Home Minister reviewed BPR&D's work on implementing new criminal laws and urged it to address grassroots policing challenges while improving the police's global image.
- BPR&D was established in 1970 under the Home Ministry, with the primary the objective of modernisation of the police force.
Overview of Police Organization in India
- State Subject: Policing is primarily governed by states under the Indian Constitution.
- Centre’s Assistance to States: Central police forces assist State Police with intelligence and internal security challenges (e.g., insurgencies).
- Functions of Police: Enforce laws and investigate crimes, maintain law and order, provide security and ensure public safety.
- Accountability of Police: Ministers have superintendence and control over police forces to ensure accountability.
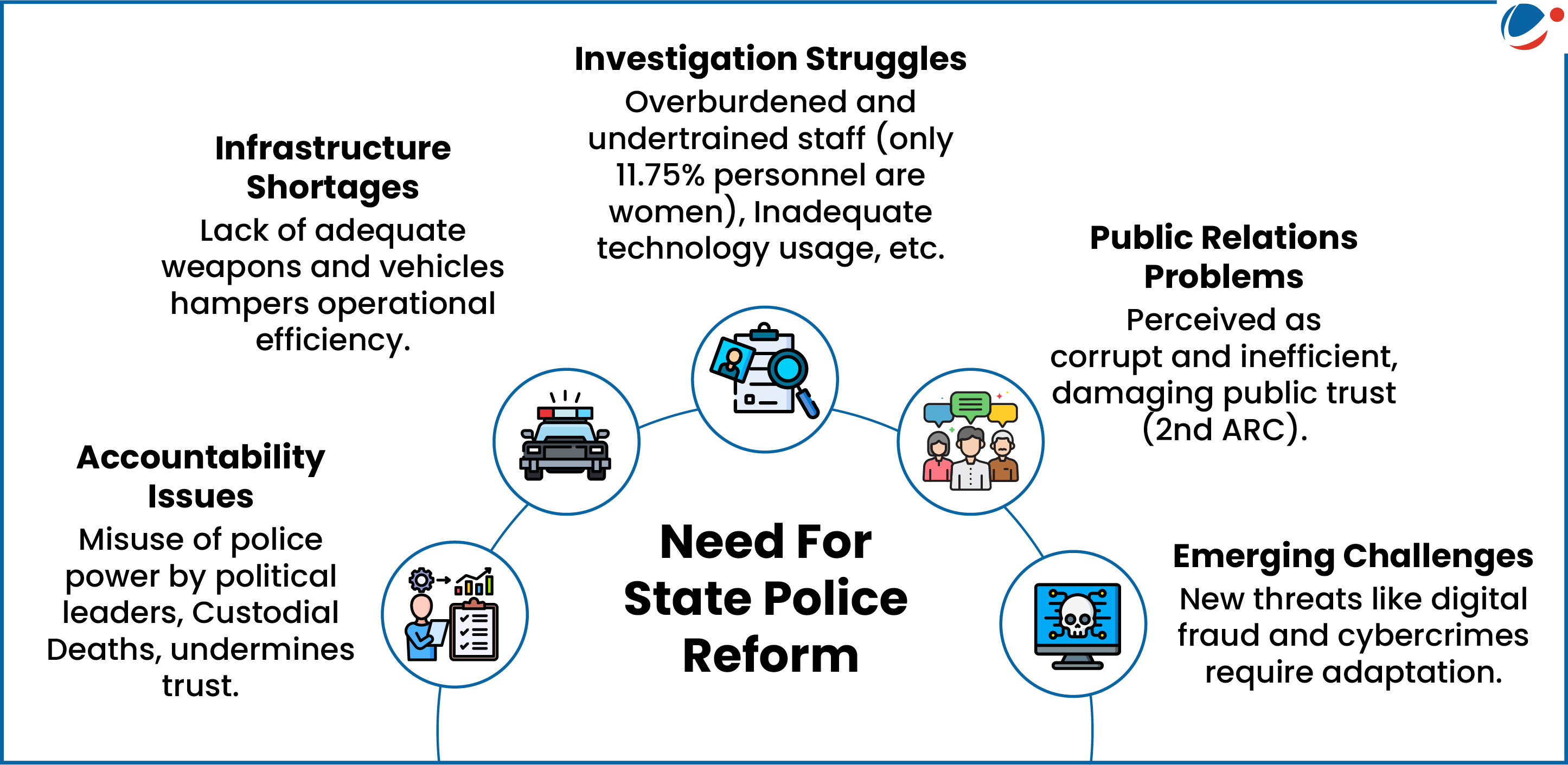
Initiatives for State Police Reform
- Modernisation of State Police Forces (MPF) Scheme: A five-year program (2021-26) with 15 sub-schemes to improve police infrastructure and operations.
- SMART Policing: Introduced by the Prime Minister in 2014, focusing on making police SMART (Strict and Sensitive; Modern and Mobile; Alert and Accountable; Reliable and Responsive; Tech-savvy and Trained
- Women Representation: MHA advised States/UTs to set up all-women police stations in each district and increase women personnel to 33%.
Strengthening state police can be further achieved through community policing, and implementing the Supreme Court’s directions in the Prakash Singh vs Union of India (2006) case, etc.




