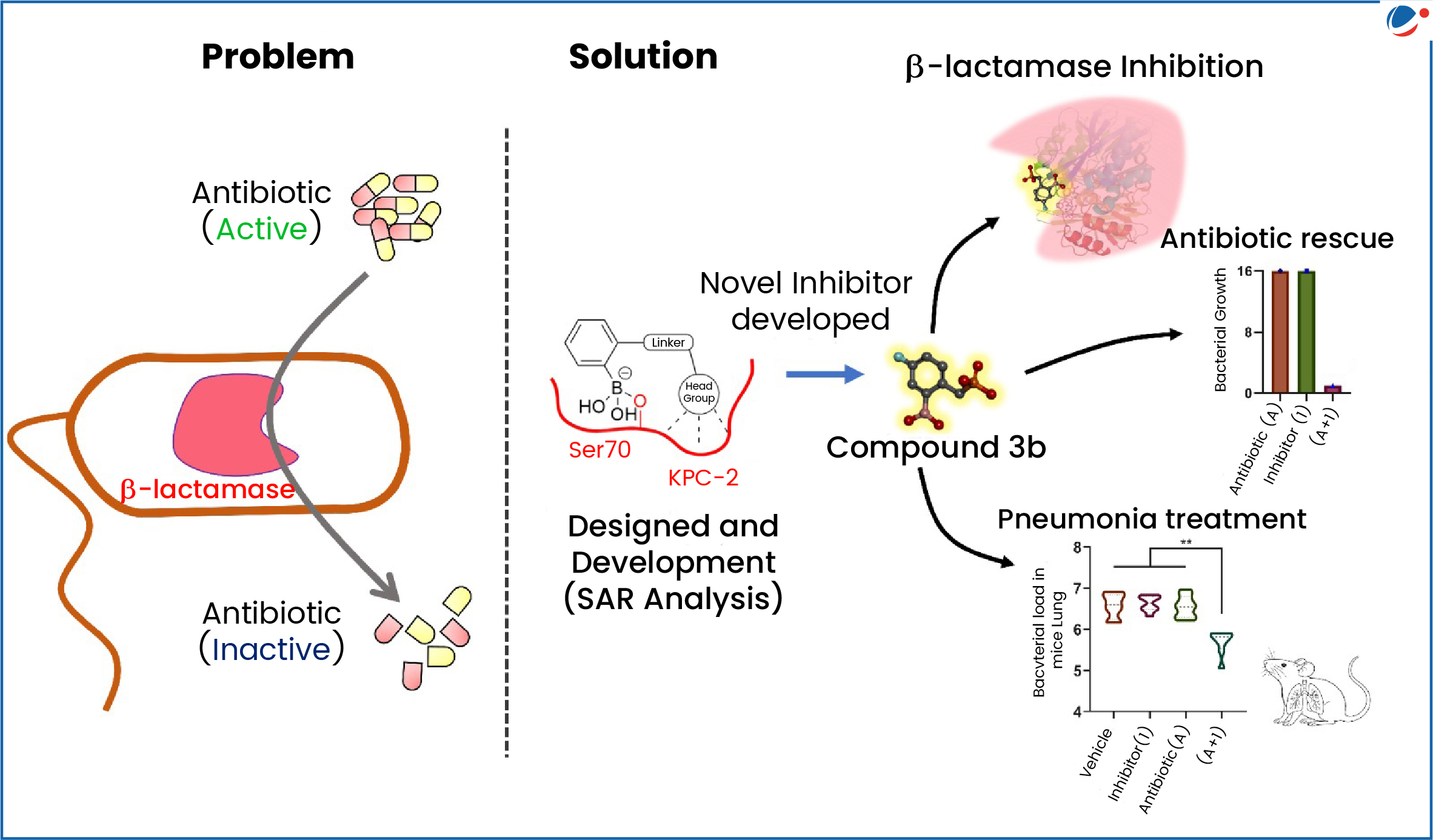
The novel molecule/drug candidate, named Compound 3b, neutralizes the resistance mechanism and shows strong therapeutic results in preclinical model.
Key Highlights of the Discovery
- Compound 3b works alongside the antibiotic Meropenem to treat infections caused by KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae, a superbug listed among the WHO's top-priority threats.
- Compound 3b molecule belongs to a class of β-lactamase inhibitor drugs.
- Beta-lactamase inhibitors (having very little antibiotic activity of its own) are a class of medicine, that blocks the activity of beta-lactamase enzymes (also called beta-lactamases), preventing the degradation of beta-lactam antimicrobials.
- Beta- lactamases are enzymes that inactivate the beta-lactam ring, which is a common chemical structure to all beta-lactam antimicrobials.
- Compound 3b molecule belongs to a class of β-lactamase inhibitor drugs.
About Anti-Microbial Resistance (AMR)
- Meaning: It occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites no longer respond to antimicrobial medicines.
- Antimicrobials, including antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, and antiparasitic, are medicines used to prevent and treat infectious diseases in humans, animals and plants.
- Consequences: Antibiotics and other antimicrobial medicines become ineffective increasing the risk of spread of diseases, has significant economic costs (As per World Bank, AMR could result in US$ 1 trillion additional healthcare costs by 2050).
- Major factors contributing to AMR: Industrial waste from the production of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs), Landfill leachate, untreated wastewater, and sewage effluents etc.
- Initiatives taken: One Health approach; Global Action Plan (GAP) on AMR adopted during 2015 World Health Assembly of the World Health Organisation, etc.





