The deal aims to bring an end to decades of conflict between the two South Caucasus countries.
Key Provisions of the deal
- Cessation of Hostilities: Both nations agreed to end armed conflict, establish diplomatic relations.
- Trump Route for International Peace and Prosperity" (TRIPP): New transit route linking Azerbaijan to its exclave Nakhchivan through Armenian territory.
- US has exclusive development rights.
- US Cooperation Deals: Both countries also signed separate agreements with the United States to enhance cooperation in energy, technology, and the economy.
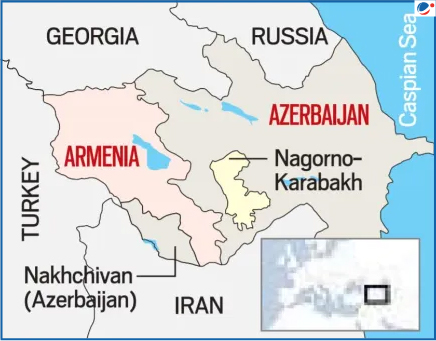
Background of the Conflict
The Armenia–Azerbaijan conflict is mainly over Nagorno-Karabakh, a mountainous region inside Azerbaijan but predominantly populated by ethnic Armenians.
- 1980s: Nagorno-Karabakh broke away from Azerbaijan with Armenia’s support.
- 1991: Both countries gained independence from the Soviet Union, but the dispute continued.
- 2023: Azerbaijan regained full control, causing nearly 100,000 Armenians to flee to Armenia.
India’s Interest
India supports the peace deal, calling it an “important achievement” for dialogue and diplomacy. The deal is important for India as:
- Armenia is the only country in the region with which it has a Friendship and Cooperation Treaty (signed in 1995).
- Azerbaijan falls on the International North-South Transport Corridor route, connecting India with Russia through central Asia.





