The Study conducted over Bay of Bengal, focusing on centuries to millennia timescales, reported a 50% drop in food availability for marine life due to extreme monsoon events.
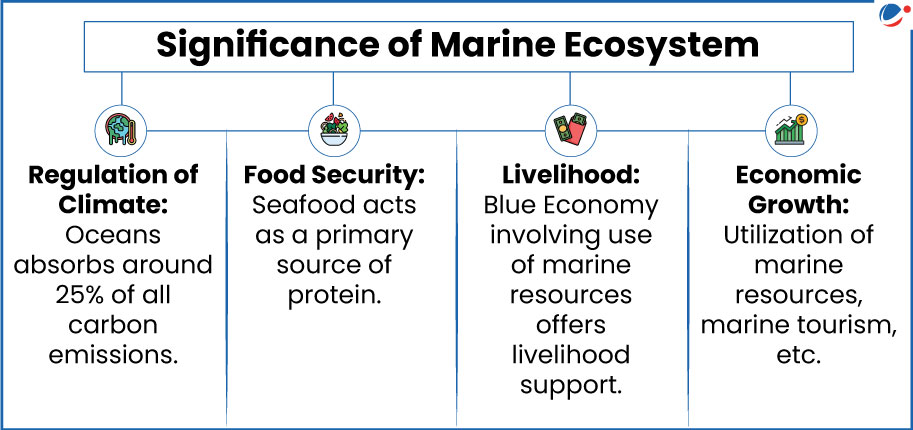
Impact of Climate Change on Marine Ecosystem
- Reduced Plankton Growth: Extreme monsoon conditions interfere with the vertical movement of nutrient-rich waters from the deep ocean to the surface, where plankton flourishes.
- Planktons include phytoplankton (tiny plants) and zooplankton (weak-swimming animals), that form the base of the food chain.
- They produce their own food releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
- Loss of Marine Biodiversity: Climate Change reduces diversity of marine species including fisheries threatening food security.
- Impact Nutrient Supply: Climate Change may reduce wind intensity impacting the mixing of different layers of water.
- Ocean Acidification: Climate change causes drop in ocean pH reducing the availability of calcium carbonate required for organisms like corals for their structural integrity.
Some Initiatives to Safeguard Marine Ecosystems
- Global
- United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS): Legal framework for conservation and sustainable use of marine resources.
- International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL): Reducing shipping activities’ impact on marine ecosystem.
- Indian
- The Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Extends protection to Marine wildlife.
- National Plan for Conservation of Aquatic Eco-systems: Comprehensive plan for conservation and management of aquatic ecosystems.






