Why in the News?
RBI revises priority sector lending (PSL) guidelines to promote small loan in economically disadvantaged districts with low average loan sizes.
Revised Priority Sector Lending Norms
- Incentive framework: It establishes an incentive framework for districts with lower credit flow starting from FY25.
- More weight (125%) will be given to fresh priority sector loans in districts where loan availability is low (less than Rs 9,000 per person).
- Disincentive framework: In districts with high loan availability (more than Rs 42,000 per person), the loans will have a weight of 90%.
- Other districts: With exception of outlier districts with low credit availability and those with high loan sizes, all other districts will continue to have the current importance level of 100%.
- MSME loans: All bank loans to MSMEs shall qualify for classification under PSL.
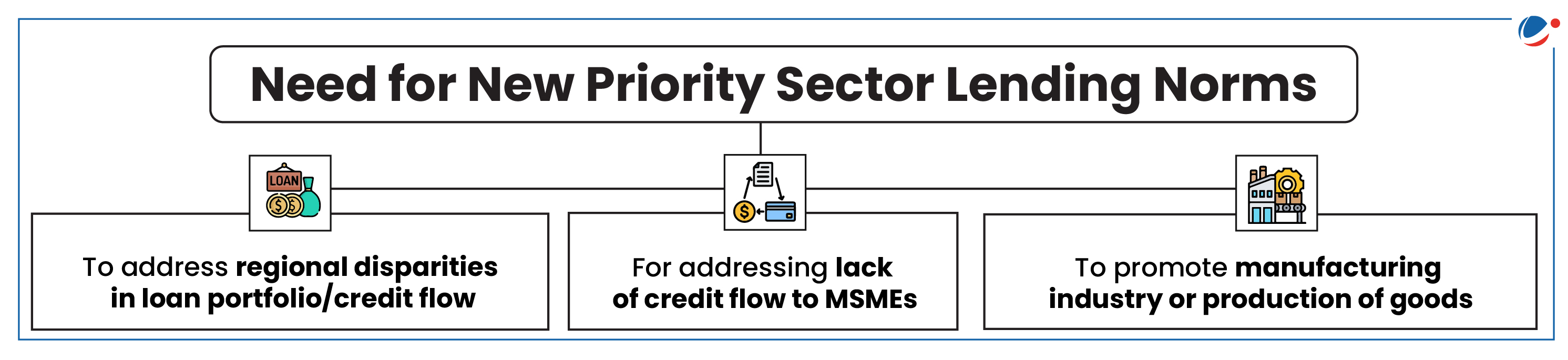
About Priority Sector Lending (PSL)
- Priority Sector means those sectors which Government and RBI consider as important for development of the country and are to be given priority over other sectors.
- Objective
- To ensure that vulnerable sections of society and underdeveloped areas get access to credit.
- To direct a portion of bank credit to specified sectors and sub-sectors that impact large segments of the population and are crucial for the economy.
- PSL was formalized in 1972 to facilitate flow of credit to such sectors, which though creditworthy, are unable to access credit from formal financial institutions.
- Various Committees associated with PSL includes:
- Gadgil Committee, 1969 recommended adoption of Area Approach based on which 'Lead Bank Scheme' was adopted.
- Ghosh Committee (1982) in which Priority sector categories very revised.
Categories under Priority Sector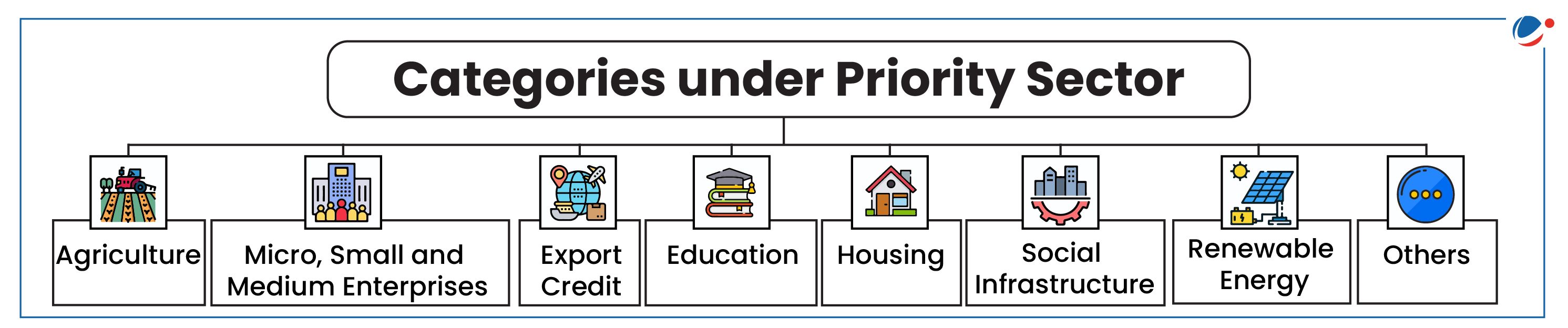
The sections have further sub-targets for the *Category of Weaker Sections. * For example, Small and Marginal Farmers in Agriculture Category.
| ||||||||||||
Targets /Sub-targets for Priority sector Lending for Different Types of Banks | ||||
Categories | Domestic commercial banks & foreign banks with 20 branches and above | Foreign banks with less than 20 branches | Regional Rural Banks | Small Finance Banks |
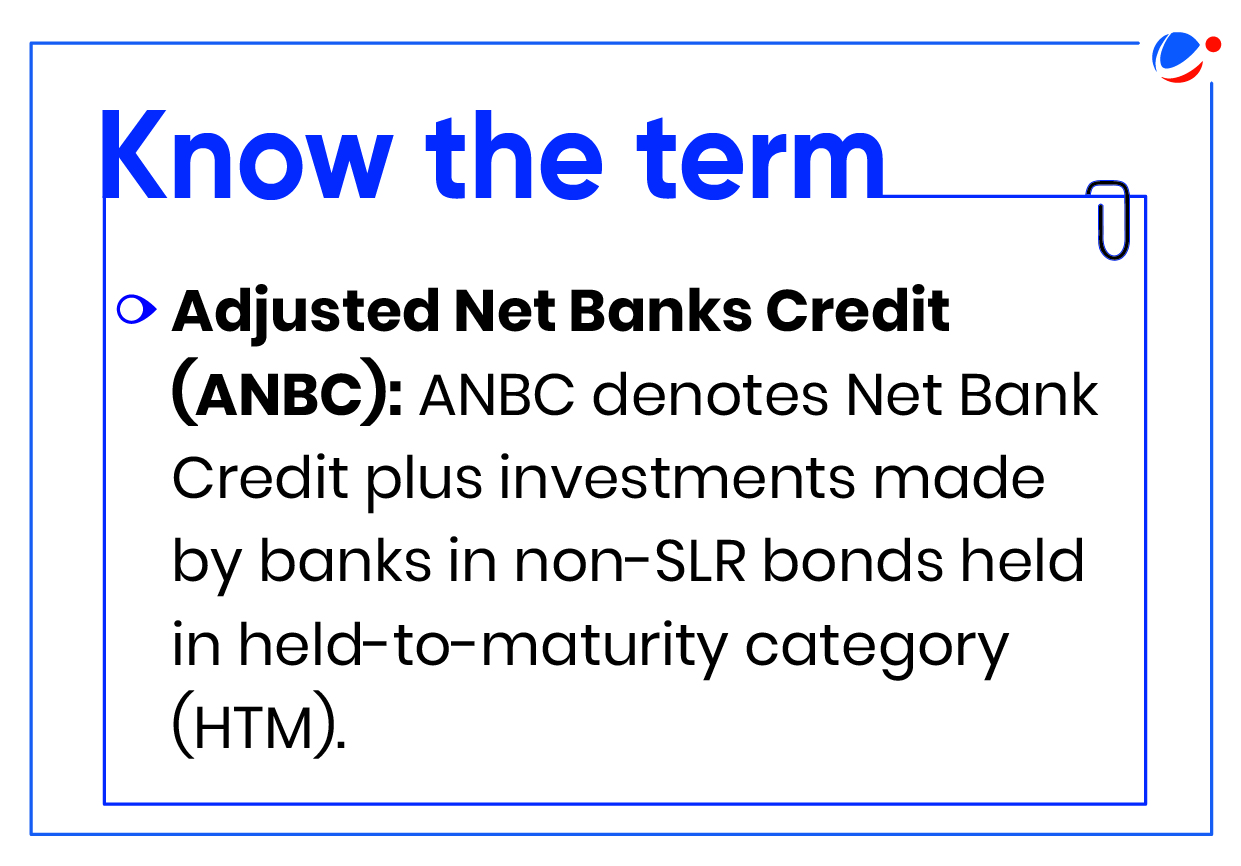
Total Priority Sector | 40% of ANBC or Credit Equivalent of Off-Balance Sheet Exposures (CEOBE), whichever is higher | Same as Domestic commercial bank | 75% of ANBC or CEOBE whichever is higher | 75% of ANBC or CEOBE whichever is higher. |
Agriculture | 18% of ANBC or CEOBE, whichever is higher; out of which a target of 10% is prescribed for Small and Marginal Farmers | Not applicable | Same as Domestic commercial bank | Same as Domestic commercial bank |
Micro Enterprises | 7.5% of ANBC or CEOBE, whichever is higher | Not applicable | Same as Domestic commercial bank | Same as Domestic commercial bank |
Advances to Weaker Sections | 12%of ANBC or CEOBE, whichever is higher | Not applicable | 15% of ANBC or CEOBE, whichever is higher | Same as Domestic commercial bank |
Note: Priority Sector Lending guidelines is also applicable on Primary Urban Co-operative Banks. | ||||
Positive Impact of priority sector lending on Indian economy:
- Financial Inclusion: PSL norms ensure that credit reaches under banked segments of population e.g. SMFs, women, and weaker sections.
- Support to Agriculture: Agricultural credit increased from 2000 to 2020 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.81% due to mandatory 18% lending by commercial banks & other policies.
- Promotion of MSMEs: By facilitating credit flow to MSMEs, PSL helps in creating jobs and boosting local economies.
- Income Augmentation: A case study of Andhra Pradesh showed that Beneficiaries reported enhanced income.
Issues with PSL
- Non-Performing Assets (NPAs): Outstanding loan in priority sector has significant negative impact on banks.
- According to some studies, PSL was found responsible for more NPA generation and writing-off of NPA as well.
- Increased costs: PSL increased administrative and transactional cost of banks.
- Other issues with PSL: Low banks Profitability, increased Government Interference etc.

Way-forward
- Strengthen Microfinance Institutions and Encourage Opening of "Small" Finance Banks: MFIs could significantly increase the credit supplied to unbanked rural and semi-urban areas through their vast distribution network and business model of "last mile connectivity."
- Use of Technology: E.g. Mobile banking app for loan approval to farmers to Reduce Cost of Credit Delivery and increase the reach and efficiency of PSL, especially in rural and remote areas.
- Create a robust credit infrastructure and Risk Assessment Tools: To better evaluate the creditworthiness of borrowers and reduce the incidence of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs).







