SafeEXO-Cas, exosome-based platform has been developed by Scientists at Columbia University.
- Exosomes are naturally occurring vesicles (small cellular containers) that have the potential to be manipulated to become promising drug delivery vehicles for on-demand in vitro and in vivo gene editing.
- It significantly enhances the delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing components to specific cells.
- It will also facilitate development of the precision medicine and will improve cancer treatment.
- Precision medicine (aka personalized medicine) involves disease prevention and treatment that takes into account differences in people’s genes, environments, and lifestyles.
About CRISPR/Cas9 Technology
- Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats Associated protein 9 (CRISPR-Cas9) is a type of genome editing technology.
- It is ecogniz to change genetic code or edit Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) at particular locations.
Working:
- Works as cut and paste mechanism on DNA Strands. Genetic codes that need to be changed are identified.
- Cas9 protein is used as a pair of molecular scissors to cut off a part from strand, allowing modifications to the genome.
Applications of CRISPR:
- Edit genes in human embryo; Change genetic codes of crops to improve crop resilience; treating diseases like sickle cell disease etc.
India’s Deeptech Dawn: Forging Ahead’ Report released by NASSCOM.
- Report highlights the different attributes of DeepTech startups.
Key findings
- Despite having the 3rd largest pool of DeepTech startups, India ranked 6th among the top 9 DeepTech ecosystems in the world.
- India currently has 3600+ DeepTech startups.
- Indian DeepTech startups have raised a cumulative $10 Bn in the last 5 years (2023-2019).
- In 2023, witnessed 77% decline in funding (in comparison to 2022).

About DeepTech Startups
- DeepTech startups leverage advanced technologies like AI, IoT, Blockchain, and Augmented Reality (AR)/Virtual Reality (VR) to create novel solutions for complex problems, often combining multiple technologies to redefine or create new markets. Ex: Agnikul, GalaxyEye, Sarvam AI
- Characterized by extended development timelines, high capital intensity, etc.
- Key Potential Areas: Promotes utilisation of Deep Technologies to reshape sectors like healthcare (AI-powered Diagnostics & Precision Medicine), Agriculture (Agribots & Automation), etc.
Key Challenges
- During the pre-commercialization phase, lacks access to the necessary infrastructure.
- Limited understanding of business operations and market dynamics.
- Competition from large enterprises for adequately skilled talent.
Steps needs to be taken by Government
|
Google DeepMind and Isomorphic Labs have developed a new AI model, AlphaFold-3, that can predict structure of proteins, DNA, RNA, ligands, etc., and how they interact.
About Alphafold-3
- It can computationally predict the structure and interactions of all life’s molecules with unprecedented accuracy and speed.
- Given an input list of molecules (proteins, DNA, etc.), it generates their joint 3D structure, revealing how they all fit together.
- It can model chemical modifications to the molecules which control the healthy functioning of cells, that when disrupted can lead to disease.
According to the FAO, nuclear technologies are important tools for food safety.
- Role of Nuclear technologies has been highlighted at the International Symposium on Food Safety and Control, held in Vienna, Austria.
- Event was organized by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
Nuclear technologies offer solutions to combat hunger, reduce malnutrition, enhance environmental sustainability etc.
- Also, technologies are complimentary to the One Health approach.
- One Health is an integrated, unifying approach that aims to sustainably balance and optimize the health of people, animals and ecosystems.
Role of Nuclear Technologies in Food system
- Animal health: Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) tests, a molecular nuclear technique, will rapidly detect diseases.
- Soil and water management: Radioactive nuclides left behind after nuclear events can help scientists determine the health of soil and rate of erosion.
- Insect pest management: Nuclear based Sterile Insect Technique (SIT) to manage pest.
- Technique involves mass-rearing the insects then sterilizing them through ionizing radiation before releasing them.
- Food safety and control: Food irradiation (the application of ionizing radiation to food) improves the safety and extends the shelf life of foods by reducing or eliminating microorganisms and insects.
- Plant Breeding and Genetics: Desired Genetic changes can be done by irradiation.

IIT Bombay is leading the Daksha project.
- It is leading in close collaboration with the Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR), Raman Research Institute (RRI), etc.
About the Daksha project
- It is an ambitious proposal to build two high-energy space telescopes for the study of explosive astrophysical sources.
- Each telescope will be equipped with sensors to cover Low energy to high-range energy bands
- Objectives
- Detect, localize and characterize high-energy counterparts to gravitational wave sources.
- High sensitivity detection and studies of Gamma Ray Bursts (GRB)
- GRB are short-lived bursts of gamma-ray light, the most energetic form of light.
- Significance of the project
- The two satellites will orbit on opposite sides of earth to give better coverage than existing missions.
- Will localize the source of emission of intense gravitational waves due to neutron star mergers or other reasons.
- Neutron stars are formed when a massive star runs out of fuel and collapses.
- Primordial Black Holes (PBH) mass window could be probed for the first time.
- PBH are a type of black hole formed in the first second after the birth of the universe.
TRISHNA (Thermal Infra-Red Imaging Satellite for High-resolution Natural Resource Assessment) mission is a collaborative endeavor between ISRO and CNES (French Space Agency) to monitor surface temperature and water management at regional to global scale.
About TRISHNA Mission
- Objective: Detailed monitoring of energy and water budgets of continental biosphere for quantifying terrestrial water stress and water use and high-resolution observation of water quality and dynamics.
- It will also help in a comprehensive assessment of urban heat islands, detection of thermal anomalies linked to volcanic activity and geothermal resources, etc.
- 2 Primary payloads
- Thermal Infra-Red (TIR) payload: Provided by CNES, features a four-channel long-wave infrared imaging sensor.
- Visible – Near Infra-Red – Short Wave Infra-Red (VNIR-SWIR) payload: Developed by ISRO, includes seven spectral bands designed for detailed mapping of surface reflectance.
- It will operate in a Sun-synchronous (SSO) orbit and is designed for a 5-year operational life.
- SSO is a particular kind of polar orbit in which satellites are synchronized to always be in the same position relative to the Sun.
- Significance: Climate monitoring such as droughts, permafrost changes, and evapotranspiration rates; better urban planning with detailed urban heat island maps and heat alerts; etc.
India’s international Space Cooperation
|
Recently launched Earth Cloud Aerosol And Radiation Explorer (EarthCARE Mission) is a joint venture between the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA).
- Objective: Provide a holistic view of complex interplay between clouds, aerosols and radiation, yielding new insight into Earth’s radiation balance against the backdrop of the climate crisis.
- Orbit Type: Sun-synchronous.
- On-board Instruments: Atmospheric Lidar, cloud profiling radar, multispectral imager (MSI), and broad-band radiometer.
Relationship between Clouds, Aerosol and Earth’s Radiation Balance
- Clouds: Along with aerosols, clouds play key role in Earth’s Heat Budget.
- They can either cool or warm the Earth’s surface by reflecting incoming sunlight or trapping outgoing infrared radiation.
- The extent of clouds’ warming or cooling effect on Earth depends on their shape, location, altitude, water content, and particle size.
- Aerosols: These are tiny particles such as dust and pollutants suspended in atmosphere.
- Directly they reflect and absorb solar radiation and trap outgoing radiation.
- And, indirectly they act as nuclei for cloud formation, which has a more substantial impact on the climate.
- Human activities like industrialization, agriculture, etc. significantly alter atmospheric aerosol concentrations, impacting regional climate patterns.
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope observed the symbiotic system HM Sagittae (HM Sge) in Milky Way Galaxy.
About Symbiotic System:
- It is a type of binary star system that consists of a white dwarf and a red giant.
- White dwarf is what stars become after they have exhausted their nuclear fuel.
- Red giant is a dying star in the final stages of stellar evolution.
- Here, the cooler red giant loses material which flows onto the hotter compact white dwarf star.
- The stolen material forms an accretion disk swirling around the white dwarf.
The 77th annual World Health Assembly (WHA) meeting recently concluded with an agreement on a crucial set of amendments to the IHR, 2005.
- Also, decided to extend the mandate of the Intergovernmental Negotiating Body (established in 2021) to finish its work to negotiate a Pandemic Agreement within a year.
About IHR
- Successor of the International Sanitary Regulations (1951).
- Aim: An overarching legally binding framework that defines countries’ rights and obligations in handling public health events and emergencies that have the potential to cross borders.
- Members: Comprises all 194 WHO Member States plus Liechtenstein and the Holy See.
- Need of Amendments: Experience of epidemics and pandemics, from Ebola to COVID-19, highlighted the need of better public health surveillance, response and preparedness mechanisms around the world
Key Amendments
- Defining the Pandemic emergency as a communicable disease that has a “wide geographical spread” or a high risk of one, and has exceeded or can exceed the ability of national health systems to respond.
- Establishing a Coordinating Financial Mechanism to address the needs and priorities of developing countries.
- Establish a States Parties Committee for effective IHR implementation.
- Create National IHR Authorities to improve coordination among countries.
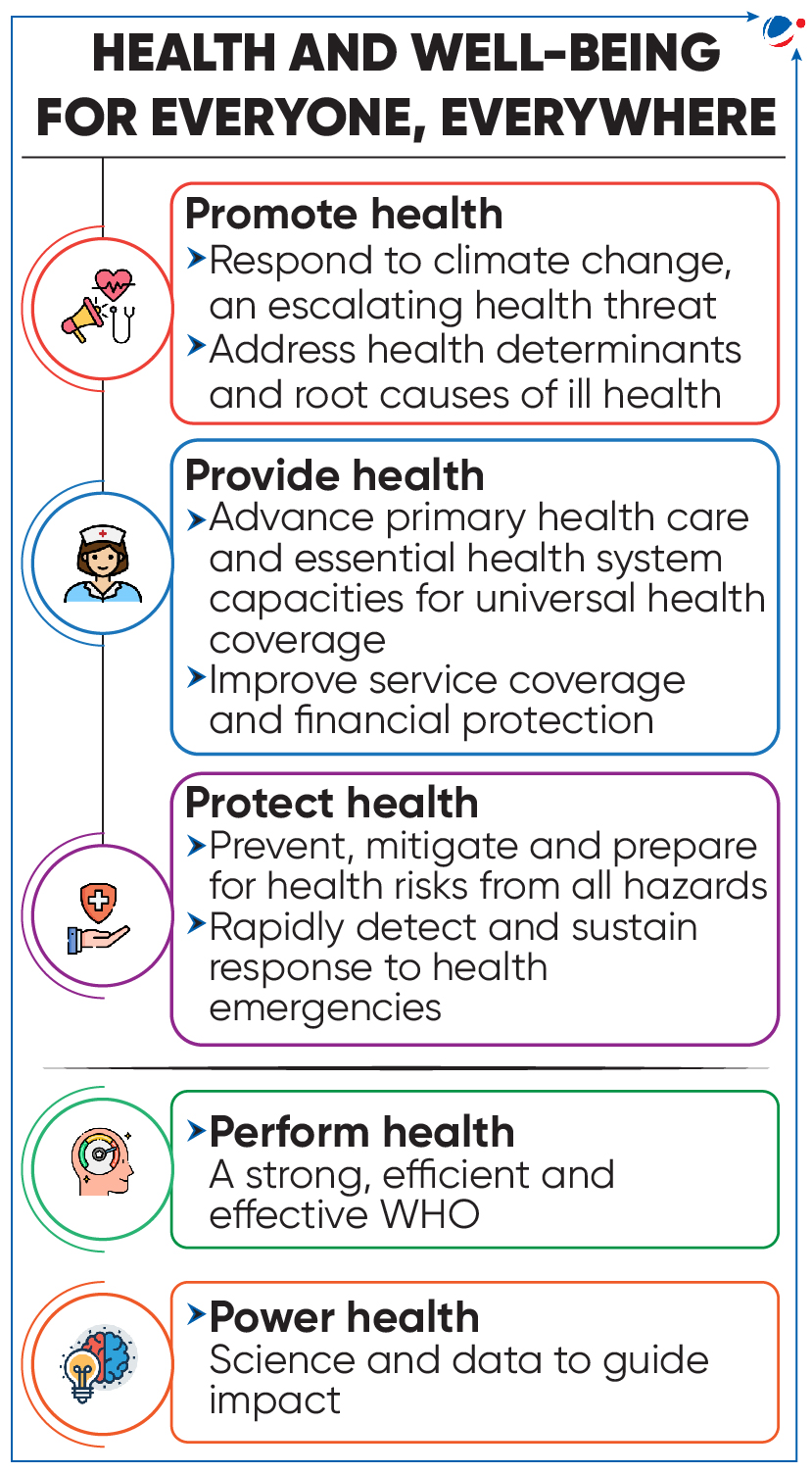
Investment Round has been launched at the 77th World Health Assembly (WHA).
- WHA is a decision-making body of World Health Organisation (WHO). The theme of the Assembly is All for Health, Health for All.
- Health for all as a concept was evolved in the Alma-Ata Declaration (1978) of WHO to promote Primary Health Care.
The Investment Round aims to mobilize resources for WHO’s core work for the next 4 years (2025-2028) (refer image).
- Under it, $ 7 Bn will be mobilized to support the countries so that they can respond to health challenges.
Funding of WHO
- WHO receives funding from two main sources-
- Assessed contributions: Due that countries pay to be a member of the Organization.
- These are a percentage of a country’s GDP as agreed by the UN General Assembly and approved every two years.
- Voluntary contributions: Comes from Members or from other partners. Major source of total funding.
- It is further categorized into Core voluntary contributions, Specified voluntary contributions etc.
- Assessed contributions: Due that countries pay to be a member of the Organization.
Challenges in funding of WHO:
Assessed contributions cover less than 20% of the total budget, Withdrawal of funding (E.g. Temporary suspension of funding by US) etc.
India, South Korea, the US, Japan, and European Union launched Biopharmaceutical Alliance in response to the drug supply shortages experienced during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The announcement was made at the inaugural meeting of the Biopharmaceutical Alliance during the Bio International Convention 2024.
Significance
- Build a reliable, sustainable, and resilient supply chain in pharmaceuticals as production of essential raw materials and ingredients is concentrated in a few countries.
- Coordinate bio policies, regulations, and R&D support measures with the member countries.
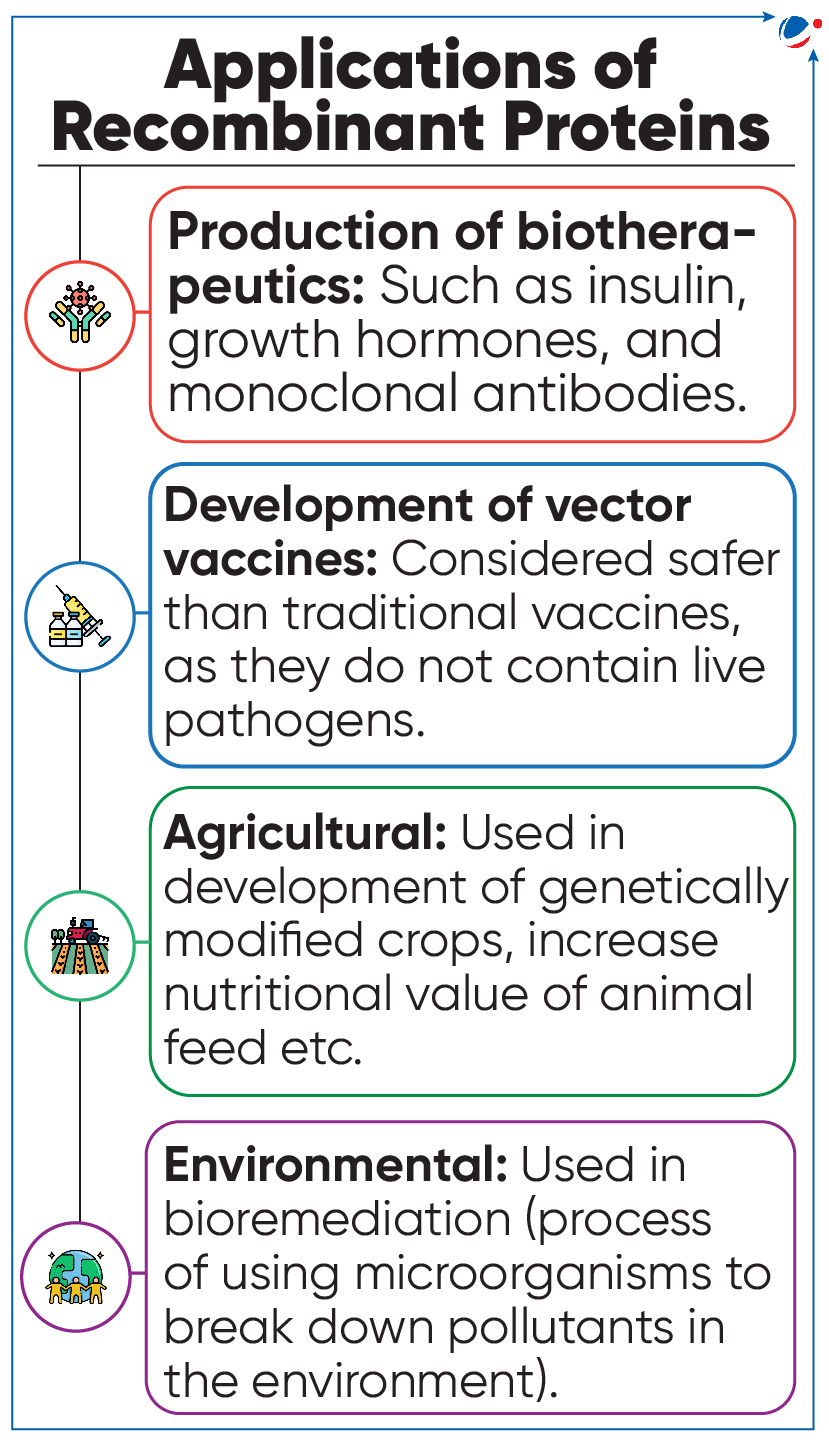
Researchers at Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have developed a new process for production of recombinant proteins.
What are Recombinant Proteins (RPs)?
- These are modified or manipulated proteins encoded by recombinant DNA (rDNA) for increasing production of proteins, modifying gene sequences, and manufacturing useful commercial products.
- rDNA is artificially made DNA strand that is formed by combination of two or more DNA molecules.
- rDNA technology can be used to combine (or splice) or transfer DNA from different species or to create genes with new functions.
Production of Recombinant Proteins
- RPs such as vaccine antigens, insulin and monoclonal antibodies, are mass-produced by growing modified bacterial, viral or mammalian cells in large bioreactors.
- Most widely used organism is yeast Pichia pastoris (now called Komagataella phaffii) and it utilizes methanol for production of RP.
- However, methanol is highly flammable and hazardous, requiring stringent safety precautions.
- Researchers have now developed an alternative safer process that relies on a common food additive called mono-sodium glutamate (MSG).
- Escherichia coli (E.Coli) is also one of the organisms of choice for RP production due to its well-characterized genetics, rapid growth, and high yield production.
New plant species (Stellaria mcclintockiae) from Kerala has been named after Barbara McClintock who won the Nobel Prize for her discovery of Jumping Genes.
About Jumping genes
- Jumping genes, aka transposable elements, are DNA sequences that can move or “jump” from one location to another within the genome, causing nearby genes to become active or inactive.
- They can replicate themselves and insert copies at new locations.
- Their movement can cause genetic mutations and contribute to genome evolution.




