The ongoing extreme cold spell in USA & Canada is attributed to arctic blast due to southward expansion of the polar vortex.
What is Polar Vortex?
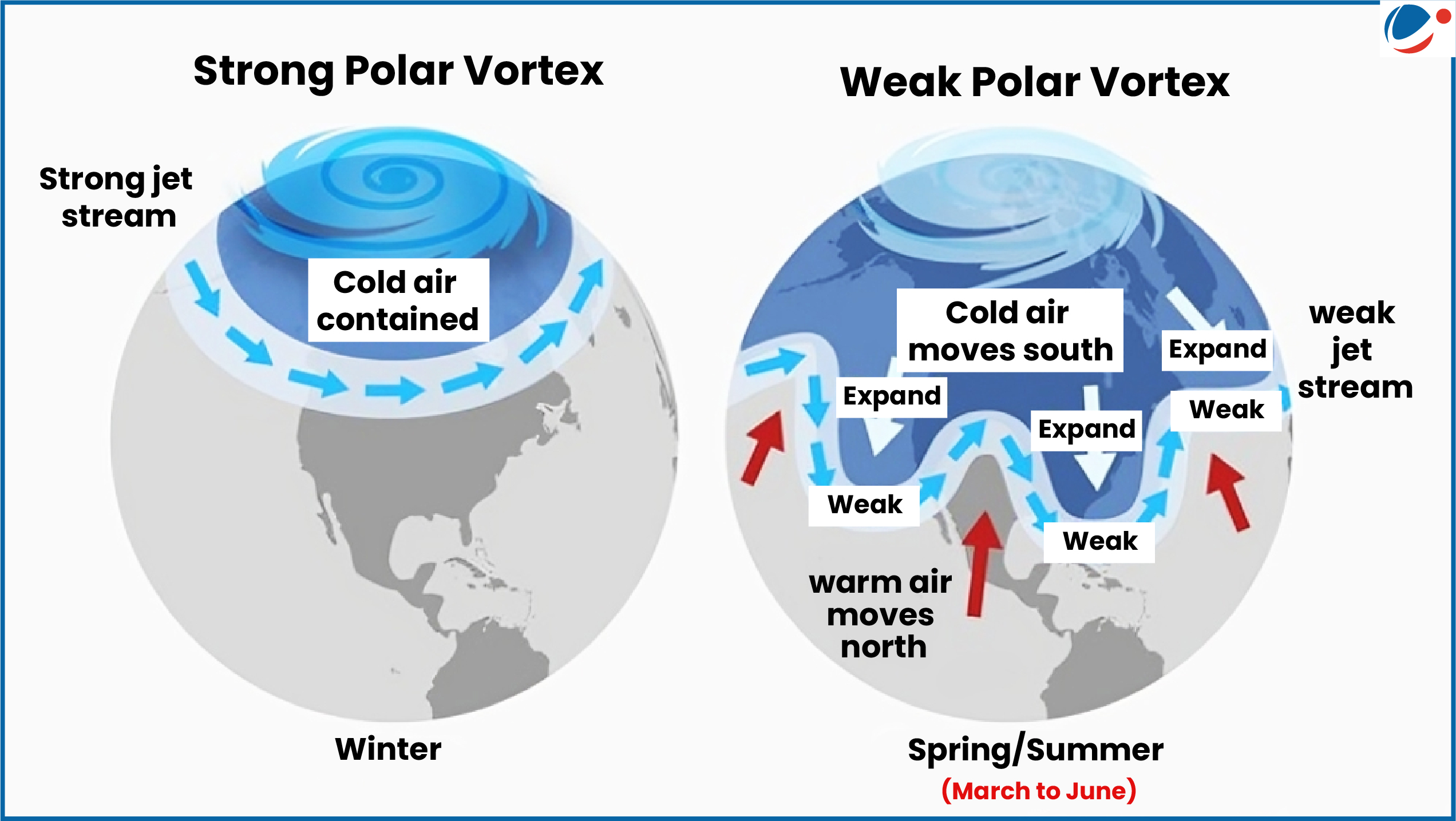
- Definition: It is a large area of low-pressure and cold air that swirls like a wheel (counter-clockwise) around both of the Earth’s poles.
- Types:
- Tropospheric Polar Vortex: It forms in the lowest atmospheric layer, extending from surface to 10-15 km.
- Stratospheric Polar Vortex: It forms at around 15 km to 50 km high.
- Unlike tropospheric polar vortex, the stratospheric polar vortex disappears during summer & is strongest during the autumn.
Impacts of Polar Vortex
- Arctic Blast: It is sudden and intense surge of cold air in USdue to disruptions in the polar vortex, which usually keeps cold air confined to the Arctic region.
- Extreme Weather Events: A weakened vortex can cause the jet stream to dip southward, bringing cold Arctic air to lower latitudes & triggering extreme weather events.
- Ozone Depletion: The trapped cold air in the vortex accelerates ozone depletion, particularly over Antarctica, leading to the ozone hole.
- Impact on India: A weakened polar vortex results in more western disturbances, bringing heavy snowfall to the western Himalayas and colder temperatures to northern India.




