Oreshnik Hypersonic missile is based on the design of a Russian Inter-Continental Ballistic Missile (ICBM).
- Hypersonic missiles are missiles that can travel at speeds of at least Mach 5—five times the speed of sound.
Ballistic Missile (BM)
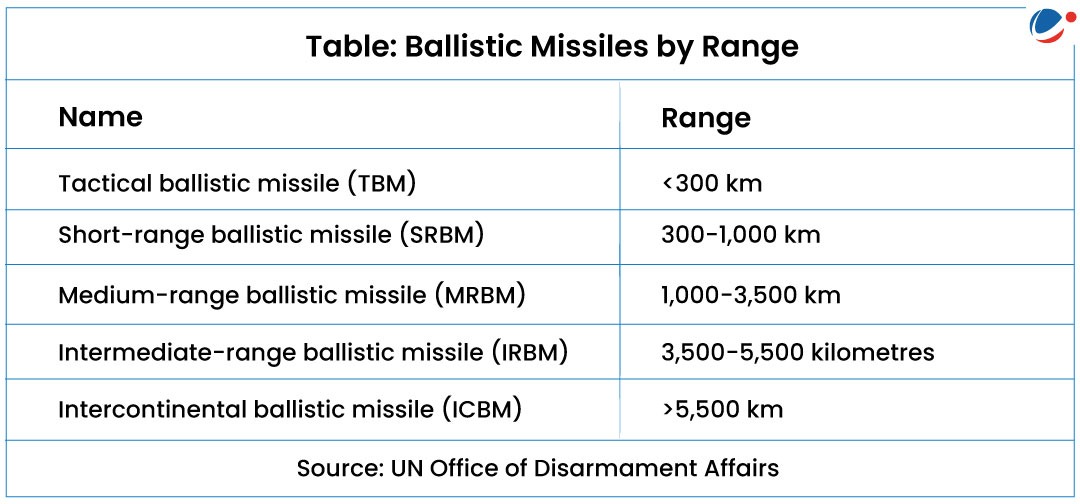
- BM is a type of missile that utilizes projectile motion (utilizing gravity) to deliver warheads to a designated target.
- These are powered only during the initial phase of flight and then follow a free-falling trajectory governed by the laws of physics.
- In contrast, cruise missiles remain powered throughout their flight, traveling within the atmosphere at low altitudes for precise, guided targeting.
- BM can carry either nuclear or conventional warheads.
India’s Ballistic Missile Capabilities
- Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP): Ballistic missiles such as Prithvi, Agni developed under this program.
- Sea-based Ballistic Missiles such as Dhanush, K-15 Sagarika and under-development K-4.
- Ballistic Missile Defence System consisting of Prithvi Air Defence (PAD) missile, Advanced Air Defence (AAD) missile, and long-range interceptor missiles systems.
Treaties to regulate missile development
- Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR): Formed in 1987, it is an informal political understanding among states that seek to limit the proliferation of missiles and missile technology.
- Hague Code of Conduct Against Ballistic Missile Proliferation (HCOC): Adopted in 2002, it curbs the proliferation of WMD (Weapons of Mass Destruction)-capable ballistic missiles.





