A landslide refers to any form of mass wasting characterized by movement of rocks, soil, or other debris downhill assisted by gravity.
- Landslides are generally classified by type of movement (slides, flows, spreads, topples, or falls) and type of material (rock or debris).
Causes of Landslide
- Natural Causes: Groundwater pressure, Earthquake, Volcanic eruptions, heavy rains, etc.
- Anthropogenic causes: Deforestation, cultivation, and construction, Vibrations from machinery or traffic, tunnelling, etc.
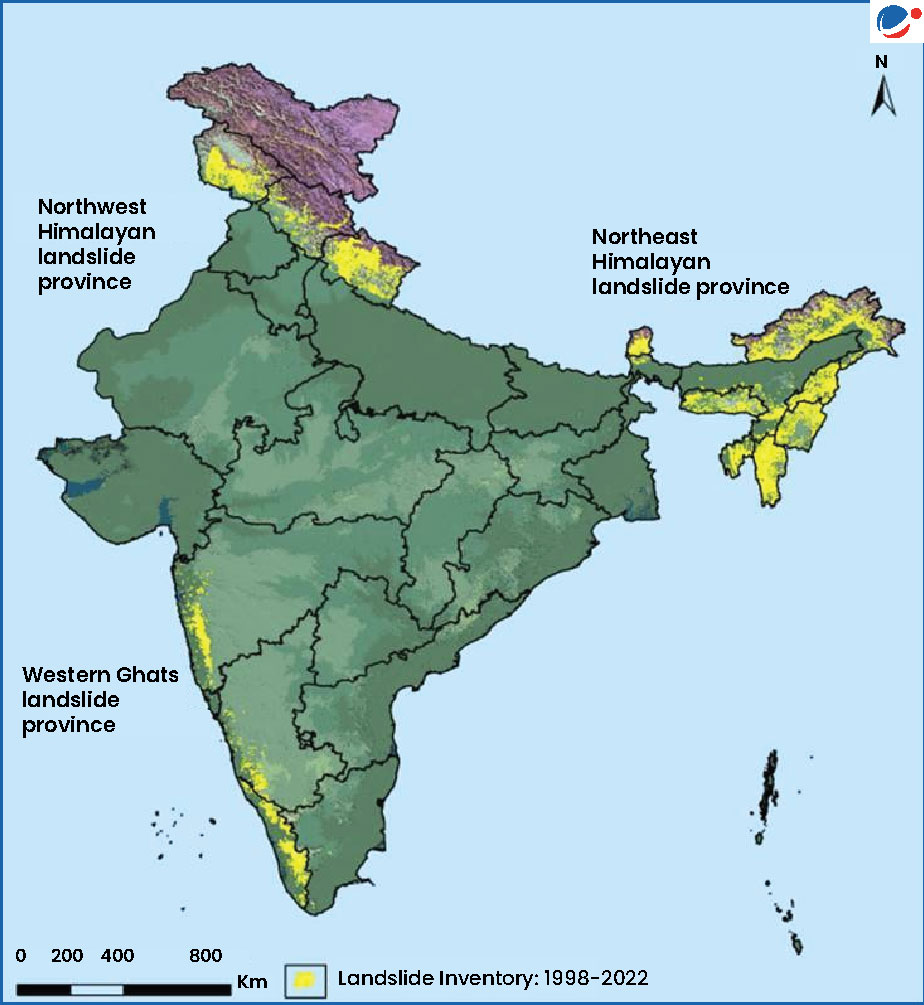
Landslide Vulnerability in India
- According to Landslide Atlas of India by ISRO, India is considered among the top four landslide-prone countries globally.
- Excluding snow covered areas, approximately 12.6 per cent of the country’s geographical land area (0.42 million sq km) is prone to landslides (refer map).
- The Northwest Himalayas contribute- 66.5% of landslides in India, followed by the Northeast Himalayas -18.8% and the Western Ghats - 14.7%.
Mitigation Strategies
- National Landslide Risk Management Strategy guidelines 2019: It addresses hazard mapping, monitoring and early warning system etc.
- Landslide Risk Mitigation Scheme (LRMS) by NDMA: It provides financial support for site specific Landslide Mitigation Projects.
- National Landslide Susceptibility Mapping (NLSM): To create a dynamic Geodatabase for India.







