As per Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL) crossed 50 billion Units (BUs) generation in financial year 2024-25, first time in its operation history.
- This helped avoid nearly 49 million tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions.
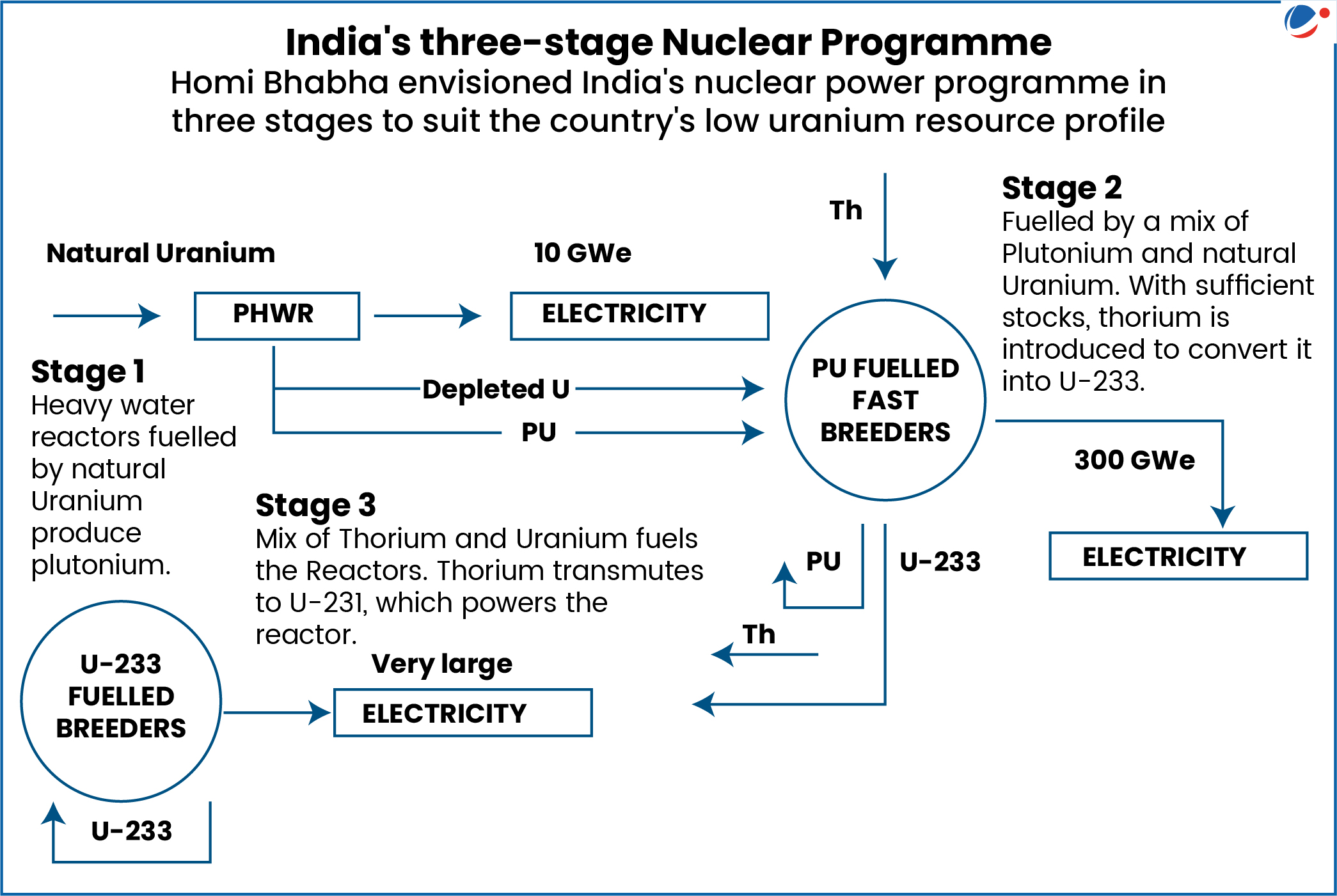
Nuclear Power in India
- India adopted a three-stage nuclear power programme (see infographic).
- Status: It contributes about 3% to total electricity generated. (July 2025).
- Target: 100 GW of Nuclear Power Capacity by 2047.
Key Initiatives to advance Nuclear Power in India
- Nuclear Energy Mission: Launched in Union Budget 2025-26 focussing on Research and Development (R&D) of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
- SMRs are advanced nuclear reactors with power capacity of up to 300 MW(e) per unit, about one-third of generating capacity of traditional nuclear power reactors.
- Developing Bharat Small Reactors: BSRs are 220 MW Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) with a proven safety and performance record.
- PHWR is a heavy water cooled and heavy water moderated natural uranium based fuel reactor.
- Key Achievements towards Enhancing Capacity:
- First two units of indigenous 700 MWe PHWR at Kakrapar, Gujarat (KAPS - 3 & 4) began commercial operation in FY 2023-24.
- Launch of Mahi Banswara Rajasthan Atomic Power Project (MBRAPP), a 4 x 700 MWe PHWR.
- Rawatbhata Atomic Power Project (RAPP) Unit 7 –3rd indigenous 700 MWe PHWR, started commercial operation in 2025.






