It is the 2nd edition which presents an overview of the finances of all 28 States in FY 2023-24.
- The first edition of the report, ‘State Finances 2022-23’ was released in September 2025.
Key Highlights of Report
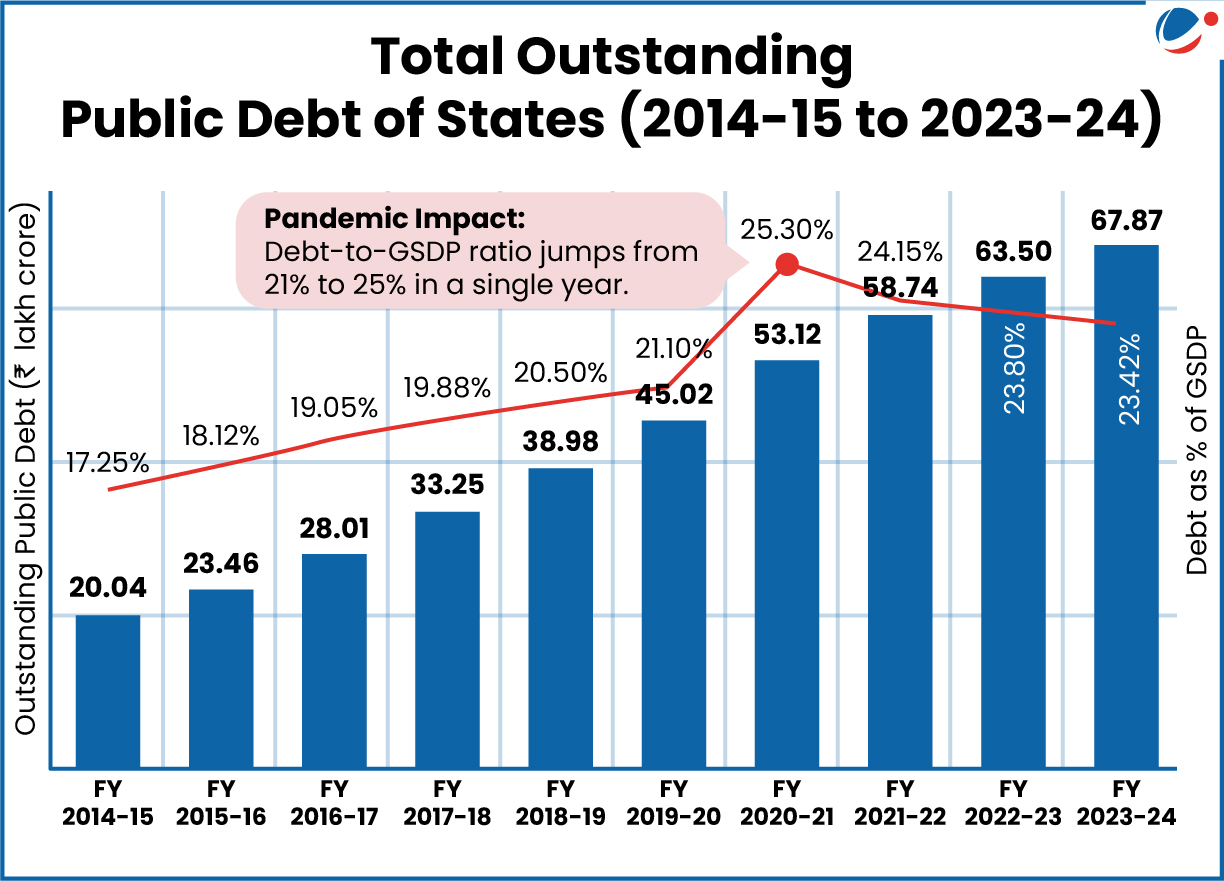
- Public Debt of States: ₹67.87 lakh crore (~23% of GSDP) as of March 31, 2024.
- Fiscal Deficit: 18 states exceeded the 3.0% of GSDP benchmark recommended by the 15th Finance Commission for FY 2023-24.
- Extreme Fiscal Rigidity: lack of "fiscal space" for new development as committed expenditure (salaries, pensions, interest, etc.) consume ~60% of total revenue expenditure.
- Reliance on the Union Tax Devolution: rising from ~21% (2014-15) to ~30% (2023-24) for revenue.
- This makes State budgets highly vulnerable to national economic fluctuations.
- Low Capital Expenditure: Revenue expenditure (maintenance and salaries) continues to dominate at ~83%, while Capital Expenditure (Capex) is only ~16%, as states are prioritizing immediate consumption over long-term investment.
- In several states, like Punjab and Andhra Pradesh, debt is being used to pay for daily expenses rather than building assets.
- Transparency Gaps: The "Shadow Budgeting" problem in form of administrative practices, such as misclassification, is obscuring the true state of finances.
CAG’s RecommendationTo address persistent lack of uniformity in how states classify spending, the CAG has mandated the harmonisation of Object Heads across the Union and States to be adopted by FY 2027-28. |





