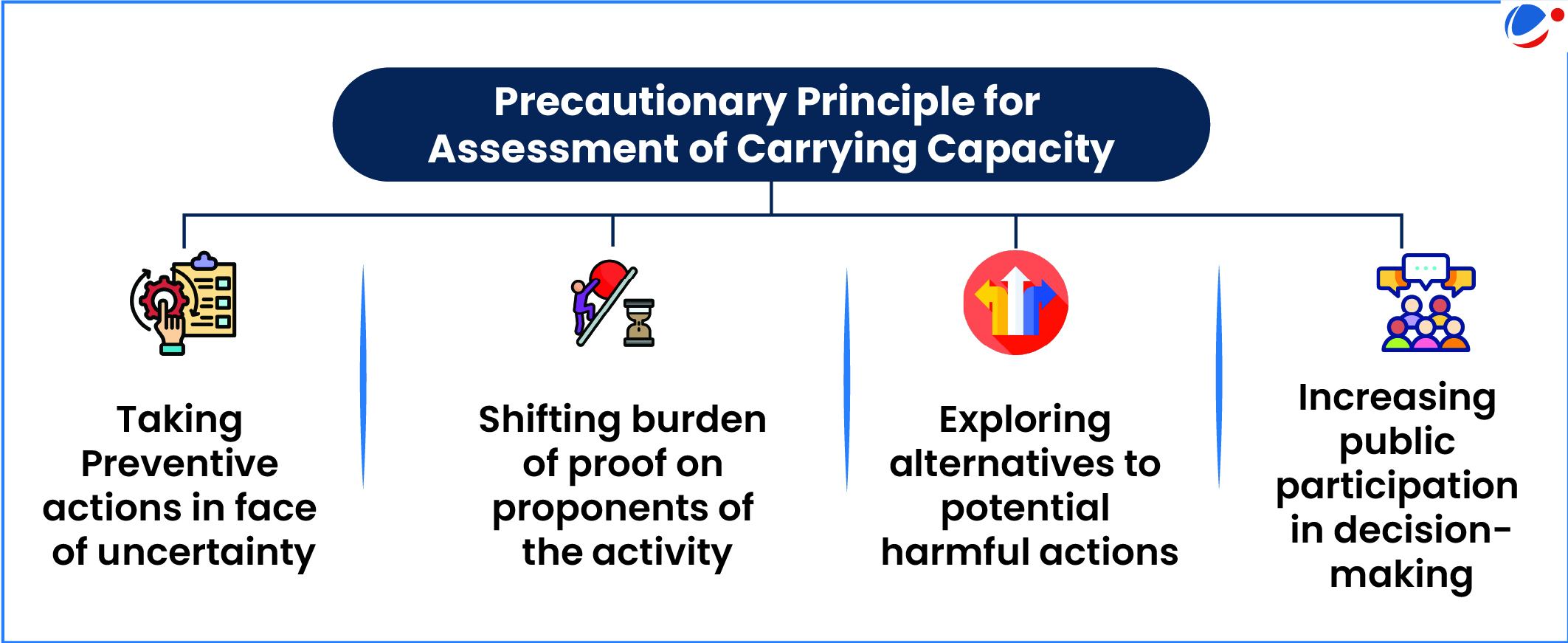
- Significance: Carrying capacity assessment based on precautionary principles (refer infographic) provides the option to practically deal with the tussle between ‘developmental governance’ and ‘sustainability of development’.